Benzodiazepines are a type of medication that are commonly used to treat a variety of medical conditions, from anxiety and insomnia to muscle spasms and seizures. But what are benzos, exactly? What do they do, and why are they so often prescribed? In this article, we will explore the purpose of benzodiazepines, how they work, and the potential benefits and risks associated with their use.
Why Benzodiazepines Are Prescribed?
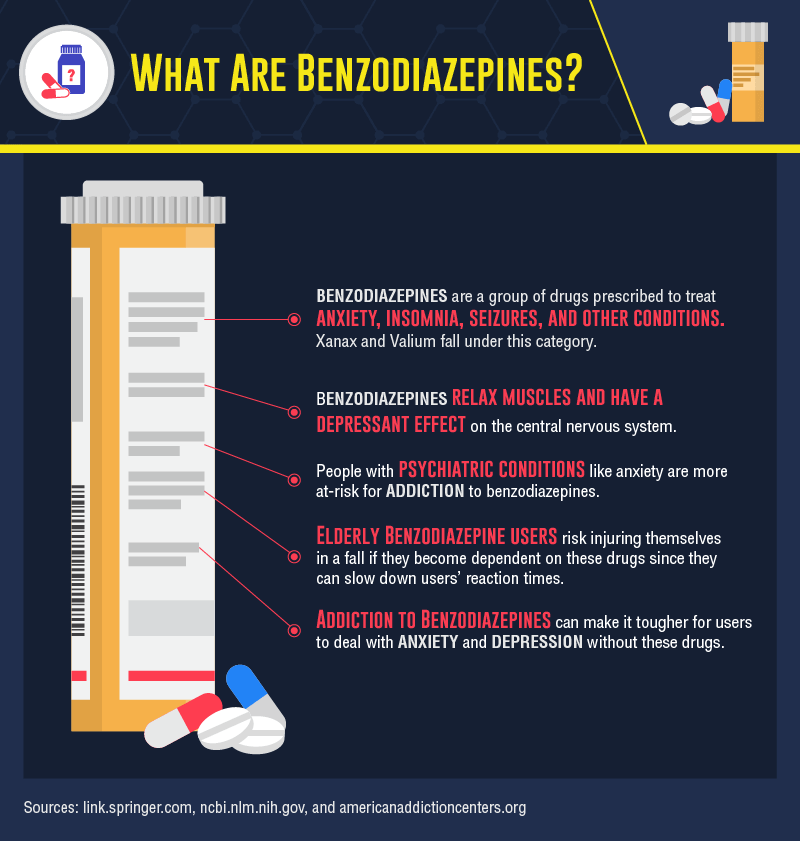
Benzodiazepines are a group of drugs classified as tranquilizers, sedatives, or anxiolytics. They are commonly prescribed to treat anxiety, insomnia, seizures, muscle spasms, and alcohol withdrawal. They work by slowing down the activity of the central nervous system, providing a calming effect. Benzodiazepines are generally considered safe when taken as prescribed, but they can be addictive if misused.
Benzodiazepines are used to treat a variety of conditions, including:
Anxiety
Benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed to treat anxiety disorders. They work by increasing the effects of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as GABA, which helps reduce anxiety. They can be taken as needed or on a regular schedule. Commonly prescribed benzodiazepines for anxiety include alprazolam (Xanax), clonazepam (Klonopin), and lorazepam (Ativan).
Benzodiazepines are typically used for short-term relief of anxiety symptoms. Long-term use of benzodiazepines is generally not recommended due to the risk of addiction and other side effects. Alternative treatments for anxiety, such as psychotherapy and lifestyle changes, are recommended for long-term management.
Insomnia
Benzodiazepines are also used to treat insomnia. They work by slowing down the activity of the central nervous system, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep. Commonly prescribed benzodiazepines for insomnia include estazolam (ProSom), temazepam (Restoril), and triazolam (Halcion).
Benzodiazepines are generally recommended for short-term relief of insomnia. Long-term use of benzodiazepines is not recommended due to the risk of addiction and other side effects. Alternative treatments for insomnia, such as cognitive behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes, are recommended for long-term management.
Seizures
Benzodiazepines are also used to treat seizures. They work by slowing down the activity of the central nervous system, which can help prevent or reduce the frequency of seizures. Commonly prescribed benzodiazepines for seizures include clonazepam (Klonopin) and diazepam (Valium).
Benzodiazepines are typically used for short-term relief of seizure symptoms. Long-term use of benzodiazepines is generally not recommended due to the risk of addiction and other side effects. Alternative treatments for seizures, such as anticonvulsants and lifestyle changes, are recommended for long-term management.
Muscle Spasms
Benzodiazepines are also used to treat muscle spasms. They work by slowing down the activity of the central nervous system, which can help relieve muscle tension and reduce spasms. Commonly prescribed benzodiazepines for muscle spasms include diazepam (Valium) and lorazepam (Ativan).
Benzodiazepines are generally recommended for short-term relief of muscle spasms. Long-term use of benzodiazepines is not recommended due to the risk of addiction and other side effects. Alternative treatments for muscle spasms, such as stretching and exercise, are recommended for long-term management.
Alcohol Withdrawal
Benzodiazepines are also used to treat alcohol withdrawal. They work by slowing down the activity of the central nervous system, which can help reduce the severity of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Commonly prescribed benzodiazepines for alcohol withdrawal include chlordiazepoxide (Librium) and diazepam (Valium).
Benzodiazepines are typically used for short-term relief of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Long-term use of benzodiazepines is not recommended due to the risk of addiction and other side effects. Alternative treatments for alcohol withdrawal, such as medication-assisted treatment and lifestyle changes, are recommended for long-term management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines, commonly known as benzos, are a type of medication used to treat a range of mental health conditions, such as anxiety, insomnia, panic disorder and seizures. They work by calming the central nervous system and helping to reduce stress and anxiety. Benzodiazepines are classified as a Schedule IV drug, meaning they have a low risk of abuse and addiction.
Why Are Benzodiazepines Prescribed?
Benzodiazepines are prescribed to treat a range of mental health conditions, such as anxiety, insomnia, panic disorder and seizures. They work by calming the central nervous system and helping to reduce stress and anxiety. They can also be used to help with symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and can be used before surgery to help reduce anxiety. Benzodiazepines can also be prescribed to help with short-term relief from muscle spasms and to help with symptoms of withdrawal from other sedative drugs.
What Are the Side Effects of Benzodiazepines?
The most common side effects of benzodiazepines are drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, blurred vision, impaired balance, memory problems, and impaired coordination. Other side effects may include dry mouth, constipation, difficulty urinating, and increased appetite. Long-term use can lead to tolerance and dependence on the drug, and can also cause problems with concentration, judgment, and coordination.
Are Benzodiazepines Addictive?
Benzodiazepines are classified as a Schedule IV drug, meaning they have a low risk of abuse and addiction. However, long-term use of benzodiazepines can lead to tolerance and dependence on the drug, and can also cause problems with concentration, judgment, and coordination. It is important to take benzodiazepines only as prescribed by your doctor and not to take more than the prescribed dosage.
Are There Alternatives to Benzodiazepines?
Yes, there are alternative treatments for anxiety, insomnia, and other mental health conditions. These include cognitive behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques, exercise, and lifestyle changes such as reducing caffeine intake and getting enough sleep. Other medications such as antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and antipsychotics may also be prescribed.
What Are the Risks of Taking Benzodiazepines?
The risks of taking benzodiazepines include the potential for tolerance and dependence on the drug, as well as side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, blurred vision, impaired balance, memory problems, and impaired coordination. Long-term use can also cause problems with concentration, judgment, and coordination. It is important to take benzodiazepines only as prescribed by your doctor and not to take more than the prescribed dosage.
Prescribing benzodiazepines for anxiety
In conclusion, benzodiazepines can be an effective tool for those who suffer from anxiety disorders, insomnia, or panic attacks when used properly. While there are risks associated with taking benzodiazepines, these can be minimized when used under the supervision of a qualified medical professional. Even though benzodiazepines can be helpful in treating certain mental health conditions, it is important to remember that they should only be used as prescribed and not as a long-term solution.
