Opiate addiction is a growing problem in many parts of the world, and it can be incredibly difficult to break free from it. For those fighting opiate addiction, withdrawal can be one of the biggest obstacles. But there are treatments and therapies that can help ease the discomfort and make the transition to sobriety much easier. In this article, we’ll explore what helps with opiate withdrawal, from medications to lifestyle changes. We’ll discuss how to identify an opiate addiction and how to find the right treatment plan for you. Let’s take a closer look at what helps with opiate withdrawal.
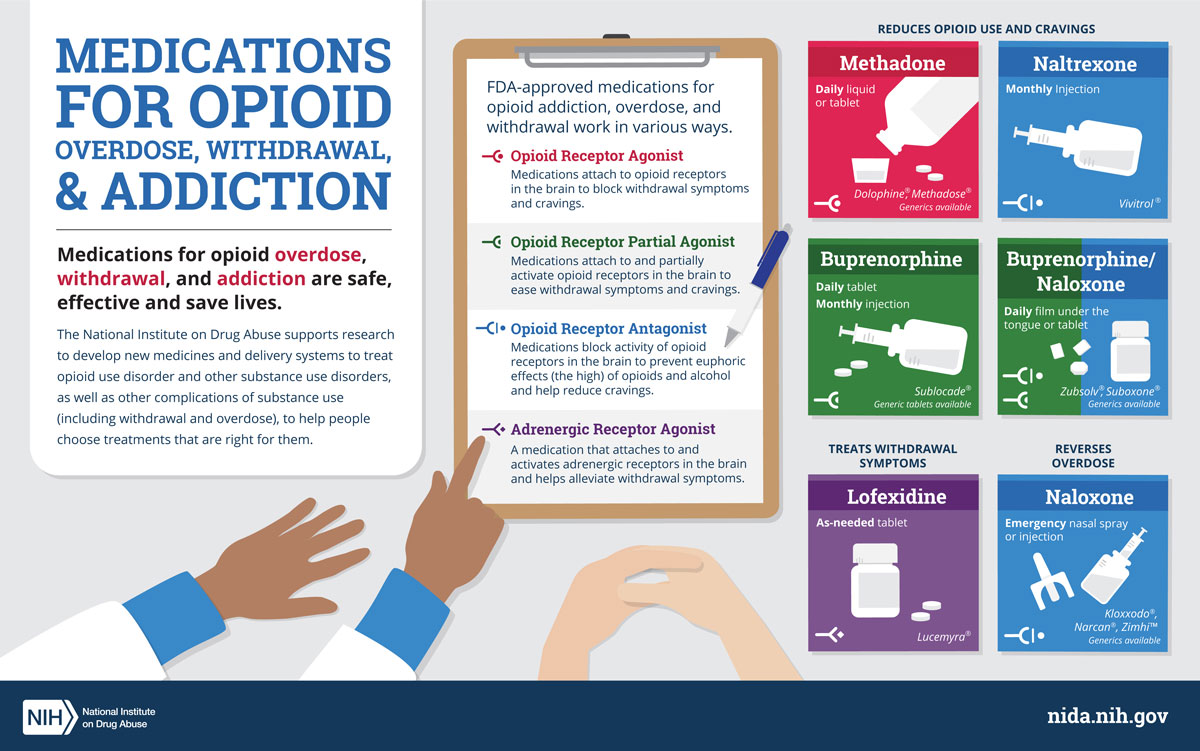
Opiate withdrawal can be difficult and uncomfortable, but there are things you can do to make the experience easier. These include getting plenty of rest, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding triggers or situations that may cause cravings. Medications such as clonidine, buprenorphine, and methadone can also help reduce symptoms like anxiety, insomnia, and sweating.
- How To Manage Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms:
1. Get plenty of rest.
2. Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates.
3. Exercise regularly.
4. Avoid triggers or situations that may cause cravings.
5. Take medications such as clonidine, buprenorphine, and methadone.
6. Seek support from family, friends, or support groups.
| Clonidine Vs Buprenorphine | Clonidine | Buprenorphine |
|---|---|---|
| Uses | Treats high blood pressure and symptoms of opioid withdrawal | Treats opioid addiction and withdrawal |
| Dosage Form | Tablet and liquid | Tablet, film, and sublingual tablet |
| Side Effects | Dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue, nausea, and headache | Constipation, nausea, headache, sweating, and insomnia |
Contents
What Helps With Opiate Withdrawal?
What is the Opiate Withdrawal?
Opiate withdrawal is a group of symptoms that can occur when someone who is dependent on opiates stops taking them. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and can last from a few days to several weeks. Common symptoms include insomnia, irritability, anxiety, sweating, and muscle aches.
Opiate withdrawal can be a difficult and uncomfortable process for those going through it. Fortunately, there are a number of things that can be done to help ease the symptoms and make the process more manageable.
Prescription Medications
One of the most common treatments for opiate withdrawal is the use of prescription medications. These medications can help to reduce the intensity and duration of withdrawal symptoms. Commonly prescribed medications include buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone.
These medications work by blocking the effects of opiates on the brain, helping to reduce cravings and prevent relapse. In addition, they can help to reduce some of the physical symptoms of withdrawal, such as nausea and vomiting.
Non-Prescription Medication
In addition to prescription medications, there are several non-prescription medications that can be used to help with opiate withdrawal symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can help to ease muscle aches and pains. Anti-nausea medications, such as Dramamine, can help to reduce nausea and vomiting.
In addition, some herbal remedies, such as kratom, have been used to help ease symptoms of opiate withdrawal. However, it is important to note that these remedies have not been extensively studied, and their effectiveness is not known.
Alternative Treatments
In addition to medications, there are several alternative treatments that can be used to help ease the symptoms of opiate withdrawal. Acupuncture, yoga, and massage can all help to reduce stress and ease muscle aches and pains. Cognitive behavioral therapy can help to address underlying emotional issues and reduce cravings.
In addition, some people find that lifestyle changes, such as getting regular exercise and eating a balanced diet, can help to make the withdrawal process easier.
Nutritional Supplements
Nutritional supplements can also be used to help with opiate withdrawal. Magnesium and other minerals can help to reduce muscle aches and pains, while vitamins B and C can help to reduce fatigue. Amino acids, such as L-tyrosine, can help to boost energy levels and reduce cravings.
Support Groups
Finally, support groups can be a valuable resource for those going through opiate withdrawal. Having the support of others who are in similar situations can be a great source of comfort and encouragement. In addition, support groups can provide helpful advice and resources for managing withdrawal symptoms.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Opiate Withdrawal?
Opiate withdrawal is a set of physical and psychological symptoms experienced when an individual stops using opiates after a period of prolonged use. Opiate withdrawal symptoms can include nausea, muscle aches, sweating, insomnia, restlessness, diarrhea, and anxiety.
What are the Stages of Opiate Withdrawal?
Opiate withdrawal can be broken down into four distinct stages. The first stage is the acute phase, which begins shortly after the last dose of opiate is taken and can last for up to 72 hours. During this time, the individual will experience intense cravings and flu-like symptoms. The second stage is the early withdrawal phase, which can last up to two weeks. During this time, the individual will experience physical and psychological symptoms such as agitation, insomnia, and depression. The third stage is the late withdrawal phase, which can last up to several weeks. During this time, the individual will experience psychological symptoms such as depression, irritability, and anxiety. The fourth and final stage is the post-acute withdrawal phase, which can last up to several months. During this time, the individual may experience cravings for opiates, difficulty sleeping, and mood swings.
What are the Natural Remedies for Opiate Withdrawal?
There are several natural remedies for opiate withdrawal that can help alleviate the symptoms and make the withdrawal process more bearable. These remedies include: exercising regularly, drinking plenty of fluids, eating a healthy diet, getting plenty of rest, avoiding alcohol and other drugs, and using relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation. Additionally, certain herbs and supplements such as valerian root, kratom, and St. John’s wort can be effective in reducing the severity of the withdrawal symptoms.
How Can Medication Help With Opiate Withdrawal?
Medication can be an effective way to manage opiate withdrawal symptoms. Medications such as buprenorphine and methadone can reduce cravings, reduce the severity of withdrawal symptoms, and help individuals transition to a drug-free lifestyle. Additionally, certain medications such as clonidine and lofexidine can help reduce symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and agitation.
What is the Most Effective Way to Deal With Opiate Withdrawal?
The most effective way to deal with opiate withdrawal is to seek professional help from a medical or addiction specialist. A medical professional can provide medication-assisted treatment, which can help reduce the severity of the withdrawal symptoms and make the withdrawal process more manageable. Additionally, a medical professional can provide counseling and other forms of therapy to help individuals cope with the psychological aspects of opiate withdrawal.
What Other Resources are Available to Help With Opiate Withdrawal?
In addition to professional help, there are several other resources available to those struggling with opiate withdrawal. These resources include support groups, online forums, and helplines. Support groups can provide individuals with an opportunity to share their experiences and receive emotional support from peers who are going through a similar experience. Online forums and helplines can provide individuals with access to resources and information about opiate withdrawal, as well as provide a safe and anonymous space to discuss their experiences and receive emotional support.
In conclusion, opiate withdrawal is a difficult process that can be managed with the right combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. There is no single “cure” to opiate withdrawal, but those who are struggling with the process can find help in many avenues. With the right help and support, those who are struggling with opiate addiction can find the support they need to overcome their addiction and begin the journey towards recovery.
