Stimulants are substances that can temporarily increase alertness, energy, and concentration. While they can be beneficial in some cases, they can also have some negative effects. In this article, we’ll explore what stimulants can cause and the potential risks associated with their use. We’ll also discuss why it’s important to consider the potential risks when considering taking stimulants.
Contents
- Stimulants and Its Effects on the Body
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What are Stimulants?
- What are the Short-Term Effects of Stimulants?
- What are the Long-Term Effects of Stimulants?
- What are the Potential Side Effects of Stimulant Abuse?
- What are some of the Warning Signs of Stimulant Abuse?
- What Should I Do if I Suspect Someone is Abusing Stimulants?
- Stimulants: Everything You Should Know
Stimulants and Its Effects on the Body
Stimulants are substances that act on the central nervous system to create a feeling of alertness and increased energy. These substances can be found naturally in food and beverages, or they can be synthetic drugs. Stimulants can be used to treat conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. However, they can also have a range of negative side effects if taken in large doses or over an extended period of time.
Stimulants work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These chemicals stimulate the brain and can lead to feelings of alertness and energy. However, too much stimulation can result in unwanted side effects, such as anxiety, insomnia, and heart palpitations.
Physical Effects of Stimulants
The physical effects of stimulants can range from mild to severe, depending on the type of stimulant and the amount taken. Common physical effects include increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, increased body temperature, and increased breathing rate. In addition, stimulants can cause a decrease in appetite, nausea, and vomiting.
Long-term use of stimulants can also lead to physical dependence, which is characterized by withdrawal symptoms when the drug is stopped. Common withdrawal symptoms include depression, fatigue, and cravings for the drug. In addition, long-term use can cause damage to the cardiovascular system and can lead to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Cognitive Effects of Stimulants
Stimulants can also have an effect on cognitive functions, such as memory, concentration, and decision-making. Stimulants can cause feelings of euphoria, which can lead to impaired judgement and increased risk-taking behavior. Additionally, stimulants can cause feelings of anxiety, irritability, and paranoia.
In the long-term, stimulants can cause changes in the structure and function of the brain. This can lead to difficulty in learning and memory formation, as well as an increased risk of developing mental health issues such as depression and schizophrenia.
Behavioral Effects of Stimulants
Stimulants can also have an effect on behavior. Stimulants can cause a person to become impulsive and can lead to reckless and dangerous behavior. Additionally, stimulants can cause a person to become aggressive and hostile.
In the long-term, stimulants can cause a person to become dependent on the drug and can lead to addiction. Stimulant addiction can lead to financial, social, and legal problems and can be very difficult to overcome.
Side Effects of Stimulants
The side effects of stimulants vary depending on the type and amount of stimulant taken. Common side effects include headaches, nausea, dizziness, and insomnia. In addition, stimulants can cause dry mouth, constipation, and sexual dysfunction.
Long-term use of stimulants can lead to an increased risk of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular problems. In addition, long-term use can lead to an increased risk of developing mental health issues such as depression and schizophrenia.
Risk Factors for Stimulant Abuse
There are certain risk factors that can increase a person’s likelihood of abusing stimulants. These risk factors include a family history of substance abuse, mental health issues such as depression or anxiety, and exposure to drugs or alcohol at a young age.
In addition, certain demographics are more at risk of stimulant abuse, including young adults, people in lower socioeconomic classes, and those who have experienced trauma or abuse.
Treatment for Stimulant Abuse
Treatment for stimulant abuse is available and can be tailored to the individual’s needs. Treatment typically begins with a detoxification process, followed by counseling and behavioral therapy. In addition, medications such as antidepressants can be used to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Long-term treatment typically includes relapse prevention, support groups, and lifestyle changes. These treatments can help individuals recover from stimulant abuse and lead a healthy, productive life.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What are Stimulants?
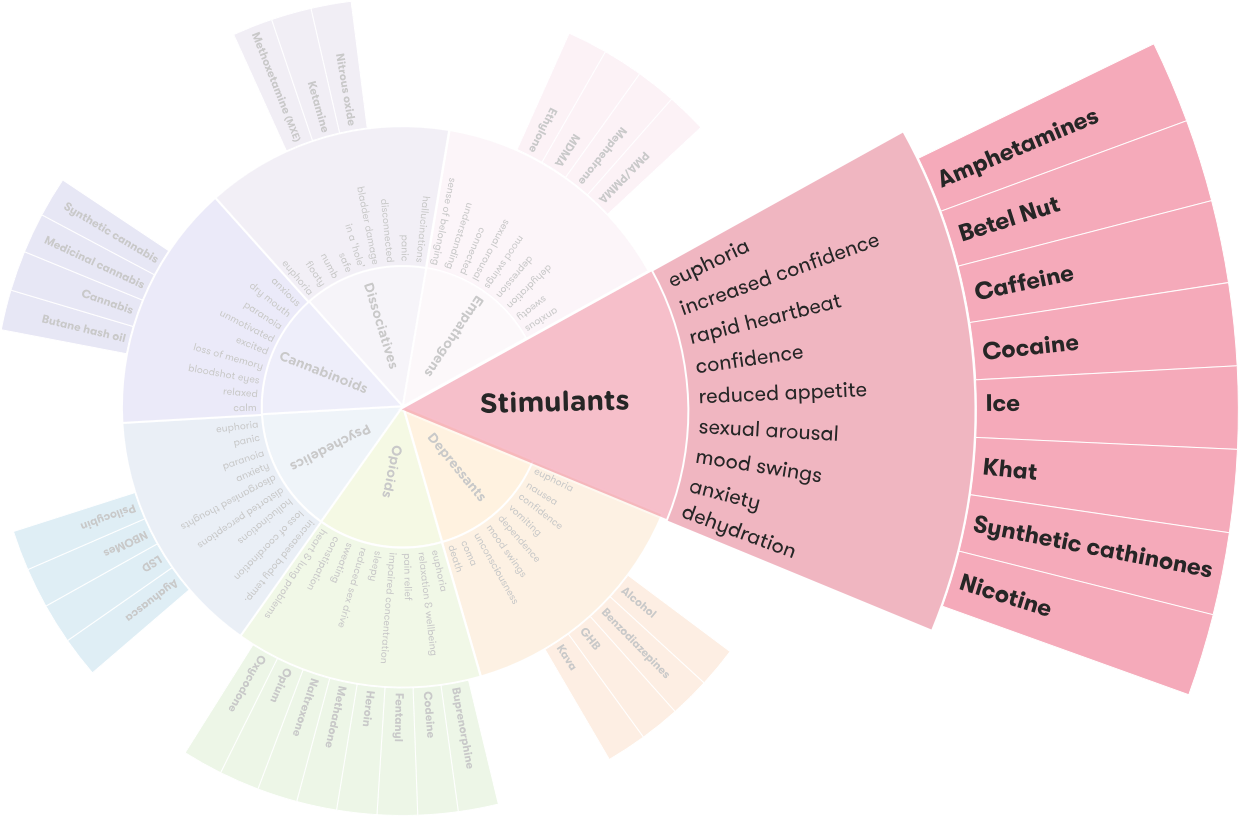
A stimulant is a type of drug that temporarily increases alertness, attention, and energy. Common examples of stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, and amphetamines. Stimulants can be found in many everyday products, such as energy drinks, coffee, and cigarettes.
What are the Short-Term Effects of Stimulants?
The short-term effects of stimulants can include increased alertness and energy, decreased appetite, increased heart rate and blood pressure, increased breathing rate, and increased physical activity. Stimulants can also cause feelings of euphoria, increased confidence, and improved concentration.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Stimulants?
Long-term use of stimulants can cause a number of physical and psychological problems, including high blood pressure, heart palpitations, restlessness, insomnia, anxiety, depression, and addiction. Stimulants can also affect the cardiovascular system, leading to an increased risk of stroke and heart attack.
What are the Potential Side Effects of Stimulant Abuse?
The potential side effects of stimulant abuse can include increased risk of heart attack and stroke, irregular heartbeat, physical and psychological addiction, anxiety, paranoia, hallucinations, and psychosis. Stimulant abuse can also lead to violent behavior, impaired judgment, and extreme weight loss.
What are some of the Warning Signs of Stimulant Abuse?
Warning signs of stimulant abuse can include sudden changes in behavior, irregular sleep patterns, increased agitation or irritability, dilated pupils, increased energy and alertness, and extreme weight loss. Other signs of stimulant abuse can include physical exhaustion, mood swings, paranoia, and financial problems.
What Should I Do if I Suspect Someone is Abusing Stimulants?
If you suspect someone is abusing stimulants, it is important to get them help as soon as possible. Talk to the person and explain your concerns in a non-judgmental way. You can also reach out to a healthcare provider, who can provide resources and treatment options. Finally, it is important to be supportive and understanding of the person and provide them with a safe and supportive environment.
Stimulants: Everything You Should Know
In conclusion, stimulants can cause a wide variety of physical and mental effects. These may range from increased alertness and energy, to slowed digestion and increased heart rate. They can also cause anxiety, agitation, and insomnia. In extreme cases, stimulants can lead to heart failure, seizures, and even death. It is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with the use of stimulants. If you are considering taking a stimulant, it is best to talk to your doctor first.
