If you or someone you know is struggling with opiate addiction, you know how difficult it can be to break free from the cycle of substance abuse. Opiate withdrawal is an uncomfortable and often painful process that can make the body feel like it’s in a state of chaos. It’s important to know that opiate withdrawal is both manageable and treatable. In this article, you will learn how to deal with opiate withdrawal and what steps you can take to make the process as smooth and comfortable as possible.
Contents
- How to Deal With Opiate Withdrawal?
- Understanding Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms
- Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
- Medications for Opiate Withdrawal
- Alternative Therapies for Opiate Withdrawal
- Related Faq
- What are the Symptoms of Opiate Withdrawal?
- What is the Best Way to Manage Opiate Withdrawal?
- How Long Does Opiate Withdrawal Last?
- What is the Best Way to Cope With Opiate Withdrawal?
- What are the Complications of Opiate Withdrawal?
- What is the Difference Between Acute and Post-Acute Withdrawal Syndrome?
- Opioid Withdrawal: What It’s Like to Detox from Opiates | MedCircle
How to Deal With Opiate Withdrawal?
Understanding Opiate Withdrawal Symptoms
Opiate withdrawal symptoms include physical and psychological symptoms. Physical symptoms include sweating, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal cramping, insomnia, and restlessness. Psychological symptoms include anxiety, depression, irritability, and drug cravings. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can last for several days or weeks depending on the severity of the addiction and the type of opiate used. It is important to understand these symptoms so that you can prepare yourself to cope with them during the withdrawal process.
Seeking Professional Help
One of the most important steps to take when dealing with opiate withdrawal is to seek professional help. A medical professional such as a doctor or addiction specialist can provide advice on how to cope with the withdrawal symptoms and can also provide medications to help ease the symptoms. It is important to discuss any concerns you have with your doctor before starting any type of treatment.
Finding Support
Finding support from family, friends, and support groups can also be beneficial during the withdrawal process. It is important to have a support system that can provide encouragement and understanding during this difficult time. Support groups can provide a safe space to discuss your feelings and provide helpful tips on how to cope with the withdrawal symptoms.
Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
Eating a Healthy Diet
Eating a healthy diet can help to reduce the severity of the withdrawal symptoms. Eating small, frequent meals that are rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to keep your energy levels up and your body nourished. It is also important to stay hydrated and drink plenty of water to help flush toxins from your body.
Exercising Regularly
Exercising regularly can help to reduce stress and improve your overall mood. Exercise can also help to reduce the intensity of the withdrawal symptoms. It is important to start with low-impact activities such as walking or yoga and gradually increase the intensity as your body adjusts.
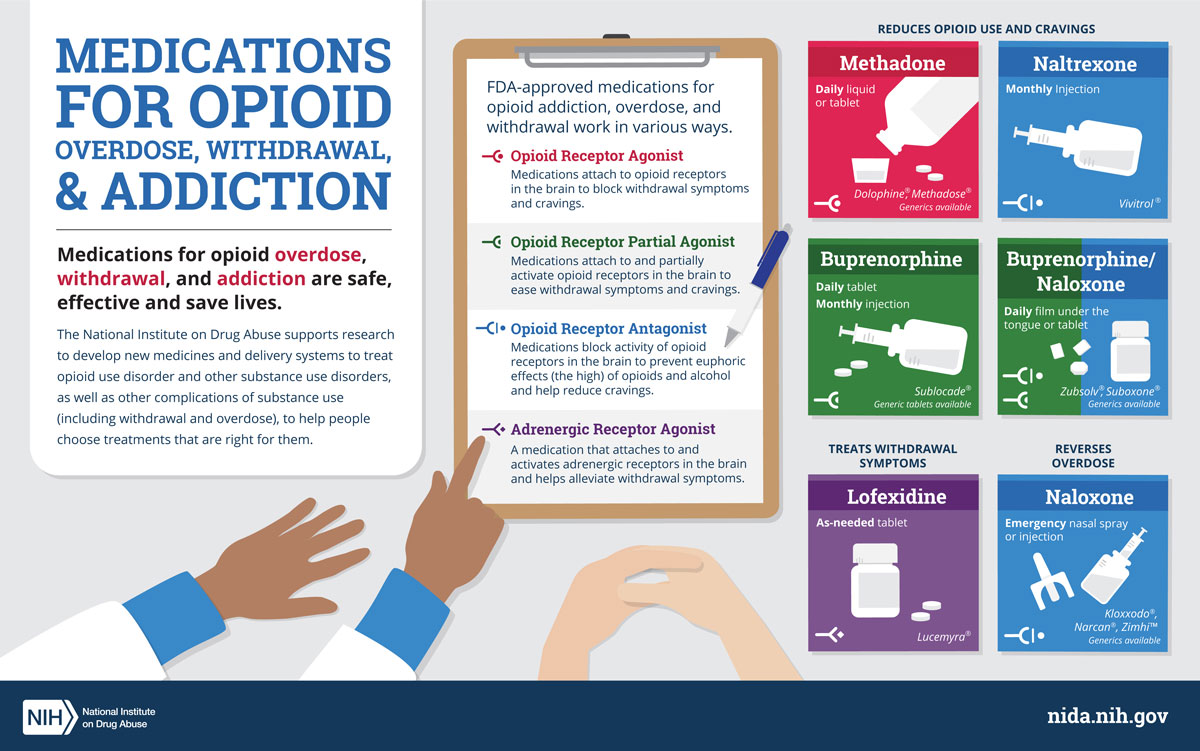
Medications for Opiate Withdrawal
Opiate Replacement Therapy
Opiate replacement therapy is a type of medication used to help ease the withdrawal symptoms. This type of therapy involves taking a synthetic opiate such as methadone or Suboxone to reduce the intensity of the withdrawal symptoms. This type of therapy is typically used for those with moderate to severe opiate addiction.
Non-Opiate Medications
Non-opiate medications such as anti-anxiety medications, anti-depressants, and sleep aids can also be used to help manage the withdrawal symptoms. These medications can help to reduce anxiety, depression, and insomnia. It is important to discuss any concerns you have with your doctor before starting any type of medication.
Alternative Therapies for Opiate Withdrawal
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an alternative therapy that can be used to help reduce the intensity of the withdrawal symptoms. This type of therapy involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to reduce pain and help relax the body. Acupuncture can also help to improve energy levels, reduce stress, and improve overall wellbeing.
Yoga and Meditation
Yoga and meditation can also help to reduce stress and improve overall wellbeing during the withdrawal process. These activities can help to relax the body and reduce the intensity of the withdrawal symptoms. It is important to find activities that you enjoy and can stick with to help manage the withdrawal symptoms.
Related Faq
What are the Symptoms of Opiate Withdrawal?
Opiate withdrawal symptoms can vary depending on the type and amount of the drug used and the length of time the drug was used for. Common symptoms include restlessness, insomnia, sweating, muscle aches and pains, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, irritability, anxiety, and depression. Other symptoms can include cravings for the drug and increased sensitivity to pain.
What is the Best Way to Manage Opiate Withdrawal?
The best way to manage opiate withdrawal is to seek professional help. Treatment plans may include medications, such as methadone or buprenorphine, to help reduce the intensity of withdrawal symptoms. Other supportive therapies, such as counseling and lifestyle changes, may be recommended in order to help the person cope with physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of withdrawal.
How Long Does Opiate Withdrawal Last?
The duration of opiate withdrawal can vary, depending on the type of drug used and the length of time the person was using it. Generally, withdrawal symptoms typically peak within 48-72 hours after the last dose of the drug and can last for up to two weeks.
What is the Best Way to Cope With Opiate Withdrawal?
The best way to cope with opiate withdrawal is to seek professional help. Treatment plans should be tailored to the individual’s needs and may include medications, such as methadone or buprenorphine, to help reduce the intensity of withdrawal symptoms. Other supportive therapies, such as counseling and lifestyle changes, may be recommended in order to help the person cope with physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of withdrawal. Additionally, it can be helpful to engage in activities that are calming or distracting, such as yoga, meditation, listening to music, or reading.
What are the Complications of Opiate Withdrawal?
The complications of opiate withdrawal can include dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, seizures, and mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. These complications can be serious and should be monitored and treated by a medical professional.
What is the Difference Between Acute and Post-Acute Withdrawal Syndrome?
Acute withdrawal syndrome occurs during the initial days of withdrawal and is characterized by physical symptoms such as sweating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and muscle aches. Post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS) occurs after the physical symptoms of acute withdrawal have subsided and can last for up to two years. PAWS symptoms can include depression, anxiety, insomnia, and cognitive deficits. It is important to seek treatment for both acute and post-acute withdrawal syndrome in order to avoid complications and ensure a successful recovery.
Opioid Withdrawal: What It’s Like to Detox from Opiates | MedCircle
In conclusion, dealing with opiate withdrawal can be a difficult and trying process, but it is possible to manage the symptoms with the right approach. With the help of a doctor or addiction specialist, you can create a plan that works best for you and your situation, whether it is through medications, behavioral therapy, or other methods. No matter what, remember that you are not alone and recovery is possible.
