We’ve all heard the warnings about the dangers of smoking, but one potential side effect that doesn’t get talked about as much is anxiety. Does nicotine really increase anxiety, or is it just a myth? In this article, we’ll explore what the research says about nicotine and anxiety, and provide some tips on how to manage them.
Nicotine has been found to increase anxiety in some people. Studies have shown that nicotine can cause an increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration, which can lead to feelings of anxiety. It can also trigger the release of certain hormones, such as cortisol, which can further increase anxiety. People who are already prone to anxiety may want to avoid nicotine altogether.
Contents
Does Nicotine Increase Anxiety?
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is a stimulant found in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. It is known to increase alertness and energy levels, but it can also have other psychological effects. Some studies have suggested that nicotine may increase anxiety, while others have found no link between nicotine and anxiety.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Brain?
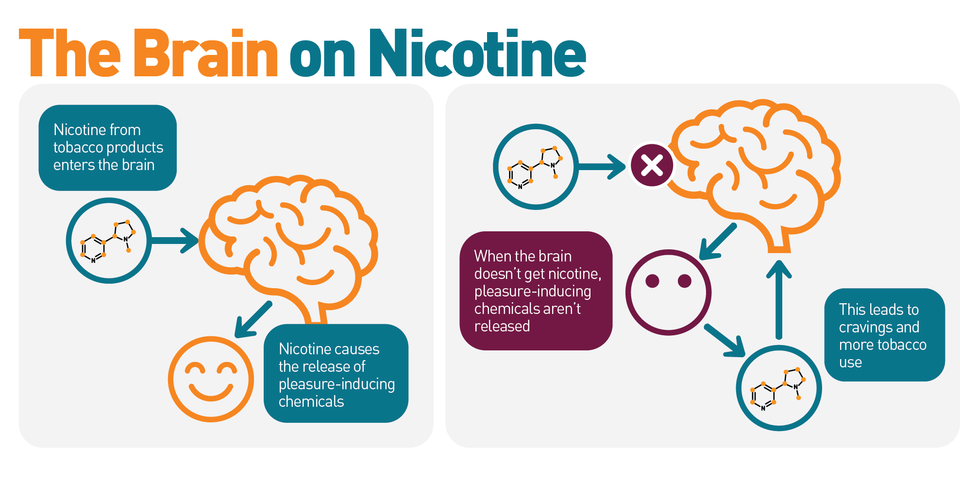
Nicotine affects the brain by increasing the production of certain neurotransmitters like acetylcholine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters have been linked to increased alertness, focus, and energy. However, nicotine may also increase the production of other neurotransmitters, like dopamine and serotonin, which are associated with feelings of pleasure and relaxation.
Does Nicotine Increase Anxiety?
Some research suggests that nicotine may increase levels of the stress hormone cortisol, which can lead to feelings of anxiety. Other studies have found that nicotine may lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, which can also contribute to anxiety. However, some experts believe that the effects of nicotine on anxiety may depend on other factors, such as the dose of nicotine and the individual’s current mental state.
The Risk of Nicotine Addiction
Not only may nicotine increase anxiety, but it can also lead to addiction. Nicotine acts on the brain’s reward system, producing feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. This can lead to a cycle of addiction, where an individual needs more and more nicotine to achieve the same effects. This can lead to a variety of physical and psychological health problems, including increased anxiety.
The Impact of Nicotine Withdrawal
When an individual stops using nicotine, they may experience uncomfortable and disruptive withdrawal symptoms, such as irritability, feeling jittery, headaches, and anxiety. These symptoms can be difficult to cope with, and they can make it hard for someone to quit nicotine.
Managing Anxiety With Nicotine
Some people may use nicotine to manage anxiety, but this is not recommended. Not only can nicotine addiction lead to increased anxiety, but it can also cause other health problems. Instead, individuals should seek professional help to manage their anxiety and find healthier ways to cope with it.
Nicotine and Other Substances
Nicotine is often found in combination with other substances, such as alcohol or caffeine. These substances can interact with nicotine and increase its effects on anxiety. For example, alcohol can increase the sedative effects of nicotine, leading to increased relaxation and decreased anxiety. However, this can also lead to an increased risk of addiction.
Nicotine and Mental Health
It is important to note that nicotine can interact with mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. Nicotine can increase the effects of these conditions and make them worse. Therefore, individuals with mental health conditions should be especially careful when using nicotine products.
The Bottom Line
Overall, nicotine may have some effects on anxiety, but the evidence is still inconclusive. There are a variety of factors that can affect how nicotine affects anxiety, including the dose and individual factors. Therefore, it is important to talk to a doctor before using nicotine products.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is an alkaloid found in certain plants, primarily tobacco, and in lower quantities, tomatoes, potatoes, and eggplant. It is an addictive stimulant and a key component of most tobacco products. It functions as a neurotransmitter, which means it transmits signals from one nerve cell to another. Nicotine is known to have both positive and negative effects on the body, depending on the amount and how it is consumed.
What are the effects of Nicotine?
The effects of nicotine vary depending on the dose and how it is consumed. In general, nicotine acts as a stimulant and can increase alertness, improve focus, and reduce fatigue. It also has other effects, such as increasing heart rate, raising blood pressure, and stimulating the release of adrenaline. On the other hand, nicotine can also cause feelings of relaxation, reduce appetite, and provide a feeling of satisfaction.
Does Nicotine Increase Anxiety?
There is some evidence that nicotine can increase anxiety in some individuals. High doses of nicotine can cause feelings of restlessness, irritability, and agitation. Additionally, nicotine can increase the levels of certain hormones, such as cortisol, which can lead to increased anxiety.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Nicotine?
The long-term effects of nicotine vary depending on the amount and how it is consumed. Regular use has been linked to increased risk of developing certain types of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic conditions. It has also been linked to increased risk of developing mood and anxiety disorders.
Is Nicotine Addictive?
Yes, nicotine is highly addictive. It acts on the brain’s reward system, which can lead to compulsive use and dependence. Additionally, nicotine withdrawal can cause physical and psychological symptoms, such as cravings, irritability, and trouble sleeping.
What are Some Ways to Reduce Nicotine Intake?
If you are trying to reduce your nicotine intake, there are several strategies you can use. These include switching to nicotine-free products, using nicotine replacement therapies (such as patches, gums, and lozenges), avoiding triggers that lead to cravings, and seeking professional help. Additionally, exercise and stress reduction techniques may also help reduce nicotine cravings.
Reductions in anxiety in smokers who quit is at least as great as for those taking anti-depressants
In conclusion, the evidence suggests that nicotine does indeed increase anxiety levels – at least in the short-term. However, the long-term effects of nicotine on anxiety are still unclear, and further research is needed to determine the true impact of nicotine on anxiety. In the meantime, it is advisable to avoid smoking or using nicotine-based products as a way to reduce stress or anxiety levels, as the risks may outweigh any potential benefits.
