The use of opiates has become increasingly widespread in recent years, and while they are often prescribed to treat pain, they can also have serious side effects. One of the most serious of these is the potential for opiates to cause heart problems. In this article, we will look at the evidence linking opiates to heart issues and discuss the potential risks associated with taking opiates.
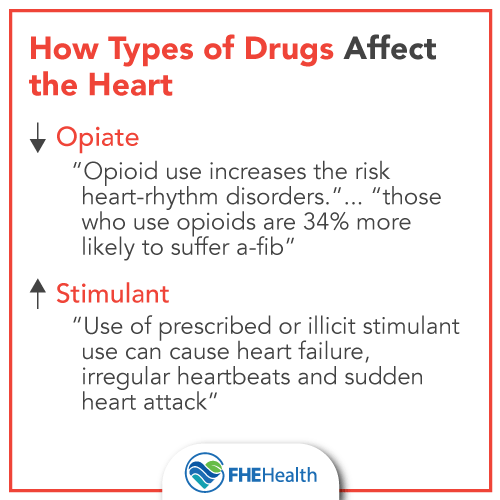
Yes, opiates can cause heart problems. Taking opiates can increase blood pressure and heart rate, and can lead to the development of coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke. Long-term use of opiates can also contribute to heart problems, including abnormal heart rhythms, congestive heart failure, and even sudden death.
Contents
- Can Opiates Lead to Cardiovascular Problems?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Question 1: What are opiates?
- Question 2: How do opiates work?
- Question 3: Can opiates cause heart problems?
- Question 4: What are the long-term effects of opiate use?
- Question 5: Are there any ways to reduce the risk of opiate-related heart problems?
- Question 6: What should I do if I think I’m having a heart problem due to opiate use?
- Can Opiate Abuse Cause Heart Problem?
Can Opiates Lead to Cardiovascular Problems?
Opiate medications are commonly used to treat severe pain, but they can have serious side effects, including cardiovascular problems. Opiates are a type of opioid, a class of drugs that act on the nervous system to reduce the perception of pain. Opiates can be prescribed by a doctor or obtained illegally, and they can lead to addiction and abuse. While opiates are effective at treating pain, they can also cause a range of cardiovascular problems, including irregular heart rate, high blood pressure, and heart failure.
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Problems
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of experiencing cardiovascular problems when using opiates. People with a history of heart problems or who have high blood pressure are at an increased risk of experiencing cardiovascular side effects from opiate use. People who use opiates in large doses or for long periods of time are also at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular problems. Additionally, people who mix opiates with other drugs or alcohol are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular issues.
Signs and Symptoms of Cardiovascular Problems
When taking opiates, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of cardiovascular problems. These can include irregular heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness. If any of these symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Additionally, it is important to report any side effects to the physician prescribing the opiates.
Treatment for Cardiovascular Problems
Treatment for cardiovascular problems caused by opiate use will vary depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. In some cases, it may be necessary to reduce or stop opiate use to reduce the risk of further complications. In other cases, it may be necessary to adjust the dose or switch to a different medication. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity and eating a healthy diet, can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Long-Term Effects of Cardiovascular Problems
The long-term effects of opiate-induced cardiovascular problems can be serious and potentially life-threatening. In some cases, prolonged use of opiates can lead to heart failure or even death. Additionally, the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular problems increases with long-term opiate use. It is important to be aware of the potential risks of opiate use and to seek medical advice if any side effects occur.
Conclusion
Opiates are a powerful and effective pain reliever, but they can also lead to serious cardiovascular problems. People who use opiates, particularly in large doses or for long periods of time, are at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular problems. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of cardiovascular problems, and to seek medical advice if any occur. Additionally, it is important to be aware of the long-term effects of opiate use and to monitor the use of opiates closely to reduce the risk of complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What are opiates?
Answer: Opiates are a type of drug derived from the opium poppy plant. Commonly used opiates include morphine, codeine, and heroin. These drugs are often prescribed to treat pain, but can be highly addictive and can lead to physical and psychological dependence.
Question 2: How do opiates work?
Answer: Opiates work by binding to opiate receptors in the brain and body and blocking the perception of pain. They also produce a range of other effects, including decreased anxiety, sedation, euphoria, and respiratory depression.
Question 3: Can opiates cause heart problems?
Answer: Yes, opiates can cause a range of heart problems, including increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and arrhythmia. Overdosing on opiates can also cause a heart attack or stroke.
Question 4: What are the long-term effects of opiate use?
Answer: Long-term use of opiates can lead to tolerance, physical and psychological dependence, and addiction. It can also lead to serious health problems, such as liver damage, kidney damage, and heart problems.
Answer: Yes, there are several ways to reduce the risk of opiate-related heart problems. These include avoiding large doses of opiates, taking the medication as prescribed, and avoiding the use of illicit substances.
Question 6: What should I do if I think I’m having a heart problem due to opiate use?
Answer: If you think you are having a heart problem due to opiate use, it is important to seek medical help immediately. You should also stop taking the opiate and seek addiction treatment if necessary.
Can Opiate Abuse Cause Heart Problem?
In conclusion, opiates can cause a range of serious heart problems and should be used with caution. While they are often prescribed to treat pain, they come with a range of risks that can have serious and long-lasting consequences. It is important to understand the full range of side effects associated with opiate use and to discuss any concerns with your doctor before taking them.
