Hallucinations can be frightening, especially when you don’t know what’s causing them. While hallucinations have many potential causes, one of the lesser known possibilities is opiate use. Opiates are a type of drug that can be prescribed for pain relief, but can also be abused. In this article, we’ll explore the potential of opiates to cause hallucinations, and what you can do if you or someone you know is experiencing them.
Yes, opioids can cause hallucinations in some people. Hallucinations can be auditory, visual, or tactile, and can range from mild to severe. They may also be accompanied by other mental health symptoms such as paranoia and confusion. If a person is experiencing hallucinations, it is important to seek medical help to determine the cause and best treatment options.
Contents
- Can Opiates Induce Hallucinations?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1. What Are Opiates?
- Q2. Can Opiates Cause Hallucinations?
- Q3. What Are the Symptoms of Opiate-Induced Hallucinations?
- Q4. Are Opiate-Induced Hallucinations Dangerous?
- Q5. How Are Opiate-Induced Hallucinations Treated?
- Q6. Is It Possible to Prevent Opiate-Induced Hallucinations?
- This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
Can Opiates Induce Hallucinations?
Opiate drugs are commonly used to help treat pain and can be found in many different forms, such as codeine, morphine, and heroin. Opiates are powerful and can cause a range of side effects, including hallucinations. This article explores whether opiates can truly cause hallucinations and what the potential risks and consequences are.
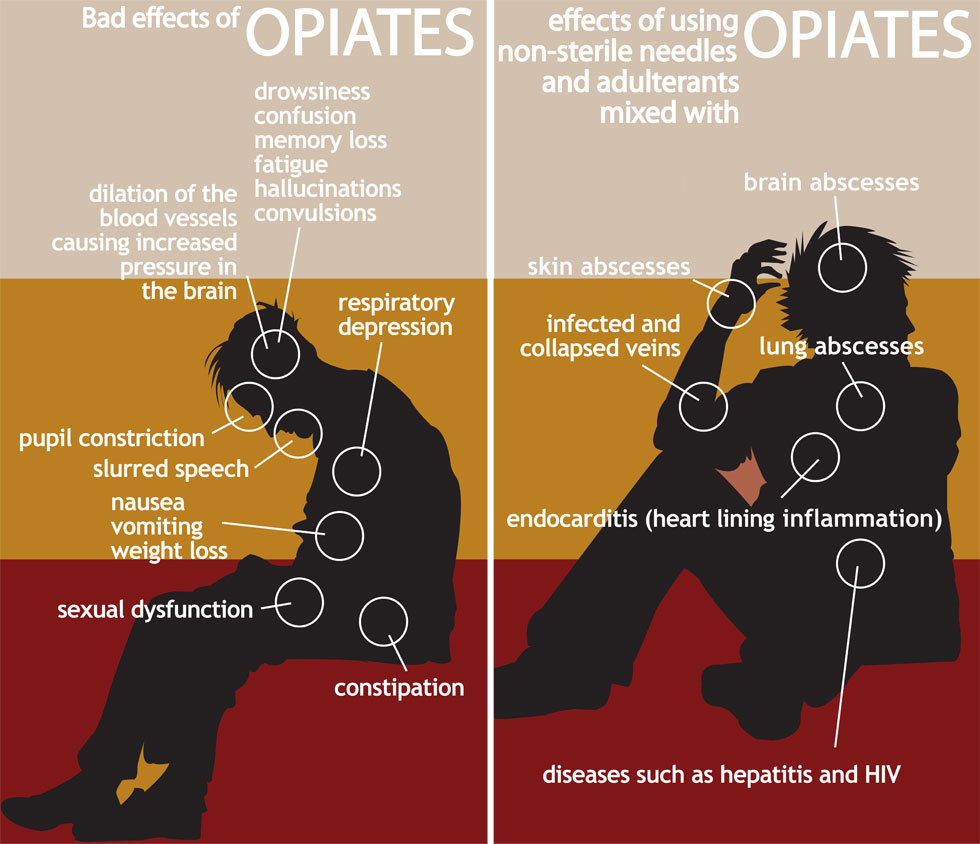
Hallucinations are defined as perceiving things that are not real. Drugs, including opiates, can sometimes cause people to experience hallucinations. Opiates can cause people to hallucinate in various ways, such as seeing, hearing, and feeling things that are not actually there. These types of hallucinations can be either visual or auditory, and can be quite intense.
The hallucination effects of opiates are often more pronounced in those who have never used the drug before, as well as those with a pre-existing mental health condition. People who have taken opiates for a long period of time and become dependent on them may also be more likely to experience hallucinations.
What Causes Opiate-Induced Hallucinations?
The exact cause of opiate-induced hallucinations is unknown, but it is believed to be related to the drug’s effect on the brain’s reward system and neurotransmitters. When opiates bind to the brain’s opioid receptors, they can cause an increase in the levels of certain neurotransmitters such as dopamine, resulting in hallucinations.
It is also believed that the hallucination effects of opiates may be due to the drug’s ability to disrupt the brain’s balance of “normal” functioning. When the brain’s normal state of functioning is disrupted, it can lead to a variety of altered mental states, including hallucinations.
What Are the Risks of Hallucinations?
Hallucinations can be a frightening experience, especially when they are unexpected and intense. People who experience opiate-induced hallucinations may feel confused, scared, out of control, or even panicked. These feelings can lead to further distress and, in some cases, even self-harm or suicide.
In addition, opiate-induced hallucinations can cause people to become detached from reality and disconnected from reality. This can make it difficult for them to engage in everyday activities, such as going to work or school, and can exacerbate pre-existing mental health issues.
How Can Hallucinations Be Treated?
If you are experiencing opiate-induced hallucinations, it is important to seek medical help. Your doctor may prescribe medications to help reduce the frequency and intensity of the hallucinations. In some cases, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) may be recommended to help manage the hallucinations and reduce their impact on your life.
It is also important to reduce or stop using opiates. If you are struggling with opiate dependence, your doctor may recommend a tapering program or other treatment options. Detoxing from opiates can be difficult, so it is important to seek professional help to ensure a safe and successful detox.
Can Opiate-Induced Hallucinations Be Prevented?
The best way to prevent opiate-induced hallucinations is to avoid taking opiates altogether. If you are prescribed an opiate medication, be sure to take it as directed and only as needed. Additionally, be sure to discuss any potential side effects with your doctor before taking opioids.
It is also important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of opiate dependence. If you find yourself needing more and more of the drug to achieve the same effect, or if you are experiencing withdrawal symptoms when you try to stop taking the drug, it may be time to seek help.
Can Hallucinations Be Dangerous?
Hallucinations can be a frightening and disorienting experience, and can sometimes lead to dangerous behaviors. If you are experiencing opiate-induced hallucinations, it is important to seek help from a medical professional. With the right treatment, it is possible to reduce the frequency and intensity of the hallucinations and manage them in a safe and healthy way.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What Are Opiates?
A1. Opiates are a type of drug derived from the opium poppy plant. They are used to produce pain relief, sedation, and euphoria. Examples of opiates include morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and heroin. Opiates are highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Q2. Can Opiates Cause Hallucinations?
A2. Yes, opiates can cause hallucinations. Hallucinations are a type of psychological symptom that occurs when someone experiences sensory perceptions that are not actually real. Examples of hallucinations that can be caused by opiates include visual, auditory, and tactile experiences.
Q3. What Are the Symptoms of Opiate-Induced Hallucinations?
A3. Common symptoms of opiate-induced hallucinations include seeing and hearing things that others do not, feeling sensations that do not exist, and having an altered sense of time or reality. Other symptoms can include confusion, agitation, and paranoia.
Q4. Are Opiate-Induced Hallucinations Dangerous?
A4. Opiate-induced hallucinations can be dangerous if they lead to risky or dangerous behavior. If someone experiencing opiate-induced hallucinations is not properly monitored and treated, they may be at risk of harm to themselves or others.
Q5. How Are Opiate-Induced Hallucinations Treated?
A5. Opiate-induced hallucinations are typically treated with a combination of medications and psychotherapy. Medications used to treat opiate-induced hallucinations may include antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants. Psychotherapy can help people learn to manage and cope with their symptoms.
Q6. Is It Possible to Prevent Opiate-Induced Hallucinations?
A6. The best way to prevent opiate-induced hallucinations is to avoid using opiates. If opiates are being used, they should be taken as prescribed and monitored closely by a doctor. It is also important to avoid taking higher doses than what is prescribed and to avoid taking opiates with other substances, such as alcohol.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates can cause hallucinations. While they may not be as common as other side effects, they are still a very real possibility. It is important to be aware of all of the potential side effects of taking opiates, and to be on the lookout for any strange or unexpected changes in behavior or mental state. If these side effects do occur, it is important to speak with a doctor right away and get the appropriate medical attention.
