Opiate withdrawal can be an incredibly uncomfortable experience, with symptoms ranging from restlessness and anxiety to nausea and muscle aches. But one of the lesser known side effects of opiate withdrawal is that it can cause high blood pressure. In this article, we will explore how opiate withdrawal can lead to hypertension, the dangers of high blood pressure, and what can be done to prevent it.
Yes, opiate withdrawal can cause high blood pressure. High blood pressure is one of the most common symptoms of opiate withdrawal. Other symptoms include anxiety, nausea, sweating, chills, insomnia, and muscle aches. In some cases, withdrawal can also cause an increase in heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure.
Contents
- Can Opiate Withdrawal Result in High Blood Pressure?
- Related Faq
- Q1. Is it normal for someone to experience high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal?
- Q2. What other symptoms may accompany high blood pressure in opiate withdrawal?
- Q3. How long does high blood pressure usually last during opiate withdrawal?
- Q4. Can high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal cause other health issues?
- Q5. What can be done to reduce the effects of high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal?
- Q6. Is it possible to prevent high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal?
- The science of opioid withdrawal
Can Opiate Withdrawal Result in High Blood Pressure?
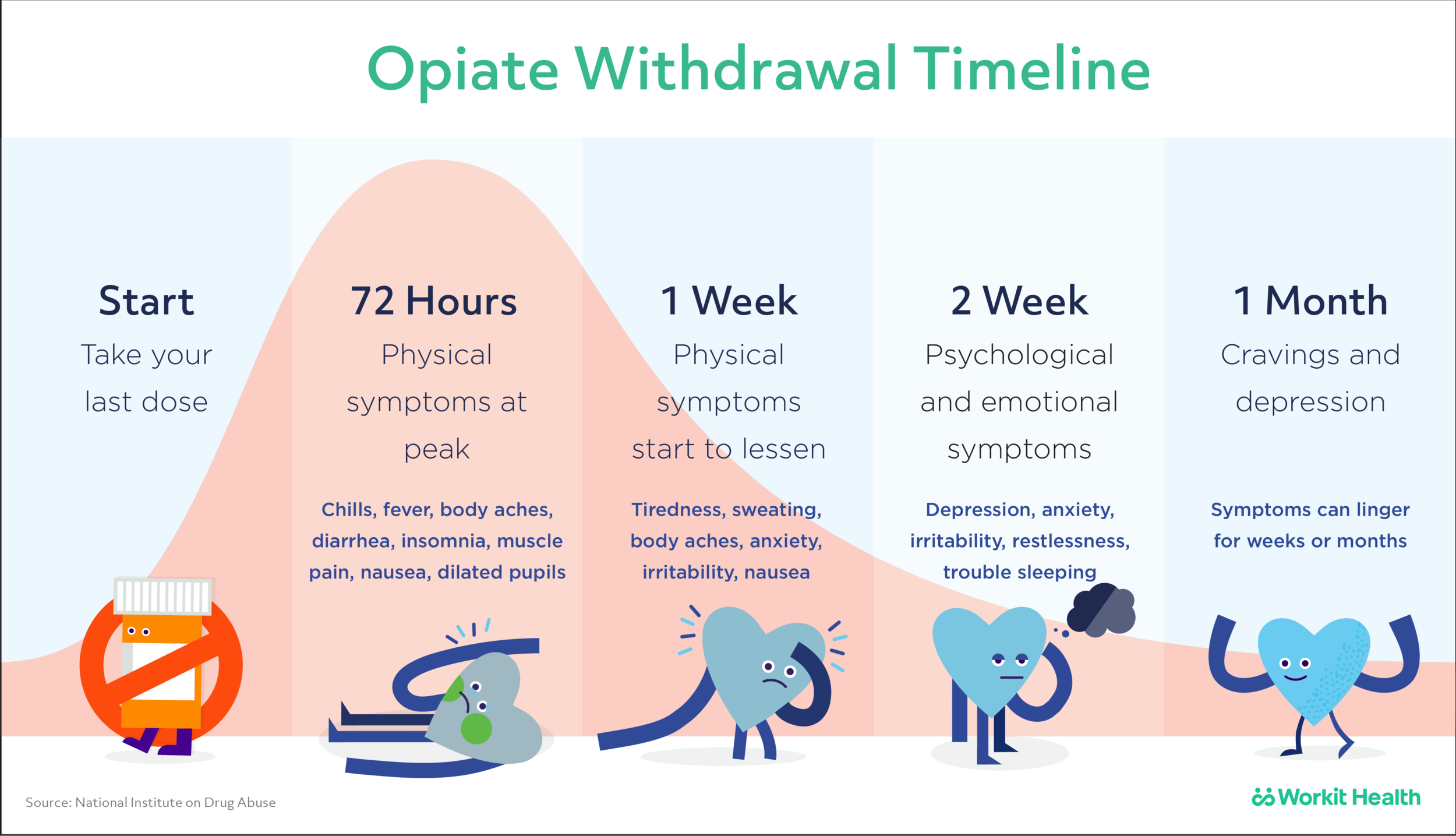
Opiate withdrawal is a set of physical and psychological symptoms that occur after a person stops using opiates or reduces their dosage. It is a difficult process and can cause many uncomfortable symptoms, including high blood pressure. The intensity and duration of withdrawal symptoms vary depending on the person and the type of drug used. This article will discuss the connection between opiate withdrawal and high blood pressure and how to manage it.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a condition in which the force of the blood against the artery walls is too high. When the body is exposed to opiate withdrawal, it can go into a fight-or-flight state, where the heart rate and blood pressure both increase. This is the body’s way of trying to cope with the changes and adjust to the new situation. Unfortunately, this can lead to long-term increases in blood pressure, which can be dangerous.
Fortunately, there are ways to manage and reduce high blood pressure caused by opiate withdrawal. The most important step is to seek professional medical help. It is important to find a doctor who is knowledgeable about opiate withdrawal and can provide the necessary treatment. Additionally, there are lifestyle changes that can help manage high blood pressure, such as eating a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing stress.
What Causes High Blood Pressure During Opiate Withdrawal?
When a person stops using opiates or reduces their dosage, their body is forced to adjust to the new situation. This can cause a wide range of physical and psychological symptoms, such as sweating, nausea, fatigue, and irritability. It can also cause the body to go into a fight-or-flight state, where the heart rate and blood pressure both increase. This is the body’s way of trying to cope with the changes and adjust to the new situation. Unfortunately, this can lead to long-term increases in blood pressure, which can be dangerous.
How to Manage High Blood Pressure During Opiate Withdrawal
The most important step in managing high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal is to seek professional medical help. It is important to find a doctor who is knowledgeable about opiate withdrawal and can provide the necessary treatment. Additionally, there are lifestyle changes that can help manage high blood pressure, such as eating a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing stress.
Medication Options for Managing High Blood Pressure
In some cases, medications may be necessary to manage high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal. Common medications used to treat hypertension include beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics. It is important to speak to a doctor before taking any medications, as they can have side effects and may interact with other medications.
Tips for Managing Opiate Withdrawal
There are several things a person can do to help manage the symptoms of opiate withdrawal and reduce the risk of high blood pressure. These include getting plenty of rest, drinking plenty of fluids, avoiding alcohol and drugs, and eating a balanced diet. Additionally, it is important to stay connected with supportive friends and family and to seek professional help if needed.
Conclusion
Opiate withdrawal is a difficult process and can cause many uncomfortable symptoms, including high blood pressure. Fortunately, there are ways to manage and reduce high blood pressure caused by opiate withdrawal. The most important step is to seek professional medical help. Additionally, there are lifestyle changes and medications that can help manage high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal. Finally, it is important to get plenty of rest, drink plenty of fluids, avoid alcohol and drugs, and stay connected with supportive friends and family.
Related Faq
Q1. Is it normal for someone to experience high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal?
A1. Yes, high blood pressure is a common symptom of opiate withdrawal. It can occur due to the body’s reaction to the sudden lack of opiates in the system. This can lead to a spike in blood pressure, which can lead to further complications. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal.
Q2. What other symptoms may accompany high blood pressure in opiate withdrawal?
A2. Other symptoms that may accompany high blood pressure in opiate withdrawal include sweating, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, headaches, muscle aches, insomnia, and anxiety. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as they can be indicative of a serious health issue.
Q3. How long does high blood pressure usually last during opiate withdrawal?
A3. High blood pressure during opiate withdrawal can last anywhere from a few hours to a few days, depending on the individual. Generally, the longer the person has been using opiates, the longer the withdrawal symptoms may last. It is important to seek medical attention if high blood pressure persists for more than a few days.
Q4. Can high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal cause other health issues?
A4. Yes, high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal can lead to further health issues, such as stroke and heart attack. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as they can be indicative of a serious health issue.
Q5. What can be done to reduce the effects of high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal?
A5. There are a few things that can be done to reduce the effects of high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal. It is important to get plenty of rest, drink plenty of fluids, and avoid caffeine and alcohol. Additionally, your doctor may prescribe medication to help reduce the effects of high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal.
Q6. Is it possible to prevent high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal?
A6. It is possible to reduce the risk of experiencing high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal. It is important to seek professional help if you are planning to quit using opiates. Additionally, it is important to have a proper diet and to get regular exercise, as this can help to reduce the risk of high blood pressure during opiate withdrawal.
The science of opioid withdrawal
In conclusion, it is clear that opiate withdrawal can cause high blood pressure. While it is not a common symptom, it is important to be aware of this possibility, as it can be dangerous. Those who are going through opiate withdrawal should be monitored closely and seek medical attention if they experience any symptoms of high blood pressure. With proper care and monitoring, opiate withdrawal can be safe and successful.
