Cocaine is a powerful and highly addictive drug that has been used recreationally for decades. But why is cocaine so addictive? This article explores the physiological and psychological factors that contribute to cocaine addiction and explains why it is one of the most dangerous drugs on the market. We’ll also look at the various treatments available for those struggling with cocaine addiction.
Cocaine is an addictive drug due to its stimulating effects on the central nervous system. It increases levels of dopamine in the brain, which produces feelings of pleasure and reward. This causes users to crave the drug and leads to compulsive cocaine use. Cocaine use can quickly lead to tolerance, physical dependence, and addiction.
Contents
Why is Cocaine Addictive?
The Neurochemistry of Cocaine
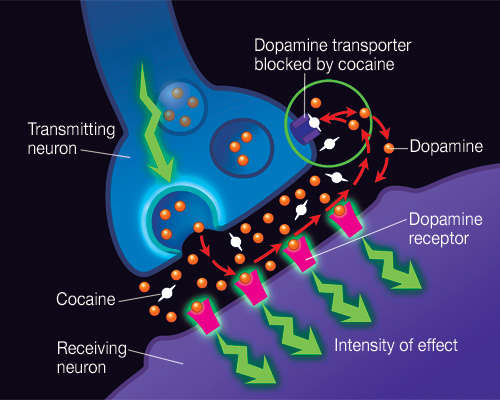
Cocaine is a powerful stimulant that affects the central nervous system. It works by blocking the re-uptake of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the brain. This causes a flood of these neurotransmitters to be released, resulting in an intense feeling of euphoria. The flood of neurotransmitters is what gives cocaine its addictive properties. Additionally, cocaine activates the reward pathways in the brain, causing people to experience an intense feeling of pleasure when they use it.
The brain is wired to seek out pleasurable experiences, and cocaine is no exception. When people use cocaine, the reward pathways in their brain become activated and they become addicted. As the brain becomes used to the effects of cocaine, it requires more and more of the drug to achieve the same level of pleasure. This is why many people who start using cocaine will eventually become addicted.
Also, cocaine affects the brain’s reward system by releasing large amounts of dopamine. This dopamine then binds to the receptors in the brain, causing an intense feeling of pleasure. This dopamine release is what makes cocaine so addictive.
The Impact of Cocaine on the Body
Cocaine also has a significant impact on the body. It can raise heart rate and blood pressure, which can lead to serious health problems. It can also cause insomnia, nausea, and anxiety. Additionally, long-term cocaine use can damage the heart, lungs, and other organs.
Another major health concern associated with cocaine use is the risk of overdose. Cocaine is a highly potent drug, and taking too much of it can lead to serious health complications, including coma and death. Cocaine overdoses can also lead to seizures, heart attacks, and strokes.
Overall, cocaine is a powerful and potentially dangerous drug. The short-term effects of cocaine can be pleasurable, but the long-term effects can be devastating.
The Psychological Effects of Cocaine
In addition to the physical effects of cocaine, the drug can have a significant impact on mental health. Cocaine use can lead to feelings of depression, anxiety, and paranoia. It can also cause cognitive impairments, such as memory loss and decreased concentration.
Cocaine use can also lead to a loss of interest in activities that used to be enjoyable. People who use cocaine can become isolated and withdrawn, which can lead to further mental health issues.
Lastly, cocaine can lead to addiction. When people become addicted to cocaine, they become dependent on the drug in order to feel normal. This can lead to severe psychological issues, such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis.
The Social Factors That Make Cocaine Addictive
Cocaine use is often associated with certain social factors that can make it more addictive. For example, cocaine use is often seen as a sign of wealth and success, which can make it more attractive to some people. Additionally, cocaine is often used as a way to cope with stress or depression, which can make it more difficult to quit.
Another factor that can make cocaine addictive is peer pressure. Many people start using cocaine because their friends are doing it, and it can be hard to resist the pressure to join in. Also, some people use cocaine as a way to fit in with a certain social group.
Finally, cocaine is often easier to obtain than other drugs. Cocaine is relatively inexpensive and widely available, which makes it attractive to many people.
The Role of Genetics in Cocaine Addiction
Genetics can also play a role in cocaine addiction. Studies have shown that certain genetic variations can predispose people to addiction. Additionally, people with a family history of addiction are more likely to become addicted to cocaine.
Also, certain environmental factors can increase the risk of addiction. For example, people who are exposed to cocaine at a young age are more likely to become addicted. Additionally, people who have experienced trauma or abuse are more likely to turn to drugs like cocaine for relief.
Conclusion
Overall, cocaine is a powerful and potentially addictive drug. Its ability to block re-uptake of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the brain is what gives it its addictive properties. Additionally, it affects the reward pathways in the brain, leading to an intense feeling of pleasure. Furthermore, its physical and psychological effects can be devastating. Lastly, certain social and genetic factors can increase the risk of addiction.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cocaine?
Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant drug derived from the leaves of the coca plant native to South America. It is commonly used as a recreational drug and is a white powder that is snorted, smoked in a pipe, or dissolved in water and injected. It is also known as coke, crack, ice, or blow.
How Does Cocaine Affect the Brain?
When cocaine enters the bloodstream, it causes a surge in the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is associated with feelings of pleasure and reward. This surge creates an intense and pleasurable feeling that is highly addictive. The brain also becomes accustomed to the surge of dopamine, which causes it to become dependent on cocaine in order to feel the same pleasurable feeling.
What are the Short-Term Effects of Cocaine Use?
The short-term effects of cocaine use include increased alertness, energy, and excitability. Other effects may include increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, dilated pupils, and feelings of euphoria. It can also cause paranoia, anxiety, restlessness, and irritability.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Cocaine Use?
Long-term use of cocaine can lead to physical and mental health problems. It can cause an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and seizures. It can also lead to an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and paranoia. Long-term use can also cause damage to the brain, lungs, and kidneys.
What are the Signs of Cocaine Addiction?
The signs of cocaine addiction include changes in behavior such as a decrease in school or work performance, an increase in risk-taking behavior, changes in sleep patterns, changes in eating habits, and an increase in secrecy and isolation. Other signs include a preoccupation with obtaining and using cocaine, a lack of interest in activities that were once enjoyable, and an inability to stop using cocaine despite negative consequences.
What are the Treatment Options for Cocaine Addiction?
Cocaine addiction is a serious and potentially deadly condition that requires professional treatment. Treatment may include therapy, medication, and support groups. Medications used to treat cocaine addiction include antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and medications to help reduce cravings. Therapy may include cognitive-behavioral therapy, group therapy, and family therapy. Support groups such as Narcotics Anonymous and Cocaine Anonymous can also provide support and guidance for those struggling with addiction.
How alcohol influences cocaine addiction
In conclusion, cocaine is an incredibly powerful and dangerous drug that can lead to addiction due to its effects on the brain. The drug can cause a surge of dopamine, which can lead to intense cravings and a strong desire to continue using it. Additionally, cocaine use can lead to physical and psychological dependence, making it difficult for people to stop using the drug despite the negative consequences. For these reasons, it is important to understand the risks and dangers of cocaine use and if addiction has already taken hold, to seek help from a professional right away.
