NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are one of the most commonly used medications for treating pain and inflammation. They are available over the counter, and are widely prescribed by doctors for a variety of conditions. But what exactly is a NSAID? In this article, we’ll take a look at what NSAIDs are, how they work, and what conditions they are used to treat.
A Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID) is a medicine used to reduce inflammation and pain. It works by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation. Common NSAIDs include aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib. NSAIDs can be used to treat a variety of conditions, such as headaches, muscle aches, arthritis, and menstrual cramps. They may also be used to reduce fever and to help prevent blood clots.
What is a Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)?
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are medications used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. They are commonly used to treat a wide range of conditions, including arthritis, headaches, and muscle pain. NSAIDs work by blocking the production of certain inflammatory chemicals in the body, which helps reduce pain and swelling.
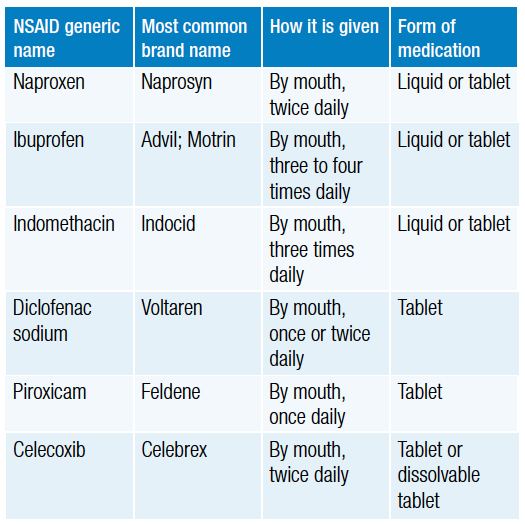
NSAIDs are available in both over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription forms. OTC NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, are commonly used to treat minor aches and pains. Prescription NSAIDs, such as diclofenac and celecoxib, are usually reserved for more severe conditions.
Types of NSAIDs
There are two main types of NSAIDs: nonselective and selective. Nonselective NSAIDs block both the COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, while selective NSAIDs block only the COX-2 enzyme.
Nonselective NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, are the most commonly used type of NSAID. They are effective for relieving pain and inflammation, but they can also increase the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding.
Selective NSAIDs, such as celecoxib and diclofenac, are generally reserved for more severe conditions. They are less likely to cause stomach ulcers and bleeding, but they may not be as effective for relieving pain and inflammation.
Risks and Side Effects
NSAIDs are generally safe and well-tolerated, but they can cause side effects in some people. Common side effects include stomach upset, nausea, and diarrhea. More serious side effects, such as liver damage, kidney damage, and increased risk of heart attack and stroke, are also possible.
It’s also important to note that taking NSAIDs can increase the risk of bleeding, so they should be used with caution in people who have bleeding disorders or take blood thinners.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to talk to your doctor before taking NSAIDs, especially if you have a pre-existing medical condition or take other medications. Your doctor can help you determine which type of NSAID is right for you and monitor you for any potential side effects.
If you experience any side effects while taking NSAIDs, such as stomach pain, nausea, or dizziness, you should stop taking the medication and talk to your doctor right away.
Dosage and Administration
NSAIDs are available in many different forms, including tablets, capsules, gels, creams, and patches. The dosage and administration of NSAIDs vary depending on the type and severity of your condition.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions when taking NSAIDs, as taking too much or taking them for too long can increase your risk of side effects.
Alternatives to NSAIDs
NSAIDs are not the only medications available for treating pain and inflammation. Other medications, such as acetaminophen, opioids, and corticosteroids, may be used to relieve pain and inflammation.
Physical therapy, exercise, and lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and quitting smoking, can also help reduce pain and inflammation. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment plan for your condition.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is a NSAID Drug?
Answer: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications typically used to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. They are some of the most commonly used drugs in the world, and they are available both over-the-counter and by prescription. Examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin.
How Do NSAIDs Work?
Answer: NSAIDs work by blocking the body’s production of prostaglandins, which are substances that cause inflammation and pain. By blocking the production of prostaglandins, NSAIDs reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. NSAIDs also block the production of other substances in the body, such as thromboxanes, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
What Conditions Are Treated with NSAIDs?
Answer: NSAIDs are commonly used to treat a variety of inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis, bursitis, tendinitis, and gout. They are also used to treat pain and fever associated with colds, flu, and other illnesses. NSAIDs are sometimes used to treat headaches and menstrual cramps.
Are There Risks Associated with NSAIDs?
Answer: Yes, there are risks associated with the use of NSAIDs. Some of the risks include gastrointestinal issues, such as stomach upset, ulcers, and bleeding. Long-term use of NSAIDs can also increase the risk of cardiovascular problems, such as heart attack and stroke. People with a history of kidney disease should also be cautious when using NSAIDs, as they can increase the risk of kidney damage.
Who Should Avoid Taking NSAIDs?
Answer: People with certain medical conditions should avoid taking NSAIDs. This includes people with a history of stomach ulcers, kidney disease, high blood pressure, heart disease, and bleeding disorders. Pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and children should also avoid taking NSAIDs. It’s important to talk to your doctor before taking any NSAIDs to make sure they are safe for you.
Are There Alternatives to NSAIDs?
Answer: Yes, there are alternatives to NSAIDs. Acetaminophen is one of the most common alternatives, and it is available both over-the-counter and by prescription. Acetaminophen is typically used to treat mild to moderate pain and fever, and it does not carry the same risks as NSAIDs. Other alternatives include topical pain relievers, such as creams, gels, and patches, as well as natural remedies, such as herbs and supplements.
Anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs) Drugs, Pharmacology, Animation
In conclusion, Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are a type of medication that can be used to treat a variety of conditions, such as pain, inflammation, and fever. They work by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation and pain. While they are generally safe and effective, they can have serious side effects and should be used with caution. It is important to discuss any potential risks and benefits of taking NSAIDs with your doctor before beginning any treatment regimen.
