Opiate abuse is a serious issue in the United States, and it is important to understand the effects these drugs can have on the body and mind. Understanding what opiates are and how they work can help to reduce the risk of opiate abuse. In this article, we will explore the common opiates, their uses, and the potential dangers of opiate abuse. We will also discuss how to recognize and respond to opiate addiction. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the common opiates, their uses, and the risks associated with their use.
What are Commonly Used Opiates?
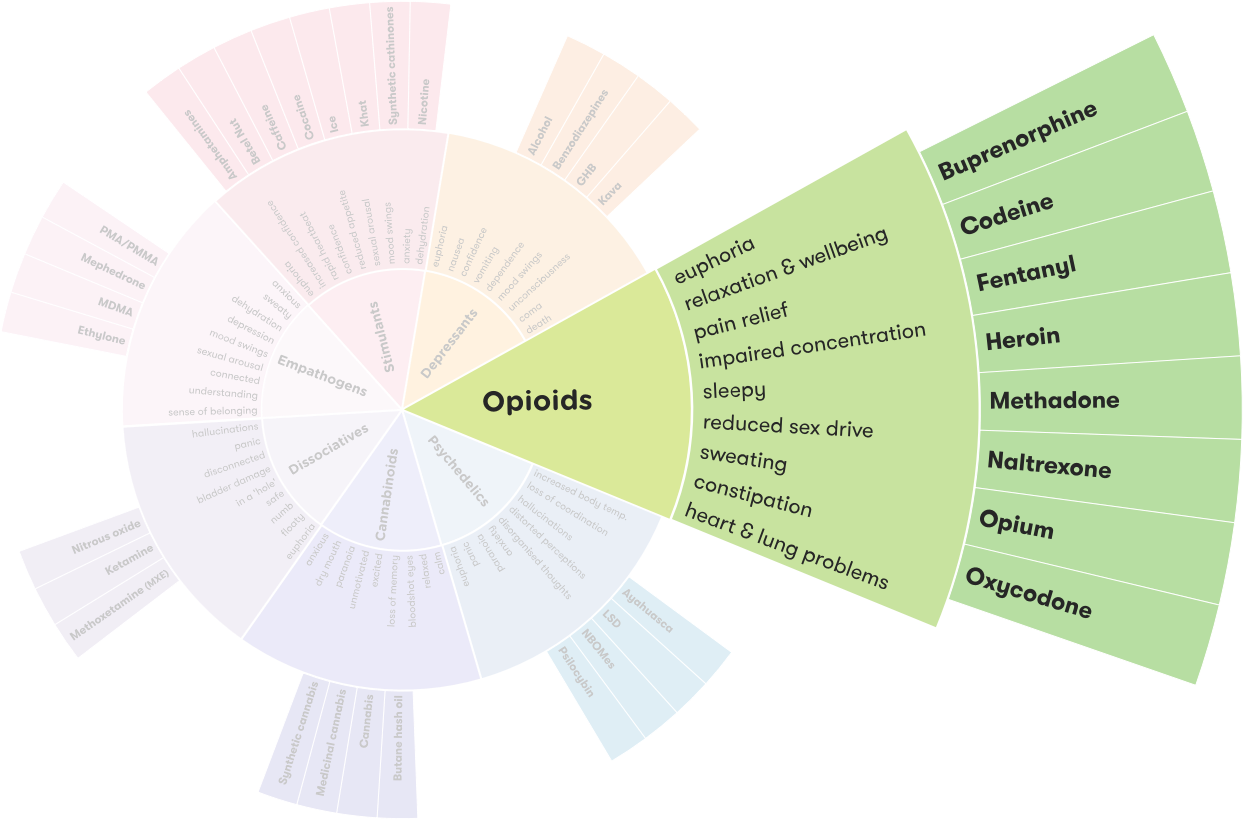
Opiate drugs are narcotic painkillers derived from the opium poppy plant, and are commonly referred to as opioids. Opiates are used to treat severe pain and for recreational purposes, and have been used for centuries. Common opiates include morphine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and codeine. These drugs are highly addictive and can cause serious side effects.
Opiate drugs are classified as either natural or synthetic. Natural opiates are derived directly from the opium poppy plant and include morphine and codeine. Synthetic opiates are created in a laboratory and include oxycodone and hydrocodone. These drugs work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking pain signals. They also produce a feeling of euphoria, which can be highly addictive.
Opiate drugs are available in a variety of forms, including tablets, capsules, liquids, and injections. The most commonly used opiates are morphine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and codeine. Morphine is typically used to treat severe pain, such as that associated with cancer, and is available in both short-acting and long-acting forms. Oxycodone and hydrocodone are both used to treat moderate to severe pain and are available in both immediate-release and extended-release forms. Codeine is typically used to treat mild to moderate pain and is available in both short-acting and long-acting forms.
Morphine
Morphine is a naturally occurring opiate derived from the opium poppy plant. It is used to treat moderate to severe pain, such as that associated with cancer, and is available in both short-acting and long-acting forms. Morphine works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking pain signals. It also produces a feeling of euphoria, which can be highly addictive. Common side effects of morphine include sedation, constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
Morphine is available in a variety of forms, including tablets, capsules, liquid, and injections. It is usually prescribed in the form of an oral tablet or capsule, and is typically taken every 4-6 hours as needed for pain. It is also available as an extended-release tablet or capsule, which is taken once a day and is designed to provide a steady level of medication throughout the day.
Oxycodone
Oxycodone is a synthetic opiate that is used to treat moderate to severe pain. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking pain signals. It also produces a feeling of euphoria, which can be highly addictive. Common side effects of oxycodone include sedation, constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
Oxycodone is available in a variety of forms, including tablets, capsules, liquid, and injections. It is usually prescribed in the form of an oral tablet or capsule, and is typically taken every 4-6 hours as needed for pain. It is also available as an extended-release tablet or capsule, which is taken once a day and is designed to provide a steady level of medication throughout the day.
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone is a synthetic opiate that is used to treat moderate to severe pain. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking pain signals. It also produces a feeling of euphoria, which can be highly addictive. Common side effects of hydrocodone include sedation, constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
Hydrocodone is available in a variety of forms, including tablets, capsules, liquid, and injections. It is usually prescribed in the form of an oral tablet or capsule, and is typically taken every 4-6 hours as needed for pain. It is also available as an extended-release tablet or capsule, which is taken once a day and is designed to provide a steady level of medication throughout the day.
Codeine
Codeine is a naturally occurring opiate that is used to treat mild to moderate pain. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking pain signals. It also produces a feeling of euphoria, which can be highly addictive. Common side effects of codeine include sedation, constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
Codeine is available in a variety of forms, including tablets, capsules, liquid, and injections. It is usually prescribed in the form of an oral tablet or capsule, and is typically taken every 4-6 hours as needed for pain. It is also available as an extended-release tablet or capsule, which is taken once a day and is designed to provide a steady level of medication throughout the day.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Common Opiates?
Answer: Opiates are a class of drugs that are derived from the poppy plant. Common opiates include morphine, codeine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and heroin. Opiates are used to treat pain and have a calming effect, but they can also be highly addictive and lead to physical and psychological dependence.
How Do Opiates Work?
Answer: Opiates work by binding to receptors in the brain and spinal cord, where they activate the brain’s reward system and produce feelings of pleasure and relaxation. They also act on the brain’s pain-control system, reducing the perception of pain. Opiates can also reduce feelings of anxiety, depression, and stress, which can lead to further physical and psychological dependence.
What Are the Side Effects of Opiates?
Answer: The side effects of opiates can vary depending on the type of opiate and the amount used. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, confusion, constipation, slowed breathing, and slowed heart rate. Long-term use of opiates can lead to more serious side effects, such as liver and kidney damage, respiratory depression, and an increased risk of overdose.
What Are the Risks of Taking Opiates?
Answer: The use of opiates can lead to both physical and psychological dependence, which can increase the risk of addiction. Long-term use of opiates can also lead to tolerance, meaning that higher doses are needed to achieve the same effects. Additionally, opiates can lead to impaired coordination and judgment, making it more difficult to perform activities like driving or operating machinery. Finally, opiates can interact with other drugs, increasing the risk of dangerous side effects.
How Are Opiates Abused?
Answer: Opiates are commonly abused by taking them in higher doses than prescribed, taking them for longer periods of time than prescribed, or taking them without a prescription. Other forms of abuse include snorting, smoking, or injecting the drug to achieve a faster and more intense high. Abusing opiates can lead to addiction, overdose, and other dangerous side effects.
How Can Opiate Abuse Be Treated?
Answer: Treatment for opiate abuse typically includes a combination of medication and psychotherapy to help individuals manage their cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Medications such as methadone or buprenorphine can be used to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, while psychotherapy can help individuals learn new coping strategies and develop better ways of managing their addiction. Additionally, support groups such as Narcotics Anonymous can provide valuable support and accountability for individuals in recovery.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates are a class of drugs that are derived from the poppy plant and are used to reduce pain and induce feelings of euphoria. Commonly used opiates include codeine, morphine, oxycodone, and heroin. Although opiates can be effective in treating pain, they can also be highly addictive and lead to tolerance, dependence, and overdose if not used properly. As such, it is important to only use opiates under the guidance of a physician and to adhere to the prescribed dosage.
