Weed is a commonly used drug, but is it a form of drug addiction? While some claim that it is not addictive, others argue otherwise. In this article, we will explore the debate surrounding weed and whether it has the potential to become an addiction. We will look at the research, evidence and testimonies to get a better understanding of the topic. So, let’s dive in and examine if weed is a drug addiction or not.
Yes, Weed is considered a drug addiction. There are many short-term and long-term effects of marijuana use. In the short-term, marijuana impairs the user’s ability to think and make decisions, and can cause anxiety, paranoia, and even psychosis. Long-term use has been linked to memory problems, impaired lung function, and an increased risk of mental health problems, such as depression.
Contents
What is Marijuana?
Marijuana, also known as cannabis, is a psychoactive drug obtained from the cannabis plant. It is commonly used as a recreational drug and is used for medicinal purposes in some countries. It has psychoactive and physiological effects when consumed. The main active ingredient in marijuana is THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, which is responsible for its psychoactive effects.
Marijuana is typically smoked in the form of a joint, pipe, or bong, and it can also be ingested in edible forms such as brownies and cookies. The effects of marijuana vary depending on the user and the amount consumed, but typically include feelings of relaxation, altered perception, and euphoria.
The Potential for Addiction
The potential for marijuana addiction is a subject of debate. Some studies have suggested that marijuana use can lead to psychological dependence, and that chronic use can lead to physical dependence. However, many experts argue that marijuana does not have the same addictive potential as other substances like alcohol or opioids.
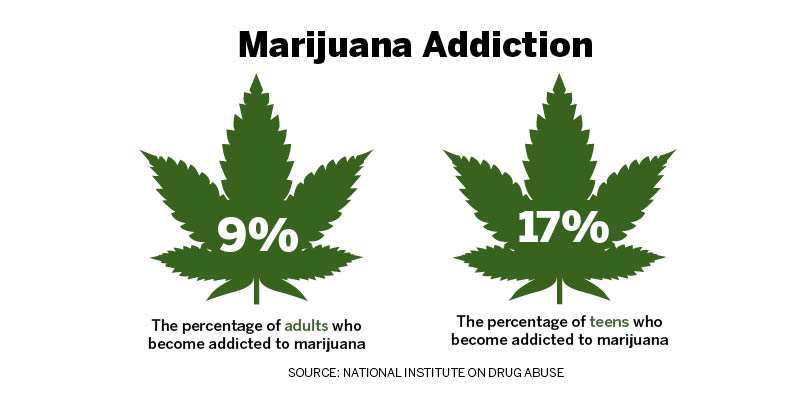
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) notes that while some people may become dependent on marijuana, this is not the same as addiction. They explain that physical dependence can occur with the use of marijuana, but that psychological dependence is less common. They estimate that only about 9% of people who use marijuana will become dependent on it.
The Risk of Dependence
Despite the potential for physical dependence, the risk of marijuana addiction is relatively low. The NIDA notes that the risk of marijuana addiction is lower than the risk of addiction to other drugs, such as alcohol and opioids.
The NIDA also notes that there is no evidence to suggest that marijuana use leads to an increase in the use of other drugs. They explain that marijuana does not appear to be a “gateway” drug, and that the majority of people who use marijuana do not go on to use other illicit drugs.
The Impact of Marijuana Addiction
The impact of marijuana addiction can vary greatly depending on the individual. For some, it may lead to significant disruption in their lives, including problems at work, school, and in relationships.
Mental Health Impacts
Marijuana addiction can have an impact on mental health. Studies have shown that chronic marijuana use may be associated with an increase in anxiety and depression. It may also lead to an increase in the risk of developing psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia.
Physical Health Impacts
Marijuana addiction can also lead to physical health problems. Chronic marijuana use has been linked to an increased risk of respiratory problems, such as bronchitis and asthma. It has also been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular problems, such as heart attack and stroke.
Treatment Options for Marijuana Addiction
Treatment for marijuana addiction is available and can be effective in helping people break their dependence on the drug. Treatment typically includes a combination of talk therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is used to help people recognize patterns of behavior that are associated with marijuana use and to develop strategies to avoid or reduce marijuana use. It can also be used to address underlying issues that may be contributing to the addiction.
Medication
Medications are sometimes used to help reduce cravings for marijuana and to help manage withdrawal symptoms. However, there are currently no medications that are specifically approved for marijuana addiction.
Preventing Marijuana Addiction
Preventing marijuana addiction is possible through education and awareness. Parents, teachers, and other adults can help to educate young people about the risks of marijuana use and the potential for addiction.
Promoting Healthy Coping Strategies
It is also important for adults to help young people develop healthy coping strategies for stress and other issues. Research suggests that having positive coping strategies can help to reduce the risk of marijuana use and addiction.
Encouraging Positive Behaviors
Finally, it is important to encourage positive behaviors and discourage marijuana use. This includes not just discouraging marijuana use, but also rewarding positive behaviors such as academic achievement and involvement in activities.
Related Faq
What is Weed?
Weed, also known as marijuana, is a psychoactive drug derived from the cannabis plant. It is usually smoked or ingested in edible form, and its effects can vary from person to person. Weed can produce feelings of relaxation and euphoria, as well as increased appetite, increased heart rate, and impaired coordination.
Is Weed a Drug?
Yes, weed is a drug. It is an illegal drug in most countries, and it is classified as a Schedule I drug in the United States. This means that it has no accepted medical use and has a high potential for abuse.
Can Weed Cause Addiction?
Yes, weed can cause addiction. People who use weed regularly can develop a tolerance to the drug, meaning that they need more of it to achieve the same effects. This can lead to physical dependence, and when a person stops using weed, they may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and irritability.
What Are the Signs of Addiction to Weed?
The signs of addiction to weed can include using more of the drug than was intended, spending a lot of time obtaining and using the drug, and continuing to use the drug despite negative consequences. Other signs include cravings for the drug, changes in mood, and social and occupational problems.
What Are the Risks of Weed Addiction?
The risks of weed addiction include cognitive and memory deficits, respiratory problems, and an increased risk of anxiety and depression. In addition, long-term use of weed can increase the risk of developing other substance abuse disorders.
Can Weed Addiction Be Treated?
Yes, weed addiction can be treated. Treatment usually involves a combination of behavioral therapies, support groups, and medication. Treatment can help individuals learn how to manage their cravings, cope with stress, and develop healthier habits. It can also help individuals address underlying issues that may have contributed to the addiction.
Why marijuana is more addictive now
In conclusion, marijuana is a drug and can be addictive for some users. It is important for individuals to understand the potential risks associated with using marijuana, as well as the potential for addiction. While there is still much to be learned about the effects of marijuana, it is important to remember that it does have the potential to be addictive and that individuals should be aware of the potential consequences of using the drug.
