Lysergic acid diethylamide, or LSD, is a powerful hallucinogenic drug known for its ability to alter a person’s perception of reality. It has been used for centuries for spiritual and recreational purposes, and its effects have been studied extensively. But what classification does LSD fit into? Is it a stimulant, depressant, or hallucinogen? In this article, we will explore the different effects of LSD and provide an answer to this question.
LSD is often described as a psychedelic drug due to its ability to alter a person’s perception of reality. Its effects on the brain are complex and varied, making it impossible to classify LSD as one particular type of drug. However, experts believe that LSD’s effects can be broadly categorized as a hallucinogen, stimulant, or depressant. We will investigate each of these characteristics to better understand how LSD works and how it affects the body.
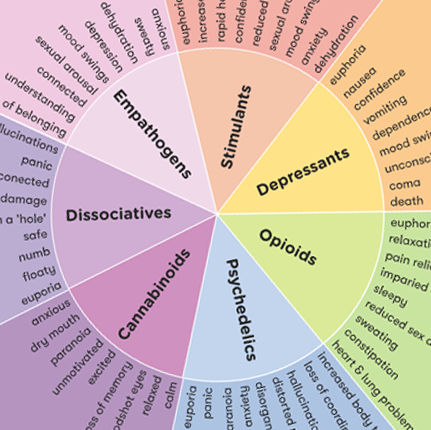
Contents
What is LSD?
Lysergic acid diethylamide, commonly known as LSD, is a synthetic drug derived from ergot, a fungus found on rye and other grasses. It is a powerful hallucinogenic drug that can cause intense visual and auditory hallucinations, altered states of consciousness, and drastic changes in perception. LSD is one of the most potent psychedelic drugs known to man and has been used for hundreds of years for its hallucinogenic properties.
LSD is a Schedule I substance in the United States, meaning that it is illegal to possess or distribute. Despite this, LSD continues to be used recreationally and by some people looking for a spiritual experience or to increase creativity.
Is LSD a Stimulant, Depressant or Hallucinogen?
LSD is classified as a hallucinogen, meaning that it alters a person’s perception, thoughts, emotions, and sensations. It is not considered a stimulant or depressant, as these drugs affect the CNS or cardiovascular system. Instead, LSD works on the serotonin system in the brain, leading to changes in perception and cognition.
The effects of LSD can be unpredictable and can vary from person to person. Common effects include visual and auditory hallucinations, altered states of consciousness, changes in perception, and feelings of euphoria. Some people may also experience anxiety, confusion, and paranoia. The effects of LSD can last for several hours and can be intense and overwhelming.
Risks of Using LSD
LSD is a powerful psychedelic drug and can be dangerous if used incorrectly. It can lead to psychological distress, increased risk of accidents and injuries, and potential long-term mental health effects. It is also possible to experience a bad trip, which can involve intense fear, paranoia, and anxiety.
In addition to the physical and psychological risks associated with LSD use, it is also illegal in the United States. Possession of LSD can result in fines, jail time, and other legal consequences.
Safety Considerations for Using LSD
If you choose to use LSD, it is important to take safety precautions to reduce the risk of injury or psychological distress. It is best to only take LSD in a setting where you feel safe and comfortable and with people you trust. It is also important to avoid using LSD while under the influence of alcohol or other drugs.
If you are using LSD for the first time, it is best to start with a very low dose and gradually increase the dose as needed. It is also important to be aware of the potential risks associated with LSD use and to seek medical attention if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide) is a potent hallucinogenic drug that is classified as a psychedelic drug. It is commonly referred to as acid, blotter, and doses.
What is LSD?
LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide) is a powerful psychoactive drug that is classified as a psychedelic drug. It is often referred to as acid, blotter, and doses. LSD is a semi-synthetic drug made from lysergic acid, which is found in ergot, a fungus that grows on rye and other grains. It was first discovered in 1938 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann and was initially used for psychiatric treatment, but its recreational use soon became popular.
LSD produces profound changes in perception, thought, and emotion that last for several hours. When taken, LSD can cause hallucinations, altered thought processes, changes in mood, and other effects. Many people who have taken LSD report feeling a sense of euphoria, increased creativity, and increased spiritual awareness.
Is LSD a stimulant, depressant, or hallucinogen?
LSD is classified as a hallucinogen, meaning that it distorts a person’s perception of reality. It alters the user’s sensory perception, which can result in hallucinations, changes in mood, and other effects. It does not act as a stimulant or depressant.
LSD acts on serotonin receptors in the brain, which are responsible for regulating mood, perception, and other cognitive processes. When the drug binds to the serotonin receptors, it creates changes in the brain’s chemistry that can cause changes in perception, thought, and emotion. The effects of LSD can be both positive and negative. Positive effects can include feelings of euphoria and increased creativity, while negative effects can include anxiety, confusion, and paranoia.
What are the short-term effects of LSD?
The short-term effects of LSD can include visual and auditory hallucinations, changes in mood, altered perception of time and space, feelings of euphoria, increased creativity, and increased spiritual awareness. It can also produce feelings of anxiety, confusion, and paranoia. LSD can also cause physical effects such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and dilated pupils.
The effects of LSD vary from person to person and depend on a variety of factors including the amount taken, the user’s mental and physical health, and the environment in which it is taken. It is important to note that the effects of LSD can be unpredictable, and users should be aware of the potential risks associated with the drug.
Are there any long-term effects of LSD?
The long-term effects of LSD are still largely unknown, as there has not been much research conducted on the subject. Some of the potential long-term effects of LSD include flashbacks, also known as hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), as well as changes in mood, anxiety, and depression.
It is important to note that LSD is not thought to be addictive, and there is no evidence that it causes physical dependence. However, LSD can be psychologically addictive, and people who use it regularly may develop a tolerance to the drug and require larger doses to achieve the same effects.
Is LSD dangerous?
LSD can be dangerous if it is not used responsibly. The effects of the drug can be unpredictable, and it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with the drug. Some of the potential risks associated with LSD include anxiety, confusion, and paranoia. In some cases, users have experienced long-term effects such as flashbacks, changes in mood, and depression.
People who are pregnant or have mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, should not take LSD. It is also important to note that LSD can interact with other drugs, including alcohol, and can cause serious health complications. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with the drug before using it.
Stimulants, Depressants, and Hallucinogens #shorts #stimulant #hallucinogen
In conclusion, LSD is classified as a hallucinogen and is famous for its ability to cause powerful, sometimes profound, changes in perception, mood, and thought. LSD is considered to have a low potential for abuse and addiction, and is no longer used as a medication in the United States. It is important to keep in mind that LSD is a powerful drug and can have unpredictable and potentially dangerous effects. With this in mind, it is important to understand the risks associated with LSD and take appropriate steps to ensure safety and minimize potential harm.
