Nicotine is a stimulant found in tobacco products and is highly addictive. It is one of the main causes of addiction to cigarettes and other tobacco products. But how long can nicotine be detected in the blood? In this article, we’ll explore the answer to this question and look at the effects of nicotine on the body.
Contents
- How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your Blood?
- What Factors Affect How Long Nicotine Stays in the Blood?
- What Tests Can Detect Nicotine in the Blood?
- How Can Nicotine Be Detected in Blood?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How long can nicotine be detected in blood?
- What is the best way to detect nicotine in the blood?
- Does nicotine stay in your blood longer if you smoke more?
- Can nicotine be detected in the blood of non-smokers?
- How does the amount of nicotine detected in the blood vary from person to person?
- What happens if nicotine levels in the blood are too high?
- How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System? (TRUTH)
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your Blood?
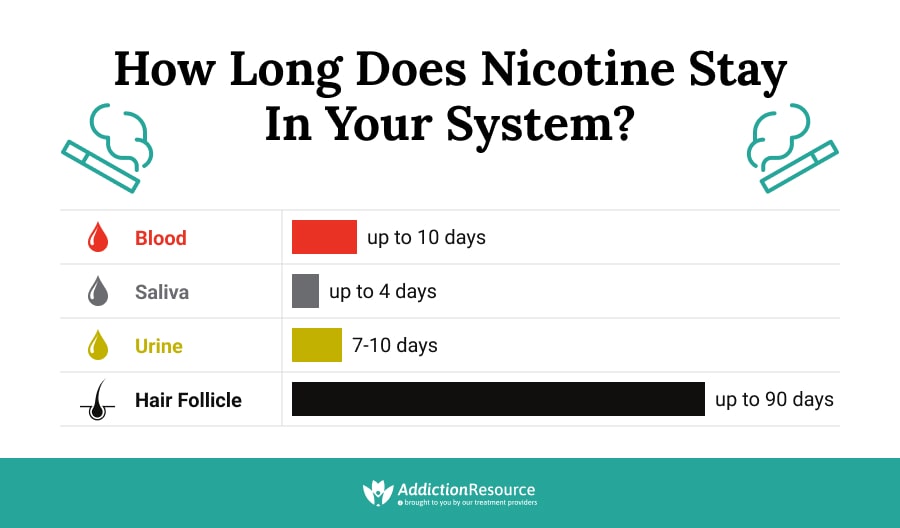
Nicotine is a chemical found in tobacco products and can be detected in the blood for up to several weeks after use. The amount of time nicotine remains detectable in the blood depends on several factors, such as the type of test used, the amount of nicotine consumed, and the individual’s metabolism. Nicotine can also be detected in saliva and urine for a shorter period of time than in blood.
The length of time nicotine stays in the blood can vary depending on how the nicotine was consumed. For instance, nicotine from smoking or vaping will likely stay in the blood for a shorter period of time than nicotine from chewing tobacco. This is because nicotine is absorbed more quickly through the lungs than through the digestive system. Additionally, the amount of nicotine consumed can have an effect on how long it stays in the blood—higher amounts of nicotine will take longer to clear from the body.
The type of test used to detect nicotine in the blood can also affect how long it stays in the body. Nicotine can be detected in blood using a variety of tests, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). ELISA tests are generally used to detect nicotine in the blood for up to 10 days after use, while HPLC tests can detect nicotine for up to 4 weeks after use.
What Factors Affect How Long Nicotine Stays in the Blood?
Several factors can affect how long nicotine stays in the blood, including the type of product used, the amount consumed, and the individual’s metabolism. Different methods of consuming nicotine, such as smoking, vaping, and chewing, can affect the length of time nicotine is detectable in the blood. Nicotine is absorbed more quickly through the lungs than through the digestive system, so smoking or vaping nicotine will typically result in a shorter detection time in the blood than chewing tobacco. Additionally, the amount of nicotine consumed can influence the length of time it stays in the blood—higher amounts of nicotine will take longer to clear from the body.
Individuals with a faster metabolism may clear nicotine from their blood more quickly than those with a slower metabolism. Metabolism can be affected by a variety of factors, such as age, gender, and body mass index (BMI). Additionally, individuals who consume nicotine regularly may have a longer detection time than those who consume it only occasionally.
What Tests Can Detect Nicotine in the Blood?
Nicotine can be detected in the blood using a variety of tests, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). ELISA tests are generally used to detect nicotine in the blood for up to 10 days after use, while HPLC tests can detect nicotine for up to 4 weeks after use.
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, or ELISA tests, are commonly used to detect nicotine in the blood. These tests use antibodies to detect nicotine and are generally used to detect nicotine for up to 10 days after use. ELISA tests can provide accurate and reliable results, making them a popular choice for testing for nicotine in the blood.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
High-performance liquid chromatography, or HPLC tests, are also used to detect nicotine in the blood. These tests use a chemical process to detect nicotine and are generally used to detect nicotine for up to 4 weeks after use. HPLC tests are more sensitive than ELISA tests and can detect lower levels of nicotine in the blood.
How Can Nicotine Be Detected in Blood?
Nicotine can be detected in the blood using a variety of tests, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). These tests use antibodies or a chemical process to detect nicotine in the blood and can provide accurate and reliable results. ELISA tests are generally used to detect nicotine in the blood for up to 10 days after use, while HPLC tests can detect nicotine for up to 4 weeks after use. The amount of time nicotine remains detectable in the blood depends on several factors, such as the type of test used, the amount of nicotine consumed, and the individual’s metabolism.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can nicotine be detected in blood?
Answer: Nicotine can be detected in blood for up to 4 days after use. Blood tests are often used to measure nicotine levels, as they can detect both current and recent nicotine use. The amount of nicotine detected in the blood depends on the type of tobacco product used and how much was used. For example, smoking one cigarette will produce a higher level of nicotine in the blood than using a nicotine patch.
What is the best way to detect nicotine in the blood?
Answer: The most reliable way to detect nicotine in the blood is through a blood test. Blood tests are able to detect both current and recent nicotine use and can provide accurate results. Urine tests can also be used to detect nicotine, but they are less reliable as they are more susceptible to false positives and false negatives.
Does nicotine stay in your blood longer if you smoke more?
Answer: Yes, nicotine will stay in your blood for a longer period of time if you smoke more. The amount of nicotine detected in the blood depends on the type of tobacco product used and how much was used. For example, smoking one cigarette will produce a higher level of nicotine in the blood than using a nicotine patch.
Can nicotine be detected in the blood of non-smokers?
Answer: Nicotine can be detected in the blood of non-smokers, but this is usually due to environmental exposure. Non-smokers can be exposed to nicotine through second-hand smoke, nicotine patches, or nicotine gum. However, it is unlikely that the levels of nicotine detected in non-smokers would be high enough to cause any health problems.
How does the amount of nicotine detected in the blood vary from person to person?
Answer: The amount of nicotine detected in the blood varies from person to person depending on the type of tobacco product used and how much was used. For example, smoking one cigarette will produce a higher level of nicotine in the blood than using a nicotine patch. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, can affect the amount of nicotine detected in the blood.
What happens if nicotine levels in the blood are too high?
Answer: If nicotine levels in the blood are too high, it can cause symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and headaches. Additionally, high levels of nicotine can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. If you suspect that your nicotine levels are too high, it is important to speak to your doctor as soon as possible.
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System? (TRUTH)
Conclusively, the detection of nicotine in blood depends on a number of factors, including the amount and frequency of smoking, the type of nicotine, and the type and sensitivity of the test used. The amount of nicotine in a person’s blood can range from undetectable to a few weeks after smoking. Therefore, it is important to understand the various factors that can affect nicotine detection in blood and consult a medical professional for advice and guidance.
