Do you ever wonder why smoking cigarettes is so addictive? Perhaps you’ve heard of nicotine, but what is it and how does it work? In this article, we’ll take a look at nicotine and its effects on the body. We’ll uncover how nicotine works in the brain to cause addiction and how it influences behavior. Finally, we’ll explore how nicotine is used as a cessation tool and what to expect when you quit using nicotine. Get ready to discover the science behind nicotine and how it works!
Contents
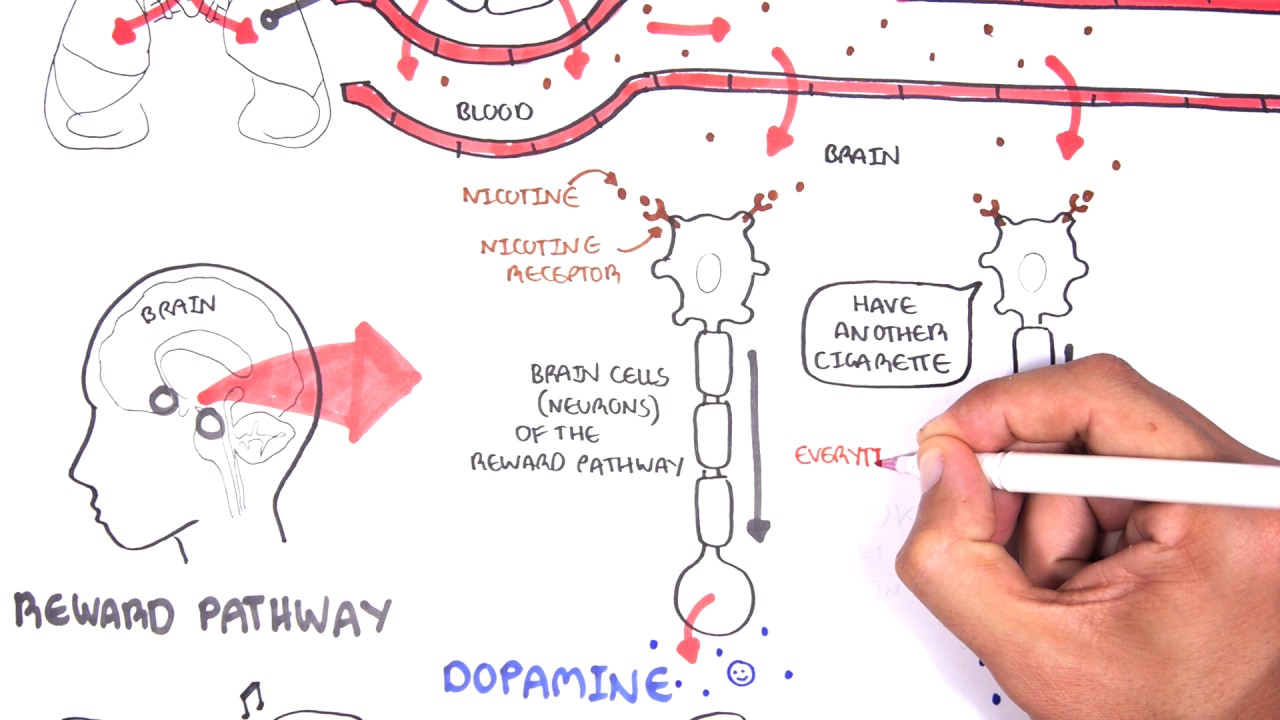
What Is Nicotine and How Does It Work?
Nicotine is a naturally occurring chemical found in the nightshade family of plants, including tobacco. It is a stimulant and has been used for centuries as a mild form of intoxication. Nicotine works by binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain and increasing the release of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and noradrenaline. When these neurotransmitters are released, it can produce feelings of pleasure and relaxation. Nicotine also affects the cardiovascular system by increasing heart rate and blood pressure.
What Are the Effects of Nicotine?
Nicotine has both short-term and long-term effects. In the short term, nicotine can produce feelings of pleasure and relaxation, as well as increased alertness and focus. However, nicotine can also produce negative effects, such as nausea, headache, and increased anxiety. In the long term, nicotine can increase the risk of cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other diseases.
What Are the Risks of Using Nicotine?
Nicotine is highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence. People who are addicted to nicotine can experience cravings, irritability, and difficulty concentrating when they try to quit. Nicotine also exposes users to numerous harmful chemicals, including tar, carbon monoxide, and formaldehyde. Additionally, nicotine can increase the risk of adverse health effects, such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other diseases.
How Is Nicotine Used?
Nicotine is most commonly used in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. Nicotine is also available in a variety of other products, including e-cigarettes, nicotine gums, patches, and lozenges. These products are designed to deliver nicotine without the harmful chemicals found in tobacco smoke.
E-Cigarettes and Vaping Devices
E-cigarettes and vaping devices are electronic devices that heat a liquid containing nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals. When the liquid is heated, it produces an aerosol that is inhaled by the user. These products are often marketed as a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes, but research has shown that they can also be dangerous and can expose users to chemicals that are toxic.
Nicotine Gums and Patches
Nicotine gums and patches are products that deliver nicotine to the body through a slower, more controlled release. They are designed to help people quit smoking by reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Nicotine gums and patches are generally considered to be safer than smoking, but they can still be dangerous if used in excess.
Conclusion
Nicotine is a stimulant that is found in tobacco products and other nicotine-containing products. It can produce feelings of pleasure and relaxation, but it can also be highly addictive and expose users to numerous harmful chemicals. E-cigarettes and vaping devices, as well as nicotine gums and patches, can deliver nicotine without the harmful chemicals found in tobacco smoke, but they can still be dangerous if used in excess.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is an alkaloid compound found in the tobacco plant and a number of other plants in nature. It is the primary component of cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products, and is responsible for the addictive properties of these products. Nicotine works by binding to receptors in the brain and central nervous system, releasing a neurotransmitter called dopamine, which produces a feeling of euphoria and relaxation. Nicotine is also known to increase alertness and focus.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Body?
Nicotine has a number of effects on the body. It can increase heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration rate. It can also cause constriction of blood vessels, which can lead to an increased risk of stroke and heart attack. Nicotine also affects the brain, increasing levels of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine, which can lead to feelings of pleasure, relaxation, and alertness. Long-term use of nicotine can lead to addiction and other health risks.
How Does Nicotine Work in the Brain?
When nicotine enters the brain, it binds to receptors in the brain and central nervous system, releasing a neurotransmitter called dopamine. This dopamine produces a feeling of pleasure and relaxation, and can lead to addiction. Nicotine also affects other neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which can lead to feelings of alertness, focus, and pleasure.
What Are the Side Effects of Nicotine?
The side effects of nicotine depend on the amount of nicotine consumed and the length of time it is used. Short-term side effects include increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and constriction of blood vessels. Long-term side effects can include addiction, increased risk of stroke and heart attack, and various other health risks.
What Is Nicotine Replacement Therapy?
Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is a form of treatment used to help people quit smoking. It involves the use of nicotine replacement products, such as patches, gum, or inhalers, to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms associated with quitting smoking. The goal of NRT is to reduce the amount of nicotine consumed, while providing the user with a less harmful alternative to smoking.
How Effective Is Nicotine Replacement Therapy?
Nicotine replacement therapy is generally considered to be an effective method for quitting smoking. Studies have shown that NRT can double or triple the success rate for quitting smoking, compared to quitting without any form of treatment. However, it is important to note that NRT is not a cure for nicotine addiction, and should be used in combination with other methods, such as counseling and support groups, for best results.
How does nicotine work
In conclusion, nicotine is a powerful and complex substance that can have both physical and psychological effects. It works by binding to acetylcholine receptors in the brain, stimulating the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and providing a feeling of pleasure and reward. While it can be addictive and is associated with negative health outcomes if used in excess, nicotine can also be used to help people quit smoking or reduce withdrawal symptoms. Understanding how nicotine works is key to understanding how it can be used responsibly and safely.
