Alcohol is a commonly used substance that is enjoyed by many for its taste and effects. But what about its impact on the senses? In this article, we will explore how alcohol affects the senses and the potential consequences of drinking too much. We will look at how alcohol can affect sight, taste, smell, touch, and hearing, as well as the long-term effects it can have on the body. We will also discuss how to keep the senses healthy while enjoying a few drinks. So, raise a glass, and let us explore how alcohol affects the senses.
Alcohol affects the senses in a variety of ways. It can reduce sensitivity to pain, impair vision, cause slurred speech, and reduce coordination. It can also cause a person to have difficulty hearing, smelling, and tasting. Drinking alcohol can also make people more emotional and less able to think clearly.
Contents
- Alcohol and Its Effects on the Senses
- Alcohol and Hearing
- Alcohol and Touch
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1. What are the effects of alcohol on taste?
- Q2. How does alcohol affect smell?
- Q3. How does alcohol influence our vision?
- Q4. How does alcohol affect our sense of hearing?
- Q5. How does alcohol affect our sense of touch?
- Q6. How can alcohol consumption lead to dizziness?
- Effects of Alcohol on the Brain, Animation, Professional version.
Alcohol and Its Effects on the Senses
Alcohol has a wide range of effects on the senses, both short-term and long-term. In the short-term, alcohol can dull pain, reduce anxiety, and grant a feeling of euphoria. In the long-term, alcohol use can lead to addiction and other health problems. In this article, we will discuss the effects of alcohol on the senses, both short-term and long-term.
Alcohol and Taste
Alcohol can have a profound effect on taste. Short-term, it can make food and drinks taste better, as alcohol tends to enhance the sweetness of foods and drinks. Long-term, alcohol can lead to a dulling of the taste buds, leading to a decreased ability to enjoy the flavors of food. Also, long-term alcohol use can lead to a decrease in appetite, leading to malnutrition.
Alcohol and Smell
Alcohol can also affect the sense of smell. This can be both good and bad. Short-term, alcohol can make the smells of food and drinks more enjoyable, as it can enhance the aromas of certain foods. Long-term, alcohol can lead to a decrease in the ability to detect smells, leading to a decreased ability to enjoy the aroma of food. Additionally, long-term alcohol use can lead to a diminished sense of smell, making it difficult to detect odors such as smoke or gas.
Alcohol and Sight
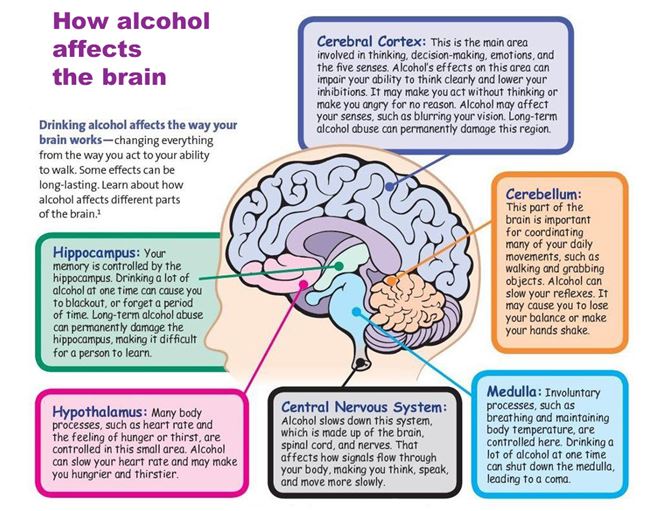
Alcohol can also affect the sense of sight. Short-term, it can cause blurred vision, impaired depth perception, and reduced reaction time. Long-term, alcohol abuse can lead to permanent vision damage, including damage to the optic nerve and impaired night vision. Additionally, long-term alcohol use can lead to a decrease in the ability to discern colors, making it difficult to distinguish between colors.
Alcohol and Hearing
Alcohol can also affect the sense of hearing. Short-term, alcohol can cause mild hearing loss and a reduced ability to distinguish sounds. Long-term, alcohol use can lead to permanent hearing damage, including tinnitus and a decreased ability to hear high-pitched sounds. Additionally, long-term alcohol use can lead to a decrease in the ability to understand speech, making it difficult to communicate with others.
Alcohol and Balance
Alcohol can also affect the sense of balance. Short-term, alcohol can cause dizziness, vertigo, and difficulty walking. Long-term, alcohol use can lead to permanent balance problems, including difficulty standing, walking, and running. Additionally, long-term alcohol use can lead to a decrease in coordination, making it difficult to perform even the simplest tasks.
Alcohol and Touch
Alcohol can also affect the sense of touch. Short-term, alcohol can cause numbness and a reduced ability to feel pain. Long-term, alcohol use can lead to a decrease in the ability to feel temperatures, making it difficult to determine whether something is hot or cold. Additionally, long-term alcohol use can lead to a decrease in the ability to feel pressure, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as typing or writing.
Alcohol and Emotion
Alcohol can also affect emotions. Short-term, alcohol can cause feelings of euphoria, relaxation, and increased confidence. Long-term, alcohol use can lead to feelings of depression, anxiety, and anger. Additionally, long-term alcohol use can lead to a decrease in the ability to feel pleasure, making it difficult to enjoy the simple pleasures of life.
Alcohol and Memory
Alcohol can also affect memory. Short-term, alcohol can cause blackouts, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating. Long-term, alcohol use can lead to permanent memory damage, including difficulty recalling recent events and difficulty forming new memories. Additionally, long-term alcohol use can lead to a decrease in the ability to remember facts, making it difficult to retain information.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the effects of alcohol on taste?
A1. Drinking alcohol can have a direct impact on taste. Alcohol can interfere with the taste buds’ ability to detect sweet, salty, sour, and bitter tastes. In addition, alcohol can cause the tongue to become numb and reduce saliva production, which can also interfere with taste. Alcohol can also increase the intensity of certain flavors, such as sweet and salty, making them more pronounced. Additionally, alcohol can alter the perception of flavors, causing foods to taste different than normal.
Q2. How does alcohol affect smell?
A2. Alcohol can impact our sense of smell by temporarily decreasing our ability to detect odors. This is because alcohol can interfere with the olfactory neurons responsible for detecting smells, as well as the neurotransmitters responsible for sending odor information to the brain. As alcohol affects our sense of smell, it can also make food and drinks taste differently than normal.
Q3. How does alcohol influence our vision?
A3. Consuming alcohol can lead to blurred vision, double vision, and a decrease in the ability to perceive colors. Alcohol can also reduce the size of the visual field and lead to impaired depth perception. Additionally, alcohol can cause the eyes to lose focus, leading to difficulty focusing on objects.
Q4. How does alcohol affect our sense of hearing?
A4. Alcohol can cause temporary hearing loss by interfering with the inner ear structures responsible for sound reception. Additionally, alcohol can cause tinnitus, a condition in which a person hears ringing or buzzing in their ears. Alcohol can also lead to impaired speech perception and reduced ability to detect subtle changes in sound.
Q5. How does alcohol affect our sense of touch?
A5. Alcohol can reduce the sensitivity of the nerve endings responsible for detecting touch, making it difficult to feel sensations. Additionally, alcohol can cause the skin to become numb, making it difficult to feel even strong sensations. Alcohol can also cause a decrease in coordination and balance, leading to clumsiness and difficulty with physical activities.
Q6. How can alcohol consumption lead to dizziness?
A6. Consuming alcohol can lead to dizziness due to the effects of alcohol on the inner ear structures responsible for balance and equilibrium. Alcohol can also cause a decrease in coordination and balance, leading to dizziness. Additionally, alcohol can cause a decrease in blood pressure, leading to a drop in blood flow to the brain, resulting in dizziness.
Effects of Alcohol on the Brain, Animation, Professional version.
Alcohol has long been known to impair the senses. It can cause blurred vision, hearing loss, dulled taste and smell, and a decrease in touch sensitivity. It is important to be aware of the effects of alcohol on the senses, as it can lead to impaired judgment and decreased coordination, which can lead to dangerous situations. Therefore, it is important to drink responsibly and in moderation to avoid any potential risks that alcohol may have on the senses.