Mental health has become an increasingly important topic of discussion in recent years, as many people have suffered from various mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety and PTSD. But what many people don’t know is that mental health can be considered a disability in certain cases, and is often eligible for disability benefits. In this article, we will explore the criteria for qualifying for disability due to mental health issues, as well as the benefits that may be available.
Yes, mental health can qualify for disability. In order to qualify, an individual must be diagnosed with a mental illness that is severe enough to impair their ability to function in a workplace setting. Depending on the type of mental illness, individuals may be eligible for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) or Supplemental Security Income (SSI).
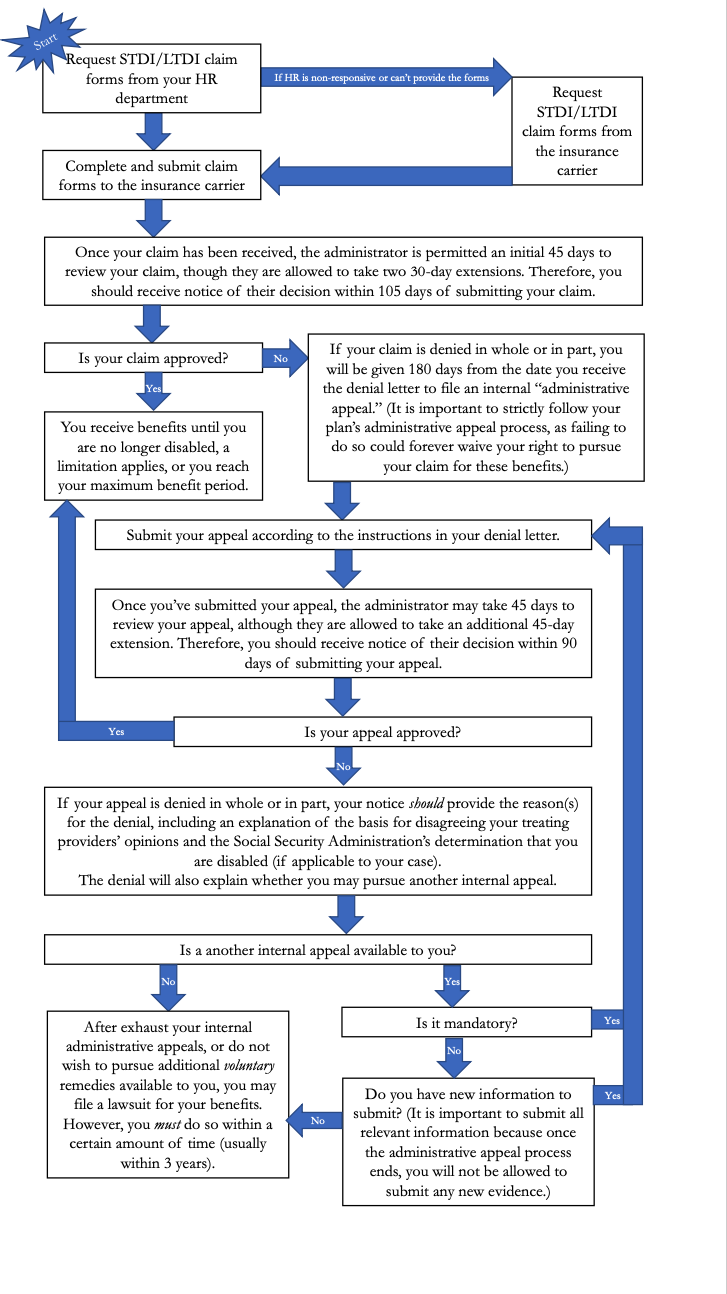
Contents
- Mental Health and its Qualification for Disability
- Related Faq
- What is Mental Health?
- Does Mental Health Qualify for Disability?
- What Documentation is Needed to Qualify for Disability?
- What Happens After I Submit My Application for Disability?
- Can I Appeal a Denial of My Application for Disability?
- What Types of Benefits are Available to Those Who Qualify for Disability?
- Applying for Disability Benefits with a Mental Illness
Mental Health and its Qualification for Disability
Mental health is an important factor affecting the overall wellbeing of an individual. It is also a determining factor when it comes to the qualification of an individual for disability. Mental health issues can be as severe as physical disabilities and can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to work and live an independent life. This article will discuss the requirements for mental health to qualify as a disability and its implications.
Defining Mental Health Disability
A mental health disability is defined as a condition that significantly impairs an individual’s ability to function on their daily activities and live a normal life. This condition must be chronic and long-term in nature, meaning that it must have been present for at least six months or longer. The disability must also prevent the individual from performing major life activities such as caring for oneself, communication, learning, and working.
The most common mental health disabilities are depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Other conditions that may qualify as mental health disabilities include obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), personality disorders, autism spectrum disorder, and eating disorders.
Qualifying for Mental Health Disability Benefits
The first step in qualifying for mental health disability benefits is to be diagnosed by a qualified medical professional. The diagnosis must be based on the criteria set by the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V). The diagnosis must also include a statement of the functional limitations that the condition has caused.
Once the diagnosis is made, the individual must then prove that the disability has caused them to be unable to perform certain life activities or has had a significant effect on their ability to do so. This can be done by providing evidence such as medical records, therapy records, and other relevant documentation.
The individual must also demonstrate that the disability is long-term and will most likely continue for at least 12 months. If the disability is expected to last longer than 12 months, the individual must provide evidence that the condition persists and that it is not likely to improve over time.
The Impact of Mental Health Disability
A mental health disability can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to work and live an independent life. It can lead to unemployment, poverty, and social isolation. It can also lead to physical health problems due to the physical side effects of certain medications used to treat mental health conditions.
The individual may also be eligible for certain government benefits such as Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and Supplemental Security Income (SSI). These benefits can provide financial assistance to help individuals with mental health disabilities to cover medical expenses and to maintain a certain quality of life.
Conclusion
Mental health disabilities can be just as debilitating as physical disabilities and can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to work and live an independent life. In order to qualify for disability benefits, an individual must be diagnosed by a qualified medical professional and must provide evidence of the functional limitations caused by the disability. These benefits can provide financial assistance to help individuals with mental health disabilities to cover medical expenses and to maintain a certain quality of life.
Related Faq
What is Mental Health?
Mental health refers to a person’s overall psychological wellbeing. It is a broad term that includes a person’s emotional, social, and psychological wellbeing. Mental health is an important part of overall health and can be affected by many factors, such as stress, diet, lifestyle, environment, and genetics.
Does Mental Health Qualify for Disability?
Yes, mental health can qualify for disability. The Social Security Administration (SSA) recognizes some mental health conditions as disabling, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder. In order to qualify for disability benefits, the individual must have a mental health condition that is severe enough to meet the SSA’s criteria.
What Documentation is Needed to Qualify for Disability?
In order to qualify for disability benefits due to a mental health condition, an individual must provide medical documentation to the SSA. Documentation should include medical records, such as diagnosis and treatment information, as well as statements from mental health professionals and other relevant evidence.
What Happens After I Submit My Application for Disability?
After submitting an application for disability, the SSA will review the individual’s medical records and other evidence to determine if the individual meets the SSA’s criteria for disability. If the individual meets the criteria, they will be approved for benefits. If the individual does not meet the criteria, the SSA will deny the application.
Can I Appeal a Denial of My Application for Disability?
Yes, an individual can appeal a denial of their application for disability. The individual can file an appeal with the SSA and submit additional evidence to support their claim. The SSA will review the additional evidence and make a decision regarding the appeal.
What Types of Benefits are Available to Those Who Qualify for Disability?
Those who qualify for disability may be eligible for a variety of benefits, such as Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and Supplemental Security Income (SSI). SSDI provides financial assistance to those who are unable to work due to a disability, while SSI provides financial assistance to those who have limited income and resources. Additionally, individuals who qualify for disability may be eligible for other benefits, such as health care coverage.
Applying for Disability Benefits with a Mental Illness
In conclusion, mental health can qualify for disability, depending on the severity of the condition, its impact on the individual’s ability to carry out day-to-day activities, and the extent to which it impairs the person’s functioning. Mental health disabilities can have a major impact on an individual’s life, and it is important for those affected to be aware of the resources available to them to help them manage their condition.
