Alcohols are a type of organic chemical compound found in a wide array of products, from beverages to cosmetics. But do alcohols have something else in common? It turns out that alcohols can also form hydrogen bonds, a type of attractive force between molecules. In this article, we’ll explore the structure of alcohols and discuss how hydrogen bonding works in alcohols. We’ll also examine the implications of hydrogen bonding in alcohols and consider how it affects their physical and chemical properties.
Contents
- What Is Hydrogen Bonding?
- Do Alcohols Have Hydrogen Bonding?
- How Do Alcohols Form Hydrogen Bonds?
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Hydrogen Bonding?
- Do Alcohols Have Hydrogen Bonding?
- What are Examples of Alcohols with Hydrogen Bonding?
- How Does Hydrogen Bonding Affect the Properties of Alcohols?
- What is the Difference Between Hydrogen Bonding and Van der Waals Forces?
- How Does Hydrogen Bonding Affect the Reactivity of Alcohols?
- Hydrogen bonding in alcohols
What Is Hydrogen Bonding?
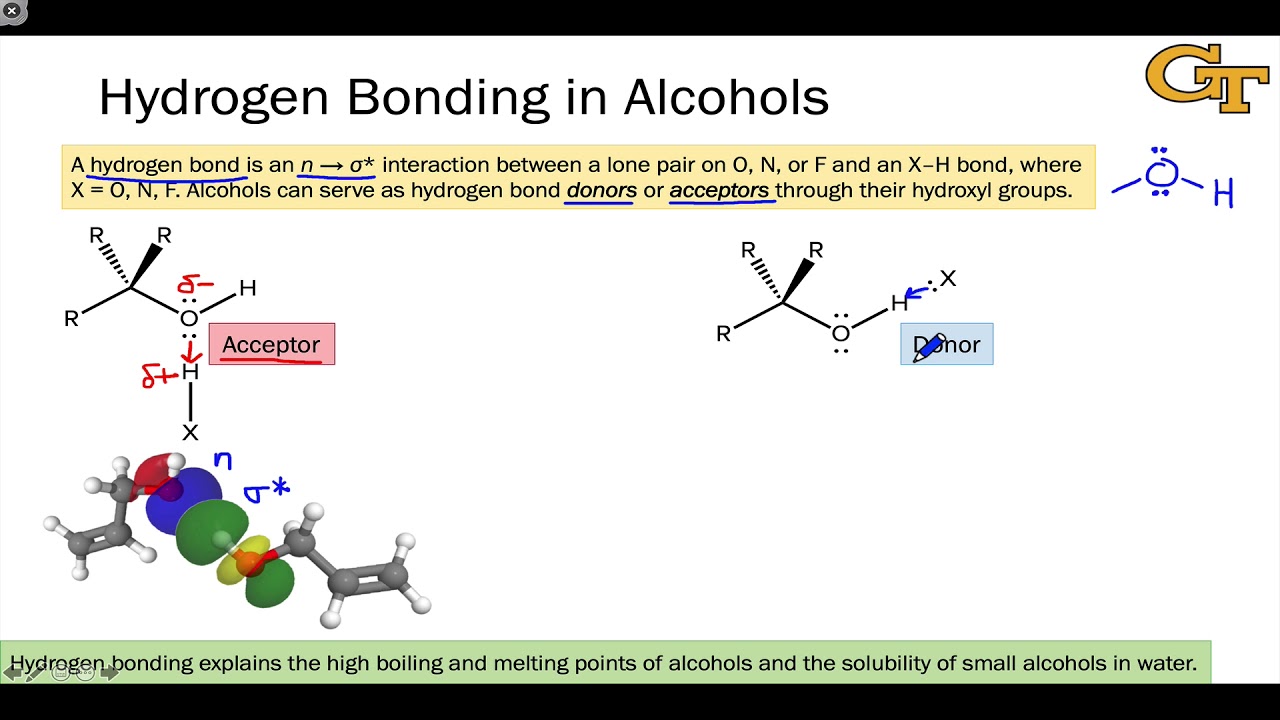
Hydrogen bonding is a type of chemical bond that occurs between molecules when a hydrogen atom is attracted to an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine. This type of bond is responsible for the stability of many molecules and is a major factor in determining the structure and properties of a compound. Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds, and the strength of the bond depends on the distance between the two atoms and the electronegativity of the atoms involved.
Hydrogen bonds are important in biochemistry because they play a role in the structure, stability, and function of proteins and nucleic acids. They are also important in the formation of intermolecular associations, such as those found in water and alcohols.
Do Alcohols Have Hydrogen Bonding?
Alcohols are organic compounds that contain an -OH group. This group has a hydrogen atom that can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules. Alcohols have a low molecular weight, which means that they can form multiple hydrogen bonds with other molecules.
The -OH group of alcohols is capable of forming hydrogen bonds with other molecules, especially with molecules that contain oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine atoms. These bonds are weaker than the covalent bonds that hold molecules together, but they are still strong enough to affect the structure, stability, and function of a molecule.
The strength of the hydrogen bond depends on the distance between the two atoms and the electronegativity of the atoms involved. Hydrogen bonds between alcohol molecules and molecules such as water, proteins, and nucleic acids are important for the stability of these molecules.
How Do Alcohols Form Hydrogen Bonds?
The -OH group of alcohols can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules due to its high electronegativity. The hydrogen atom of the -OH group is attracted to the electronegative atom of the other molecule, forming a weak bond. This bond can be between two alcohol molecules, or between an alcohol and a molecule that contains oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine atoms.
The strength of the hydrogen bond depends on the distance between the two atoms and the electronegativity of the atoms involved. Generally, the strength of the bond increases with increasing electronegativity and decreasing distance.
Hydrogen Bonds Between Two Alcohol Molecules
Hydrogen bonds can form between two alcohol molecules due to the presence of the -OH group. The hydrogen atom of the -OH group is attracted to the electronegative atom of the other molecule, forming a weak bond. This bond is weaker than the covalent bonds that hold molecules together, but it is still strong enough to affect the structure, stability, and function of a molecule.
The strength of the bond is determined by the distance between the two atoms and the electronegativity of the atoms involved. Generally, the strength of the bond increases with increasing electronegativity and decreasing distance.
Hydrogen Bonds Between an Alcohol and Other Molecules
The -OH group of alcohols can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules such as water, proteins, and nucleic acids. The hydrogen atom of the -OH group is attracted to the electronegative atom of the other molecule, forming a weak bond.
The strength of the bond depends on the distance between the two atoms and the electronegativity of the atoms involved. Generally, the strength of the bond increases with increasing electronegativity and decreasing distance.
How Do Hydrogen Bonds Affect Alcohol Molecules?
The hydrogen bonds between alcohol molecules and molecules such as water, proteins, and nucleic acids are important for the stability of these molecules. Hydrogen bonds can also affect the physical properties of alcohols, such as their boiling and melting points.
Effect on Boiling and Melting Points
The hydrogen bonds between alcohol molecules and molecules such as water, proteins, and nucleic acids can affect the boiling and melting points of alcohols. The stronger the hydrogen bond, the higher the boiling and melting points of the alcohol.
Effect on Solubility
The hydrogen bonds between alcohol molecules and molecules such as water, proteins, and nucleic acids can also affect the solubility of alcohols. The stronger the hydrogen bond, the more soluble the alcohol is in water.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Hydrogen Bonding?
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force between molecules, which occurs when a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (usually oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) is shared between two other molecules. This sharing of electrons creates a strong attraction between the molecules, which holds them together. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for many of the physical and chemical properties of molecules, such as the boiling point and solubility of water.
Do Alcohols Have Hydrogen Bonding?
Yes, alcohols have hydrogen bonding. Alcohols contain a hydroxyl (OH) group, which is highly electronegative and can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules. Alcohols can form both intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonds. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds form between two different molecules, while intramolecular hydrogen bonds form between atoms within the same molecule.
What are Examples of Alcohols with Hydrogen Bonding?
Examples of alcohols with hydrogen bonding include ethanol, methanol, and propanol. Ethanol has two hydrogen bonds, one between the oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom, and another between the two hydrogen atoms. Methanol and propanol each contain one hydrogen bond, between the oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom.
How Does Hydrogen Bonding Affect the Properties of Alcohols?
Hydrogen bonding affects the physical and chemical properties of alcohols. The presence of hydrogen bonds increases the boiling point and melting point of alcohols, and decreases their volatility. Hydrogen bonding also affects the solubility of alcohols in polar and nonpolar solvents, as well as their boiling points.
What is the Difference Between Hydrogen Bonding and Van der Waals Forces?
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force between molecules, which occurs when a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (usually oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) is shared between two other molecules. Van der Waals forces are a type of intermolecular force between molecules, which occur when there is an imbalance of electron density between two molecules, resulting in a weak attractive force. Hydrogen bonding is much stronger than Van der Waals forces.
How Does Hydrogen Bonding Affect the Reactivity of Alcohols?
The presence of hydrogen bonds affects the reactivity of alcohols. Hydrogen bonds can act as bridges between molecules, allowing them to interact and form new bonds. Hydrogen bonds can also stabilize molecules, making them less reactive. Hydrogen bonding can also affect the rate of reaction, as molecules must break the hydrogen bonds before they can react.
Hydrogen bonding in alcohols
To conclude, it can be said that alcohols do have hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is essential for the properties of alcohols and their ability to dissolve in water. This is because the hydrogen bonds between alcohol molecules and the water molecules allow for the alcohol molecules to spread out and form a solution. Therefore, without hydrogen bonding, alcohols would not be able to dissolve in water, and their properties would be drastically different.
