Drug use is a serious issue that affects people of all backgrounds, and can lead to a variety of serious health problems. One of the most serious of these is an enlarged heart, which can have a devastating effect on a person’s health. In this article, we will explore how drug use can cause an enlarged heart, the effects it can have on the body, and ways to prevent it from occurring.
Yes, drug use can cause an enlarged heart. The most common cause of an enlarged heart is long-term high blood pressure, but drug use, especially long-term drug abuse, can also cause the heart to enlarge. Drugs like cocaine, alcohol, amphetamines, and heroin can all cause the heart to enlarge.
How Can Drug Use Affect the Human Heart?
Drug use can have a significant effect on the human heart. Drugs, such as cocaine, methamphetamine, marijuana, and alcohol, can have both short-term and long-term effects on the heart. Short-term effects may include increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased oxygen demand. Long-term effects may include an enlarged heart, heart damage, and an increased risk of heart failure.
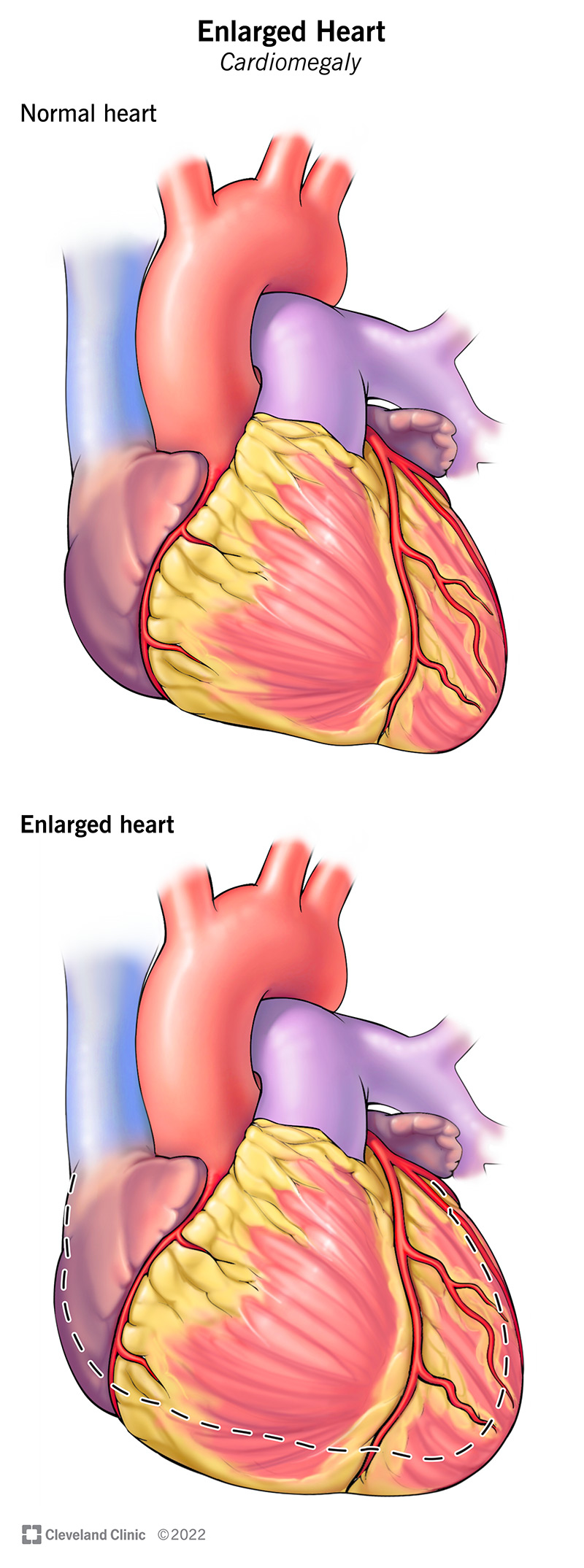
Drug use can lead to an enlarged heart, a condition known as cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly is an enlargement of the heart that can be caused by a variety of factors, including drug use. This enlargement can cause the heart to become less efficient at pumping blood around the body. Symptoms of an enlarged heart may include fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
Drug use can also cause heart damage in the form of scarring, inflammation, and abnormal electrical activity. Chronic drug use can lead to an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and congestive heart failure. It is important to note that not all drugs lead to an enlarged heart or heart damage. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with drug use and to seek medical advice if any symptoms are present.
What Drugs Can Cause an Enlarged Heart?
Certain drugs, such as cocaine and methamphetamine, are known to cause an enlarged heart. Cocaine is a powerful stimulant drug that increases heart rate and blood pressure. It can also cause an irregular and rapid heartbeat. Methamphetamine is another stimulant drug that can cause an enlarged heart. It can also cause an irregular and rapid heartbeat, as well as an increased risk of stroke and heart attack.
Other drugs, such as marijuana, alcohol, and prescription medications, can also cause an enlarged heart. Marijuana can increase heart rate and blood pressure, and can lead to an irregular and rapid heartbeat. Alcohol can also increase heart rate and blood pressure, and can lead to an irregular and rapid heartbeat. Prescription medications, such as steroids, can also cause an enlarged heart.
What Are the Risks of an Enlarged Heart?
The risks of an enlarged heart depend on the severity of the enlargement. If the enlargement is mild, there may be no symptoms and the heart may be able to function normally. However, if the enlargement is severe, it can lead to fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. An enlarged heart can also increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and congestive heart failure.
The risks of an enlarged heart can be reduced by avoiding or limiting drug use. If drug use is unavoidable, it is important to use drugs responsibly and take steps to reduce the risk of an enlarged heart. It is also important to seek medical advice if any symptoms are present.
What Are the Treatment Options for an Enlarged Heart?
Treatment for an enlarged heart depends on the underlying cause. If the enlargement is caused by drug use, the first step is to stop using the drug. Other treatment options may include lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. Medication may also be prescribed to help reduce the symptoms of an enlarged heart. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair any damage to the heart.
It is important to note that an enlarged heart can be treated, but it cannot be reversed. Therefore, it is important to take steps to reduce the risk of an enlarged heart before it becomes a problem.
How Can I Prevent an Enlarged Heart?
The best way to prevent an enlarged heart is to avoid or limit drug use. If drug use is unavoidable, it is important to use drugs responsibly and take steps to reduce the risk of an enlarged heart. It is also important to seek medical advice if any symptoms are present.
Other steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of an enlarged heart include quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and limiting alcohol intake. Additionally, it is important to be aware of any potential side effects of any medications that may be taken.
It is also important to seek medical advice if any symptoms of an enlarged heart are present. Early diagnosis and treatment can help reduce the risk of more serious complications.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is an Enlarged Heart?
An enlarged heart, also known as cardiomegaly, is a condition in which the heart is larger than normal. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and genetic abnormalities. It can also be a symptom of other diseases, such as heart failure, thyroid disease, and anemia. An enlarged heart can lead to serious health complications, including heart failure, arrhythmias, and even sudden cardiac death.
2. What are the Symptoms of an Enlarged Heart?
The most common symptom of an enlarged heart is shortness of breath, especially with physical activity. Other symptoms include fatigue, chest pain, irregular heartbeats, dizziness, and swelling in the legs, feet, or abdomen.
3. Can Drug Use Cause an Enlarged Heart?
Yes, drug use can cause an enlarged heart. Long-term use of certain drugs, such as cocaine and methamphetamines, can lead to an enlarged heart. These drugs can damage the heart muscle, causing it to become enlarged and leading to a variety of heart-related health problems.
4. What are the Risks of an Enlarged Heart?
The risks of an enlarged heart include heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. An enlarged heart can also lead to congestive heart failure, which occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can lead to shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs, feet, and abdomen.
5. How is an Enlarged Heart Diagnosed?
An enlarged heart is usually diagnosed with a physical exam and imaging tests such as an echocardiogram or CT scan. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create images of the heart, while a CT scan uses x-rays to create detailed images of the heart. Both tests can help diagnose an enlarged heart.
6. How is an Enlarged Heart Treated?
An enlarged heart can usually be treated with lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress. Medications may also be prescribed to manage high blood pressure, arrhythmias, and other conditions associated with an enlarged heart. In some cases, surgery may be needed to repair or replace the damaged heart muscle.
In conclusion, it is clear that drug use can cause an enlarged heart. Drugs can directly damage the heart and its ability to pump blood efficiently, leading to an enlarged heart. Additionally, the use of drugs can lead to other health risks, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke, which can also cause an enlarged heart. While it is important to be aware of the dangers of drug use, it is also important to take the necessary steps to prevent and treat an enlarged heart. By seeking medical help when necessary and making lifestyle changes, it is possible to protect your heart and your overall health.