Antibiotics are a crucial part of modern medicine, used for treating and preventing bacterial infections. But what exactly are antibiotics, and are they considered drugs? In this article, we will explore the answer to this question and discuss the effects of antibiotics on our bodies.
Yes, antibiotics are drugs. Antibiotics are medicines that fight bacterial infections. They work either by killing the bacteria or by stopping them from reproducing and spreading. They are usually prescribed by doctors to treat bacterial infections.
Are Antibiotics Drugs?
What are Antibiotics?
Antibiotics are medications that are used to treat bacterial infections. They work by either killing the bacteria or preventing them from reproducing. They are usually prescribed by a doctor and taken in pill form, but can also be given intravenously. Antibiotics are generally very effective in treating bacterial infections, but they do not work against viruses.
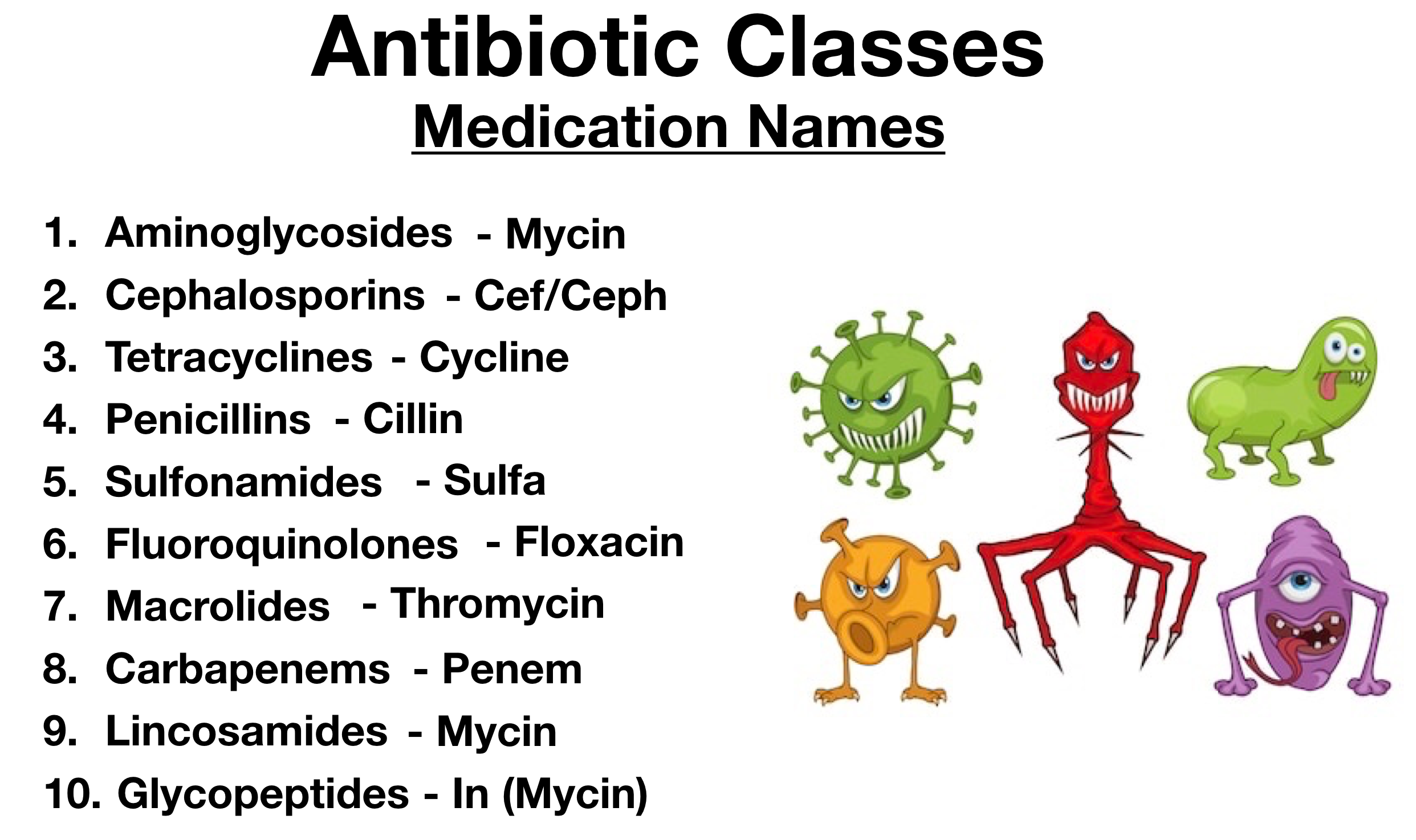
Types of Antibiotics
There are many different types of antibiotics available. These include penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones. Each type of antibiotic works differently and has different side effects. It is important to talk to your doctor about the type of antibiotic that is best for your particular infection.
Side Effects of Antibiotics
Like all medications, antibiotics can cause side effects. These include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and yeast infections. In some cases, antibiotics can also cause more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions or Clostridium difficile (C. diff) infections. It is important to talk to your doctor if you experience any side effects while taking antibiotics.
Are Antibiotics Drugs?
Antibiotics are considered drugs because they are used to treat bacterial infections. They are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and must be prescribed by a doctor. Taking antibiotics without a prescription can be dangerous and can lead to antibiotic resistance, which is when bacteria become resistant to the effects of antibiotics.
Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem and can have serious health consequences. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics can lead to bacteria becoming resistant to their effects. This can make it difficult to treat bacterial infections, as the antibiotics will no longer work. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions when taking antibiotics and to only take them when prescribed.
Preventing Antibiotic Resistance
There are several things that you can do to help prevent antibiotic resistance. These include: only taking antibiotics when prescribed by a doctor, completing the full course of antibiotics, not sharing antibiotics with others, and washing your hands regularly. Following these steps can help reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance and help keep antibiotics effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are antibiotics?
Antibiotics are drugs that are used to treat bacterial infections. They work by killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth. Antibiotics are usually taken orally or intravenously, depending on the type of infection and severity. Some antibiotics, such as penicillin, are also available as topical creams or ointments. Antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, and will not work against viruses such as the common cold or flu.
Are antibiotics drugs?
Yes, antibiotics are drugs that are used to treat bacterial infections. They are classified as prescription drugs, meaning they can only be legally obtained with a prescription from a doctor or health care provider. Antibiotics are not over-the-counter drugs and should not be taken without the advice of a doctor or health care provider.
What are the different types of antibiotics?
There are several different types of antibiotics. They can be divided into two main categories: broad-spectrum antibiotics, which are effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, and narrow-spectrum antibiotics, which are more specific and are only effective against certain types of bacteria. Examples of broad-spectrum antibiotics include penicillins, cephalosporins, and tetracyclines. Examples of narrow-spectrum antibiotics include aminoglycosides and macrolides.
Are all antibiotics the same?
No, not all antibiotics are the same. Different antibiotics are effective against different types of bacteria, and some may be more effective than others for certain types of infections. Different antibiotics also have different side effects and may interact with other medications.
What are some common side effects of antibiotics?
The most common side effects of antibiotics are nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Other potential side effects include rash, dizziness, headache, and upset stomach. Some antibiotics can also cause a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which can lead to yeast infections.
What should I do if I experience side effects from antibiotics?
If you experience any side effects while taking antibiotics, you should contact your doctor or health care provider right away. They can help determine if the side effects are due to the antibiotic or if they are a sign of a more serious problem. Your doctor or health care provider may be able to adjust your dosage or switch you to a different antibiotic.
Antibiotics – What They Are, When To Use Them, Side Effects & More
In conclusion, antibiotics are powerful drugs that are effective in treating bacterial infections. They are used with caution and should only be used when prescribed by a qualified healthcare provider. Antibiotics can save lives and help us get better, but they must be used responsibly to help reduce the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
