Benzodiazepines are a class of medications commonly used to treat anxiety and insomnia. They are effective and widely prescribed, but are all benzodiazepines the same? This article will explore the differences between the various types of benzodiazepines and how they can be used to treat different conditions. We’ll also look at the potential risks associated with each type of benzodiazepine, and discuss how to safely use these medications.
The Differences between Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs commonly prescribed to treat anxiety, panic attacks, insomnia, and other related conditions. While all benzodiazepines have similar effects on the body, they differ in their chemical structure, side effects, and potential for addiction. Understanding the differences between benzodiazepines can help a person get the best treatment for their condition.
Chemical Structure
The chemical structures of benzodiazepines vary from one to another. Some benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, have a simple structure, while others, such as alprazolam, have a more complex structure. The differences in structure can affect the way the drug works in the body, as well as its potential for addiction.
The chemical structure of a benzodiazepine also determines how long it stays in the body. Longer-acting benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, stay in the system for a longer period of time than shorter-acting benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam. This can affect the efficacy of the drug, as well as its potential for addiction.
Side Effects
The side effects of benzodiazepines can vary depending on the individual and the specific drug. Common side effects of benzodiazepines include drowsiness, confusion, and dizziness. Longer-acting benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, tend to cause more side effects than shorter-acting benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam.
Some benzodiazepines also have the potential to cause addiction. Longer-acting benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, are more likely to cause addiction than shorter-acting benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam. Additionally, some people are more likely to become addicted to benzodiazepines than others.
Potential for Addiction
The potential for addiction varies from one benzodiazepine to another. Longer-acting benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, are more likely to cause addiction than shorter-acting benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam. Additionally, some people are more likely to become addicted to benzodiazepines than others.
People who take benzodiazepines for a long period of time, or people who take high doses of the drug, are at an increased risk of developing an addiction. Additionally, people with a history of substance abuse, or people with certain mental health conditions, are also more likely to become addicted to benzodiazepines.
Choosing the Right Benzodiazepine
When choosing a benzodiazepine, it is important to consider the chemical structure, side effects, and potential for addiction. Longer-acting benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, are more likely to cause side effects and addiction than shorter-acting benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam. Additionally, it is important to consider any other medications or substances that the person is taking, as some medications and substances can interact with benzodiazepines.
It is also important to talk to a doctor about any concerns or questions. A doctor can help a person understand the risks and benefits of taking a particular benzodiazepine and can help them find the best treatment for their condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines are a group of psychoactive drugs commonly prescribed to treat a range of conditions, such as anxiety, insomnia, and muscle spasms. They are usually taken orally, but can also be taken as a nasal spray or injection. Benzodiazepines work by increasing the activity of the neurotransmitter GABA, which helps to reduce anxiety and stress.
Are all Benzodiazepines the Same?
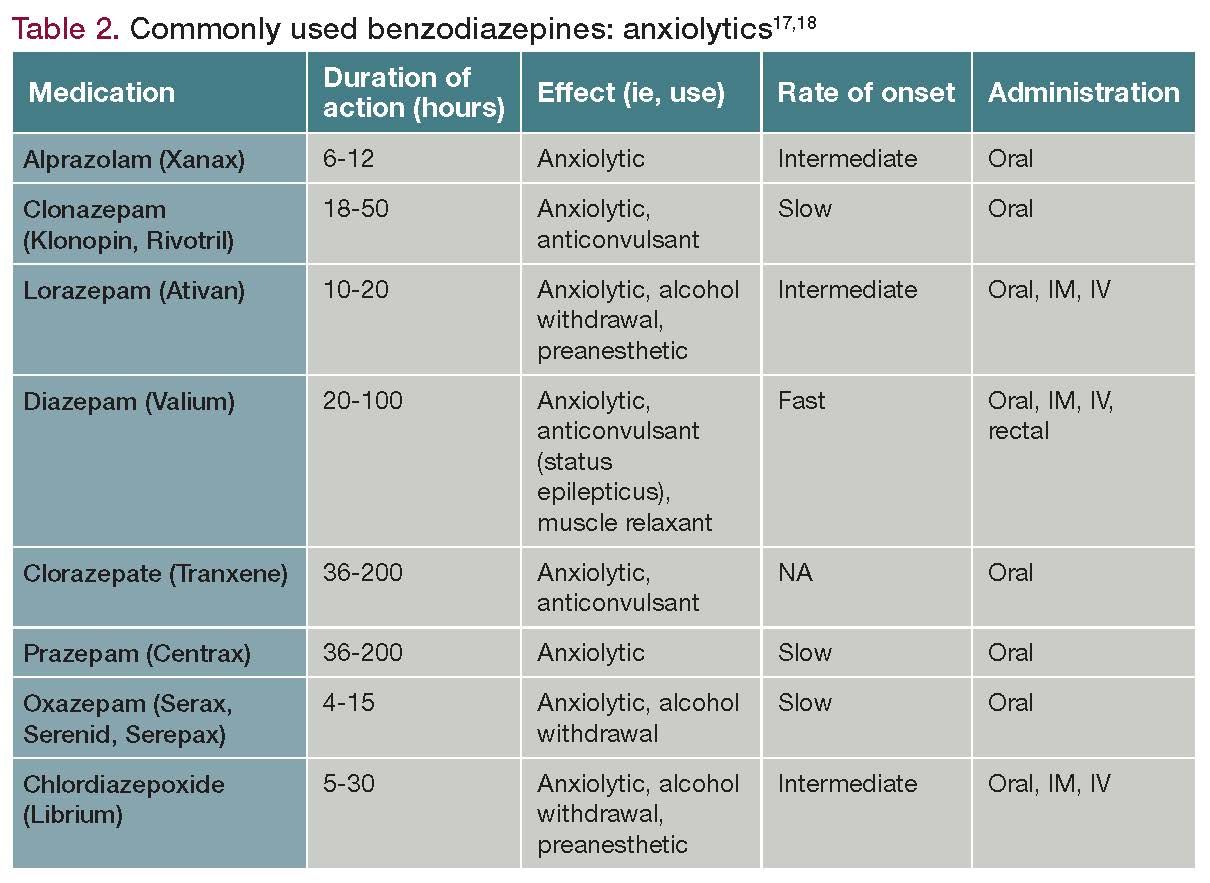
No, not all benzodiazepines are the same. Different benzodiazepines work differently and have different levels of effectiveness and side effects. Generally, there are three types of benzodiazepines: short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting. Short-acting benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam (Xanax), have a faster onset of action and a shorter duration of effects than longer-acting benzodiazepines, such as clonazepam (Klonopin). Additionally, some benzodiazepines may be more effective for treating certain conditions than others. For example, lorazepam (Ativan) is often preferred for treating anxiety, while clonazepam (Klonopin) is often preferred for treating seizure disorders.
What are the Side Effects of Benzodiazepines?
The most common side effects of benzodiazepines include drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, memory problems, and impaired coordination. Additionally, benzodiazepines can be habit-forming, so they should be used with caution. Other side effects may include changes in libido, depression, aggression, headache, nausea, and blurred vision.
What are the Risks of Taking Benzodiazepines?
The risks of taking benzodiazepines include the potential for dependence and addiction. Additionally, taking benzodiazepines over long periods of time can lead to tolerance, meaning that higher doses may be needed to achieve the same effect as when first taking the medication. Long-term use of benzodiazepines can also lead to withdrawal symptoms, such as insomnia, anxiety, and seizures, when the medication is stopped.
Who Should Not Take Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines should not be taken by people with a history of substance abuse or addiction, as they can be habit-forming. Additionally, benzodiazepines should not be taken by people with certain medical conditions, such as sleep apnea, glaucoma, or liver or kidney disease. Benzodiazepines should also not be taken with certain medications, such as other sedatives or alcohol.
Are Benzodiazepines Safe?
When taken as prescribed, benzodiazepines are generally safe. However, they can be dangerous if taken in large doses or combined with other substances, such as alcohol. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions when taking benzodiazepines and to never take more than the recommended dose.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Benzodiazepines
In conclusion, it is clear that not all benzodiazepines are the same. While they all have a similar chemical makeup, the effects they provide are quite varied. Each benzodiazepine is designed to target a certain set of symptoms, and so it is important to consult a doctor before taking any of these drugs. By understanding the differences between the various benzodiazepines, you can be sure to make the right choice for your particular needs.
