Stimulants are widely used to help people stay awake and alert, but they can also have adverse effects on the body. Understanding the potential side effects of stimulants is important for people who use them for medical or recreational purposes. In this article, we will explore the potential side effects of stimulants and how to minimize their risks.
Contents
Introduction to Stimulants and their Side Effects
Stimulants are drugs that temporarily increase alertness, focus, and energy. Stimulants are commonly prescribed to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. They can also be used in combination with other medications, such as antidepressants, to treat depression. Stimulants can have a range of side effects, both short-term and long-term.
Short-term Side Effects of Stimulants
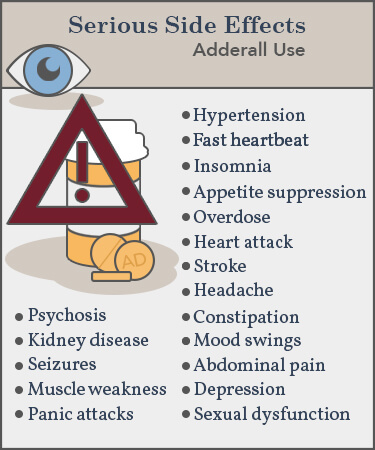
The most common short-term side effects of stimulants include nausea, headache, nervousness, insomnia, and dry mouth. Some people may experience a faster heart rate, increased blood pressure, or increased sweating. These effects usually go away after the drug leaves the body, but they can be uncomfortable.
Other potential short-term side effects include anxiety, irritability, restlessness, and dizziness. Stimulants can also affect appetite, which can lead to weight loss. People who take stimulants may experience a decrease in their overall energy level.
Long-term Side Effects of Stimulants
Long-term use of stimulants can lead to physical dependence and addiction. People who take stimulants for long periods of time may become tolerant to the drug, meaning they need higher and higher doses to achieve the same effect. This can lead to serious health problems, such as heart palpitations, seizures, and even death.
Stimulants can also cause changes in behavior and mood. People who take stimulants for long periods of time may become irritable, moody, or aggressive. They may also experience depression and anxiety.
Side Effects on the Brain
Stimulants can have long-term effects on the brain. Long-term use of stimulants can lead to changes in the brain’s structure and function. These changes can affect a person’s thinking, memory, and overall brain health.
Stimulants can also interfere with the development of the brain. This can lead to learning and behavior problems in children and adolescents who take stimulants for long periods of time.
Side Effects on the Heart
Stimulants can increase the risk of heart problems, such as heart palpitations, arrhythmias, and even heart attack. Long-term use of stimulants can also increase blood pressure and lead to stroke.
Stimulants can also affect the body’s ability to regulate temperature, which can lead to heat exhaustion and heat stroke. People who take stimulants for long periods of time may also be at an increased risk of dehydration.
Other Side Effects
In addition to the side effects mentioned above, stimulants can also lead to other problems. People who take stimulants for long periods of time may be at an increased risk of developing kidney and liver problems.
Stimulants can also lead to gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. People who take stimulants may also experience sexual side effects, such as difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What are Stimulants?
Stimulants are a class of drugs that increase activity in the central nervous system. They can be used to treat a variety of conditions such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Examples of stimulants include caffeine, amphetamines, cocaine, and methylphenidate.
What Are the Side Effects of Stimulants?
The most common side effects of stimulants include: insomnia, headaches, loss of appetite, increased cortisol levels, increased heart rate and blood pressure, restlessness, anxiety, irritability, nausea, and dizziness. Long-term use of stimulants may lead to addiction and have other serious health risks, such as heart problems, stroke, and even death.
Are Stimulants Addictive?
Yes, stimulants can be addictive. When used for a long period of time, stimulants can cause dependence, which can lead to compulsive use and abuse of the drug. Withdrawal symptoms can occur when the drug is stopped, and tolerance can build up, requiring a higher dose to achieve the same effects.
Is it Safe to Take Stimulants?
Taking stimulants can be safe when taken as prescribed and monitored by a doctor. Stimulant use should be closely monitored to avoid potential misuse or abuse. It is important to discuss any potential risks and side effects with a doctor before taking stimulants.
What Are the Alternatives to Stimulants?
There are several alternative treatments to stimulants that may be more appropriate depending on the individual’s condition and needs. These include cognitive-behavioral therapy, lifestyle changes such as exercise and diet, and certain medications such as antidepressants and non-stimulant medications.
Are Stimulants Used for Weight Loss?
Stimulants are not typically used for weight loss, and their use for this purpose is not recommended. Stimulants can have serious side effects, and their long-term use can lead to addiction and other health complications. It is important to discuss any potential risks and benefits with a doctor before taking any medication for weight loss.
Side effects of stimulants – Intro to Psychology
In conclusion, stimulants can have a wide range of side effects that can be both physical and mental. Some of these include increased blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration, headaches, insomnia, irritability, restlessness, and anxiety. While these drugs can be beneficial for those with certain medical conditions, the potential for side effects should always be taken into consideration. It is important to speak with a healthcare practitioner before beginning a stimulant regimen to ensure that the risks are understood and managed appropriately.
