Drugs have become a global problem, and their addictive qualities are a major contributing factor. But what makes a drug addictive? This article will explore the psychology and biology behind drug addiction, examining the effects of drugs on the brain and body, and how those effects lead to compulsive drug use and addiction. We’ll also look at how environmental and social factors can increase the risk of drug abuse and addiction.
Contents
The Psychological and Neurobiological Effects of Drug Addiction
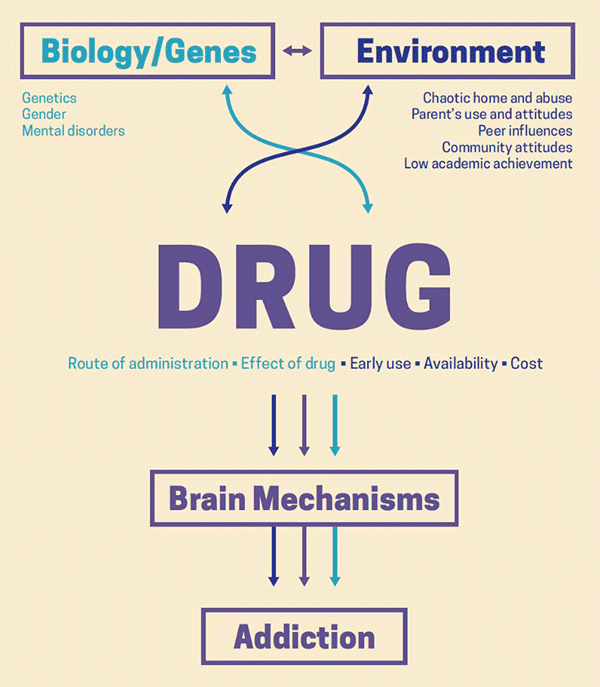
Drug addiction is a complex phenomenon that involves both psychological and neurobiological factors. Addiction is a chronic disorder that results from repeated use of a drug or other substance. It is characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behavior, a strong desire to consume the drug, and difficulty in controlling its use, even in the face of negative consequences.
The psychological effects of drug addiction are varied and complex. Drug use can lead to distorted thinking and can cause people to be unable to recognize the consequences of their actions. In addition, drug use can lead to impaired judgment, increased risk-taking behaviors, and a decreased sense of control over one’s life. These psychological effects can make it difficult for users to stop using drugs, even when they want to.
The neurobiological effects of drug addiction are also complex. Drug use can cause changes in the brain’s reward system, leading to an increased desire for the drug, even when it is no longer pleasurable. This can lead to a cycle of drug use, where users continue to take the drug in order to feel a sense of pleasure or relief. These neurobiological changes can make it difficult for users to stop taking drugs, even when the drug use is causing negative consequences.
The Role of Genetics in Drug Addiction
Drug addiction can be influenced by genetic factors, as well as environmental factors. Studies have shown that certain genes can make individuals more vulnerable to developing an addiction. For example, some individuals may be more prone to developing an addiction due to their genetic makeup.
In addition, certain environmental factors can increase an individual’s risk of developing an addiction. These factors can include stress, social isolation, and exposure to drug-using peers. All of these factors can make it more difficult for an individual to resist the urge to use drugs.
The Impact of Drug Addiction on Health
Drug addiction can have a serious impact on an individual’s physical and mental health. Long-term drug use can lead to physical health problems, such as damage to the lungs, heart, and liver. In addition, drug use can have a negative impact on an individual’s mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
Drug addiction can also have a negative impact on an individual’s relationships. Drug use can lead to strained relationships with friends and family, and can make it difficult for users to maintain meaningful connections with others.
The Social and Economic Costs of Drug Addiction
The costs of drug addiction extend beyond physical and mental health issues. Drug addiction can also have a serious impact on an individual’s social and economic well-being.
Drug users are more likely to be unemployed and to engage in criminal activities. This can lead to legal and financial problems, such as fines, jail time, and lost wages. In addition, drug users are more likely to be involved in motor vehicle accidents, which can lead to costly medical bills.
Drug addiction can also have a negative impact on society as a whole. Drug users are more likely to engage in criminal activities, which can lead to an increase in the crime rate and an increase in the costs associated with law enforcement and incarceration.
The Role of Treatment in Drug Addiction
Fortunately, there are a number of treatment options available for drug addiction. These treatments can include counseling, medication, and lifestyle changes. Treatment can help individuals to reduce their drug use and to develop healthier coping skills.
In addition, treatment can help individuals to build a support network and to reconnect with family and friends. This can help to reduce the social and economic costs of drug addiction.
The Role of Prevention in Drug Addiction
In addition to treatment, there are a number of prevention strategies that can be used to reduce the risk of drug addiction. These strategies can include educating individuals about the risks of drug use, providing support for individuals who are at risk of developing an addiction, and developing drug policies that are designed to reduce drug use.
Prevention strategies can also include increasing access to treatment and developing programs that are designed to reduce the stigma associated with drug addiction. All of these strategies can help to reduce the social and economic costs of drug addiction.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Addiction?
Addiction is a chronic brain disorder characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, despite adverse consequences. It is considered a neurological disorder, as it is caused by changes in the brain’s reward system that result from prolonged substance use or other behaviors. Addiction can involve the use of substances such as alcohol, drugs, or food, as well as behaviors such as gambling, sex, shopping, or work. These activities can become compulsive and interfere with a person’s normal functioning and relationships.
What Causes Addiction?
Drug addiction is caused by changes in the brain that occur over time with repeated use. Drugs act on the brain’s reward system, releasing large amounts of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that produces feelings of pleasure. The brain is wired to seek out activities that produce dopamine and reward us with feelings of pleasure. This reward system can become hijacked by drugs, and the person will experience cravings and compulsions to use the drug even when there may be negative consequences.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Addiction?
The signs and symptoms of addiction vary depending on the type of drug or activity involved, but some common signs include:
– Loss of control over the amount or frequency of use
– Spending a lot of time and energy to obtain and use the substance or engage in the activity
– Withdrawal symptoms when the substance or activity is stopped
– Continuing to use the substance or engage in the activity despite negative consequences
– Cravings and compulsive behaviors to use the substance or engage in the activity
What are the Consequences of Addiction?
Addiction can have serious physical, psychological, and social consequences. Physically, it can lead to an increased risk of developing health problems, such as liver damage, heart disease, and respiratory problems. Psychologically, it can cause feelings of depression, anxiety, and guilt. Socially, it can lead to strained relationships with family, friends, and coworkers. It can also lead to financial and legal problems.
What Treatments are Available for Addiction?
Treatment for addiction is tailored to the individual and may involve a combination of therapies, medications, and other strategies. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often used to help people change their behavior, and medications such as naltrexone and buprenorphine can be used to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. 12-step programs, such as Alcoholics Anonymous, can also be helpful for some people.
How Can People Prevent Addiction?
People can reduce their risk of addiction by avoiding activities and substances that can be addictive, such as drugs, alcohol, and gambling. It is also important to stay informed about the potential risks of engaging in certain behaviors and to be mindful of potential warning signs. Additionally, it is important to practice self-care, maintain healthy relationships, and build a strong support network.
Mechanism of Drug Addiction in the Brain, Animation.
In conclusion, it is clear that drugs can be highly addictive due to their ability to create a pleasurable effect or feeling of euphoria. This feeling is often difficult to give up, and leads to the compulsive use of drugs despite the negative consequences. The powerful combination of physical and psychological dependence can make drug addiction a difficult condition to overcome. It is important to seek help if you or someone you know is struggling with drug addiction.
