Urine drug screens are an important part of drug testing, as they can provide a window into an individual’s drug use. A urine drug screen is a test that detects the presence of certain drugs or their metabolites in the urine. This test can be used to detect recent drug use, as well as long-term or chronic drug use. In this article, we will explore what a urine drug screen is, how it works, and what it can tell us about a person’s drug use.
What is a Urine Drug Screen?
A urine drug screen is a test used to detect the presence of drugs and their metabolites in a person’s urine sample. Urine drug screens are commonly used to detect recent drug use, as they can detect drugs and their metabolites in a person’s urine for up to several days after they have been taken. Urine drug screens are often used as part of a drug test to screen for the presence of illegal or prescription drugs in an individual.
Urine drug screens are quick and easy to perform, and can be used to detect a variety of drugs. Commonly screened drugs include amphetamines, cocaine, marijuana, opiates, phencyclidine (PCP), and other prescription medications. The results of a urine drug screen can be used to determine if an individual has recently used drugs, and can be used to provide evidence of drug use in legal proceedings.
Urine drug screens involve collecting a sample of urine from the individual being tested, and then testing the sample for the presence of drugs and their metabolites. The sample will be tested using a variety of methods, including gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS), immunoassay, and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The results of the urine drug screen will be reported as positive or negative, depending on whether or not the drug or its metabolites are present in the sample.
How is Urine Drug Screening Performed?
Urine drug screens are typically performed in a laboratory by a qualified technician. The technician will collect a sample of urine from the individual being tested, and then test the sample using one of the aforementioned methods. If the drug or its metabolites are present in the sample, the result will be reported as a positive result. If the drug or its metabolites are not present in the sample, the result will be reported as a negative result.
The technician will also take into account any potential sources of contamination, such as food or drink, that may interfere with the results of the urine drug screen. The technician will also ensure that the sample is free from adulterants, which may be added to the sample in order to alter the results of the urine drug screen.
What is the Accuracy of Urine Drug Screening?
Urine drug screens are considered to be very accurate in detecting drugs and their metabolites in a person’s urine. The accuracy of a urine drug screen is dependent on the sensitivity of the method used to detect the drug or its metabolites, as well as the amount of the drug or its metabolites present in the sample.
Urine drug screens are considered to be very reliable in detecting drugs and their metabolites in a person’s urine. However, there are certain factors that can affect the accuracy of a urine drug screen, such as the presence of adulterants or contaminants, or the sample being incorrectly collected or stored.
What are the Benefits of Urine Drug Screening?
Urine drug screens are a quick and easy way to detect the presence of drugs and their metabolites in a person’s urine. Urine drug screens can be used to detect a variety of drugs, including illegal drugs, prescription medications, and over-the-counter drugs. Urine drug screens can also be used to detect recent drug use, as they can detect drugs and their metabolites in a person’s urine for up to several days after they have been taken.
Urine drug screens are also cost-effective and can be used to provide evidence of drug use in legal proceedings. Urine drug screens are also relatively non-invasive, as the sample is simply collected from the individual being tested.
What are the Limitations of Urine Drug Screening?
Urine drug screens are not perfect, as there are certain factors that can affect the accuracy of a urine drug screen, such as the presence of adulterants or contaminants, or the sample being incorrectly collected or stored. Urine drug screens are also not able to detect the use of certain drugs, such as inhalants or alcohol, as these drugs are not detected in urine.
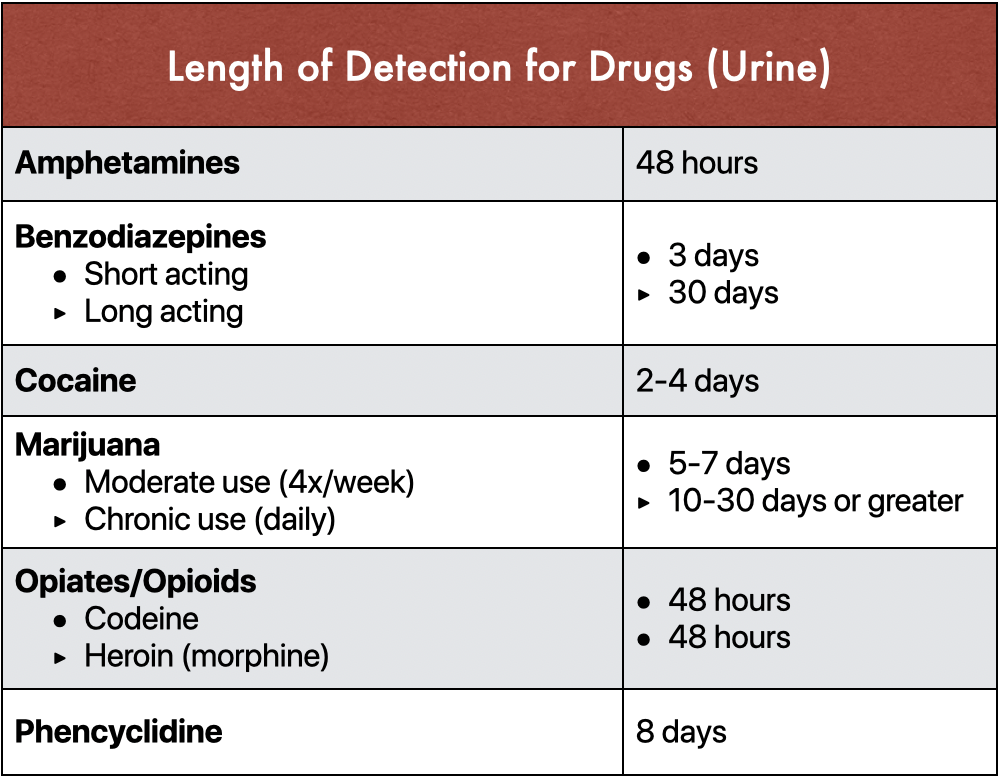
Urine drug screens also have a limited window of detection, as they can only detect drugs and their metabolites in a person’s urine for up to several days after they have been taken. This means that a urine drug screen may not be able to detect drugs that were taken more than a few days prior to the test.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Urine Drug Screen?
A urine drug screen, also known as a urine drug test, is a type of medical test that is used to identify the presence of drugs or their metabolites in a person’s urine sample. Urine drug screens are used to detect the presence of both legal and illegal substances, such as prescription medications or illicit drugs. The test is used to identify drug use or to confirm the presence of drugs in the system that may have been used recently or in the past.
What is Tested in a Urine Drug Screen?
Urine drug screens typically test for the presence of a variety of drugs and their metabolites. The specific drugs tested for depend on the type of drug test ordered. Commonly tested drugs include alcohol, amphetamines, benzodiazepines, cocaine, marijuana, opiates, and phencyclidine (PCP).
What is the Purpose of a Urine Drug Screen?
Urine drug screens are used for a variety of reasons. The most common uses include screening for drugs in pre-employment drug testing programs, periodic drug testing in the workplace, evaluating drug use in patients receiving medical care, and monitoring people on probation or parole. Urine drug screens can also be used to detect the presence of drugs in individuals suspected of driving under the influence of drugs.
How is a Urine Drug Screen Conducted?
A urine drug screen is typically conducted by collecting a urine sample from the individual being tested. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis and the results are reported back to the ordering clinician, employer, or other entity.
How Accurate is a Urine Drug Screen?
Urine drug screens are generally considered to be very accurate. The accuracy of the test depends on a variety of factors, such as the type of drug being tested for, the amount of drug present in the sample, the quality of the laboratory performing the test, and the time elapsed since the drug was last used.
What are the Limitations of a Urine Drug Screen?
The main limitation of a urine drug screen is that it only detects the presence of drugs or their metabolites in the urine. This means that the test does not provide any indication of the amount or purity of the drug present in the sample, nor does it provide insight into the manner in which the drug was used. Additionally, urine drug screens are not able to detect the presence of drugs that are rapidly metabolized or cleared from the body, such as alcohol.
Discussing Urine Drug Screen Results for Clinicians
A urine drug screen is an important tool to detect drug use and monitor the effectiveness of drug treatment. It is a fast and cost-effective way to find out if a person is using drugs. With the help of a urine drug screen, a doctor can identify potential drug abuse and help a patient get the right treatment. With the right treatment, people can lead a healthier and more productive life.
