If you’ve ever wondered how long nicotine stays in your blood after you’ve smoked or used a nicotine product, you’re not alone. With the rise of vaping and other nicotine-based products, understanding how long nicotine lingers in your system has become increasingly important. This article will provide an in-depth look at nicotine, how it affects your body, and how long it remains detectable in your blood.
Nicotine can stay in your blood for up to 1 to 3 days after exposure. The exact amount of time depends on several factors, including the amount of nicotine consumed, the route of exposure (smoking, vaping, patches, etc.), and the person’s metabolism.
Nicotine is a toxic chemical found in tobacco and other plants, and it can be absorbed into the body through smoking, vaping, patches, and chewing tobacco. Once nicotine enters the body, it is quickly broken down by enzymes in the liver and eliminated in the urine.
The half-life of nicotine, or the amount of time it takes for half of the nicotine to be eliminated, is about two hours. This means that nicotine can remain in the blood for up to 1 to 3 days after exposure. Factors that can affect the amount of time nicotine stays in the blood include the amount of nicotine consumed, the route of exposure, and the person’s metabolism.
Contents
- How Long Does Nicotine Stay in the Bloodstream?
- Testing for Nicotine in the Bloodstream
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your Blood?
- What Tests Are Used to Detect Nicotine in the Blood?
- How Does Nicotine Affect the Body?
- What Are the Side Effects of Nicotine?
- How Does Nicotine Addiction Develop?
- What Are the Treatments for Nicotine Addiction?
- How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System? (TRUTH)
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in the Bloodstream?
Nicotine is a chemical found in cigarettes and other tobacco products that causes addiction and has many negative health effects. Nicotine is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and can stay in the bloodstream for up to four days. The amount of time nicotine stays in the bloodstream depends on several factors, including how much nicotine is consumed, the person’s metabolism, and how often they smoke.
The nicotine in cigarettes is rapidly and completely absorbed into the bloodstream. This happens within minutes of inhaling smoke or chewing tobacco. Nicotine is then broken down in the liver, and the amount of nicotine in the bloodstream peaks about 30 minutes after smoking. After peaking, the amount of nicotine in the bloodstream begins to decline and is usually undetectable after four days.
However, the amount of time nicotine stays in the bloodstream can vary depending on a person’s metabolism and the amount of nicotine consumed. People with faster metabolisms break down nicotine more quickly. This means they will have lower levels of nicotine in their bloodstream. People who smoke more frequently or consume higher levels of nicotine may have nicotine in their bloodstream for a longer period of time.
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Urine?
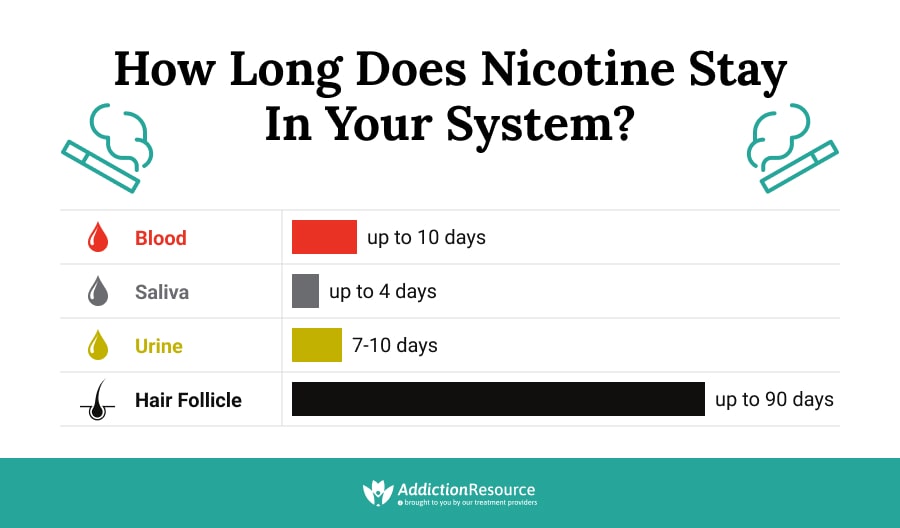
Nicotine is also present in urine, although the amount and duration of nicotine in the urine will depend on the amount and frequency of tobacco consumption. Nicotine and its byproducts can be detected in the urine for up to 3-4 days after consumption.
Urine tests are not as accurate as blood tests when it comes to detecting nicotine. Urine tests are more likely to detect nicotine in people who have been smoking for a long period of time or who smoke heavily, but may not be able to detect nicotine in people who smoke less frequently or in smaller amounts.
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Saliva?
Nicotine can also be detected in saliva. The amount and duration of nicotine in saliva will depend on the amount and frequency of tobacco consumption. Nicotine and its byproducts can be detected in saliva for up to 24 hours after consumption.
Saliva tests are not as accurate as blood tests when it comes to detecting nicotine. Saliva tests are more likely to detect nicotine in people who have been smoking for a long period of time or who smoke heavily, but may not be able to detect nicotine in people who smoke less frequently or in smaller amounts.
Testing for Nicotine in the Bloodstream
Nicotine can be detected in the bloodstream through a blood test. Blood tests are the most accurate way to detect nicotine in the bloodstream, as they measure the amount of nicotine present. Blood tests can detect nicotine in the bloodstream for up to four days after smoking.
Blood tests are often used to monitor nicotine levels in people who are trying to quit smoking. They can help doctors determine if a person is abstaining from smoking or if they are still using tobacco products.
Nicotine Metabolism
The amount of time nicotine stays in the bloodstream is affected by a person’s metabolism. People with faster metabolisms break down nicotine more quickly, which means they will have lower levels of nicotine in their bloodstream. People who smoke more frequently or consume higher levels of nicotine may have nicotine in their bloodstream for a longer period of time.
Other Factors Affecting Nicotine Metabolism
Other factors that can affect the amount of time nicotine stays in the bloodstream include age, gender, and body size. Older people tend to have slower metabolisms, which means nicotine may stay in their bloodstream longer than younger people. Women tend to have slower metabolisms than men, which means they may have higher levels of nicotine in their bloodstream. People with larger bodies tend to have slower metabolisms, which means they may have higher levels of nicotine in their bloodstream.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your Blood?
Answer: Nicotine can be detected in the blood for up to 24 hours after it has been ingested. However, the length of time nicotine will remain detectable in the blood depends on several factors, including the amount of nicotine used, the frequency of use, and the individual’s metabolism.
What Tests Are Used to Detect Nicotine in the Blood?
Answer: Nicotine can be detected in the blood with a blood test that measures cotinine, a byproduct of nicotine that is produced when the body breaks down nicotine. The cotinine test is most commonly used to detect nicotine in the blood and can detect nicotine for up to four days after use.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Body?
Answer: Nicotine is a stimulant drug that affects the body in many ways. It increases heart rate and blood pressure, increases alertness and concentration, and suppresses appetite. It can also increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and cancer.
What Are the Side Effects of Nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine can cause short-term side effects such as headaches, nausea, dizziness, and irritability. Long-term side effects can include lung and heart disease, addiction, and an increased risk of cancer.
How Does Nicotine Addiction Develop?
Answer: Nicotine addiction is caused by the body’s dependence on nicotine and the pleasure it produces. The body develops a tolerance to nicotine, meaning the individual needs to take more of the drug to get the same effect. Over time, this can lead to physical and psychological dependence.
What Are the Treatments for Nicotine Addiction?
Answer: Treatments for nicotine addiction include medications, such as nicotine replacement therapy, and behavioral therapies. Nicotine replacement therapy involves using nicotine patches, gum, lozenges, or inhalers to reduce cravings. Behavioral therapies involve counseling and support to help individuals quit smoking.
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System? (TRUTH)
In conclusion, nicotine is a highly addictive substance that can be difficult to quit. It can stay in your blood for a few days to a few weeks depending on the amount you consume. If you are trying to quit smoking, it is important to understand how long nicotine can stay in your blood and the health risks associated with it. With the right support and resources, you can be successful in quitting smoking and be on your way to a healthier lifestyle.
