Drug-induced lupus is a rare disorder that is caused by certain medications. It is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including fever, joint pain, rashes, and fatigue. If left untreated, drug-induced lupus can lead to serious and even life-threatening complications. But what drugs cause this condition? In this article, we’ll explore what medications are associated with drug-induced lupus and the possible side effects of each.
Contents
- What Drugs Can Lead to Drug-Induced Lupus?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Drug-Induced Lupus?
- What Drugs Cause Drug Induced Lupus?
- How is Drug-Induced Lupus Diagnosed?
- Are There Any Treatment Options for Drug-Induced Lupus?
- What are the Long-Term Effects of Drug-Induced Lupus?
- Can Drug-Induced Lupus Lead to Other Health Complications?
- Common Medications Can Cause Drug-Induced Lupus
What Drugs Can Lead to Drug-Induced Lupus?
Drug-induced lupus is a type of autoimmune disorder that is caused by certain medications. The disease has many of the same symptoms as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but it usually disappears after the drug is stopped. This type of lupus can be caused by many different drugs, including antibiotics, blood pressure medications, and anticonvulsants. It is important to know the risks associated with these drugs and to be aware of any changes in health that may indicate the presence of drug-induced lupus.
Drug-induced lupus is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. This can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, joint pain, skin rash, and fatigue. In some cases, the symptoms can be severe and can even lead to organ damage. The most common drugs that can cause drug-induced lupus are antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and blood pressure medications.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are medications used to treat bacterial infections. Some antibiotics, such as penicillin and sulfonamides, have been linked to drug-induced lupus. In particular, penicillin has been found to cause a rare form of lupus called drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus (DI-SLE). This form of lupus can cause a wide range of symptoms, including joint pain, skin rash, and fever.
Antibiotics are generally safe and effective, but it’s important to be aware of the potential risks. Be sure to talk to your doctor if you experience any of the symptoms of drug-induced lupus while taking antibiotics.
Anticonvulsants
Anticonvulsants are medications used to treat seizures. These drugs have been linked to drug-induced lupus in some cases. The most commonly implicated anticonvulsants are phenytoin, phenobarbital, and carbamazepine. These drugs can cause a range of symptoms, including rash, joint pain, and fever.
It’s important to talk to your doctor if you experience any of the symptoms of drug-induced lupus while taking anticonvulsants. Your doctor may recommend changing medications or adjusting the dosage of the anticonvulsant to reduce the risk of drug-induced lupus.
Blood Pressure Medications
Blood pressure medications, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), have been linked to drug-induced lupus in some cases. These drugs can cause a range of symptoms, including rash, joint pain, and fever.
It’s important to talk to your doctor if you experience any of the symptoms of drug-induced lupus while taking blood pressure medications. Your doctor may recommend changing medications or adjusting the dosage of the drug to reduce the risk of drug-induced lupus.
Other Drugs
In addition to antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and blood pressure medications, other drugs have also been linked to drug-induced lupus. These include certain chemotherapy drugs, anti-inflammatories, and immunosuppressants. It’s important to be aware of the potential risks associated with these drugs and to talk to your doctor if you experience any of the symptoms of drug-induced lupus.
Conclusion
Drug-induced lupus is a type of autoimmune disorder that is caused by certain medications. The most common drugs that can cause drug-induced lupus are antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and blood pressure medications. Other drugs, such as chemotherapy drugs, anti-inflammatories, and immunosuppressants, have also been linked to drug-induced lupus. It’s important to be aware of the potential risks associated with these drugs and to talk to your doctor if you experience any of the symptoms of drug-induced lupus.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Drug-Induced Lupus?
Drug-induced Lupus is a form of lupus that is caused by certain medications. It is characterized by a range of symptoms, including joint pain and swelling, skin rashes, fatigue, fever, and organ inflammation. Drug-induced lupus is usually temporary and reversible, meaning that when the drug causing the condition is stopped, the symptoms of lupus will go away. However, some drugs can cause permanent lupus.
What Drugs Cause Drug Induced Lupus?
There are many drugs that are known to cause drug-induced lupus. These include certain antibiotics, anticonvulsants, cholesterol-lowering medications, certain hormones, and some cancer treatments. Common antibiotics that can cause lupus include minocycline, ampicillin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Common anticonvulsants that can cause lupus are phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital. Cholesterol-lowering medications such as atorvastatin and simvastatin can also cause lupus. Additionally, hormones such as progestins and interferon alpha can cause lupus.
How is Drug-Induced Lupus Diagnosed?
If a doctor suspects a patient may have drug-induced lupus, they will typically order a series of tests to diagnose it. These tests may include blood tests to check for levels of inflammation, skin tests to check for rashes, and imaging tests to check for organ involvement. Additionally, a doctor may conduct a physical exam and ask about the patient’s history of medications that could potentially cause lupus.
Are There Any Treatment Options for Drug-Induced Lupus?
The treatment of drug-induced lupus depends on the severity of the symptoms. The first step is to stop taking the medication that is causing the lupus. If the drug-induced lupus is mild and the symptoms are not severe, a doctor may recommend lifestyle changes such as rest, avoiding sun exposure, and using cold compresses to help reduce swelling and pain. If the symptoms are more severe, a doctor may recommend anti-inflammatory medications or corticosteroids to help reduce symptoms.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Drug-Induced Lupus?
The long-term effects of drug-induced lupus depend on the severity and duration of the condition. In most cases, the symptoms of drug-induced lupus will go away once the medication causing the condition is stopped. However, some medications can cause permanent damage to the organs or can lead to other complications such as kidney failure. It is important to speak to a doctor about the potential long-term effects of drug-induced lupus.
Can Drug-Induced Lupus Lead to Other Health Complications?
Yes, drug-induced lupus can lead to other health complications. If the lupus is severe and is left untreated, it can lead to organ damage and inflammation. Additionally, if the lupus is caused by certain medications, it can lead to an increased risk of infection. It is important to speak to a doctor about the potential risks of drug-induced lupus so that the condition can be properly monitored and treated.
Common Medications Can Cause Drug-Induced Lupus
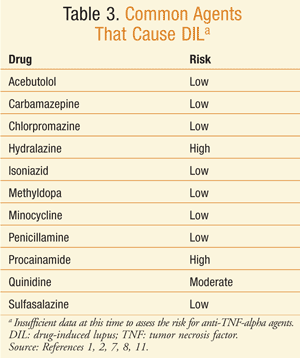
Drug-induced lupus is a rare but serious condition that can cause severe and debilitating symptoms. While the exact cause is still unknown, some drugs have been linked to the development of drug-induced lupus. These drugs include hydralazine, procainamide, quinidine, and isoniazid. It is important to discuss any potential side effects with your doctor before starting a new medication. If you experience any concerning symptoms after a drug is started, it is important to let your doctor know right away. Early diagnosis and management of drug-induced lupus can improve your quality of life and help to prevent any long-term complications.
