Metformin is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for type 2 diabetes. But what drug class does Metformin belong to? In this article, we’ll explore the answer to this question, as well as the uses, side effects, and other considerations when taking Metformin.
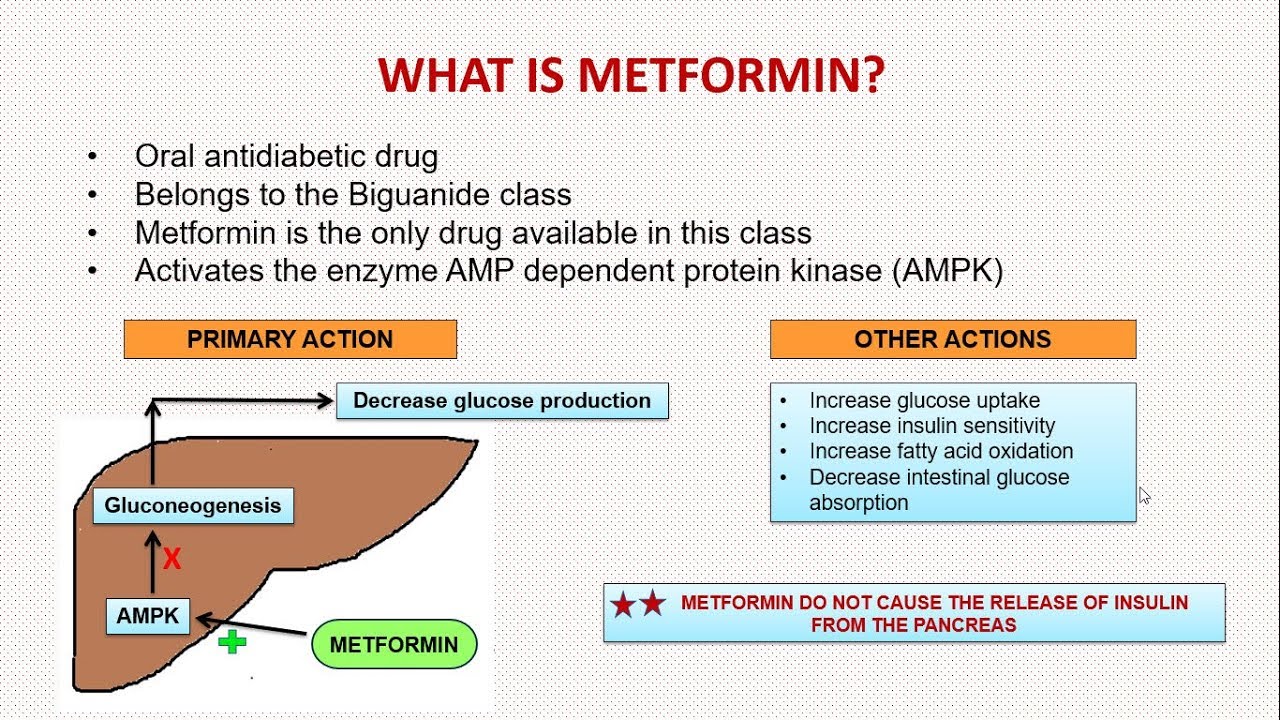
Metformin belongs to a class of drugs called biguanides. It works by decreasing the amount of sugar that the liver produces and the intestines absorb. It also helps to make your body more sensitive to the insulin that you naturally produce.
Contents
What is Metformin and What Drug Class Does it Belong To?
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is an oral medication that works by decreasing the amount of sugar produced by the liver and decreasing the amount of sugar absorbed by the intestines. Metformin belongs to the drug class called ‘biguanides’ and is one of the most widely used medications for diabetes.
Metformin works by decreasing the amount of sugar produced by the liver and decreasing the amount of sugar absorbed by the intestines. This helps to reduce the amount of sugar in the blood, which helps to control the symptoms of diabetes. In addition to decreasing the amount of sugar in the blood, metformin also increases the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which helps to regulate blood sugar levels.
Metformin is generally well-tolerated and has few side effects. Possible side effects include nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea. It is important to discuss any potential side effects with a doctor before starting metformin.
How Does Metformin Work?
Metformin works by decreasing the amount of sugar produced by the liver and decreasing the amount of sugar absorbed by the intestines. This helps to reduce the amount of sugar in the blood, which helps to control the symptoms of diabetes. In addition to decreasing the amount of sugar in the blood, metformin also increases the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which helps to regulate blood sugar levels.
Metformin works by decreasing the production of glucose in the liver and increasing the sensitivity of cells in the body to insulin. By decreasing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and increasing the sensitivity of cells to insulin, metformin helps to control blood sugar levels and reduce the symptoms of diabetes.
Metformin also helps to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke in people with type 2 diabetes. It works by reducing the levels of triglycerides and “bad” LDL cholesterol in the blood. It also helps to increase the levels of “good” HDL cholesterol in the blood.
Metformin Safety and Side Effects
Metformin is generally well-tolerated and has few side effects. Possible side effects include nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea. It is important to discuss any potential side effects with a doctor before starting metformin.
Metformin may also interact with other medications, including some antibiotics and antifungal medications. It is important to discuss any potential drug interactions with a doctor before taking metformin.
Metformin should not be taken by people with kidney disease or those who are pregnant or breastfeeding. It is also important to tell a doctor about any pre-existing conditions before starting metformin.
What is the Recommended Dosage of Metformin?
The recommended dosage of metformin depends on the individual’s age, weight, and other factors. It is important to take the medication as prescribed by a doctor. It is also important to take the medication at the same time each day.
The dosage of metformin may need to be adjusted as the patient’s condition changes. It is important to discuss any changes in dosage with a doctor.
Conclusion
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It belongs to the drug class called ‘biguanides’ and is one of the most widely used medications for diabetes. Metformin works by decreasing the amount of sugar produced by the liver and decreasing the amount of sugar absorbed by the intestines. It also increases the body’s sensitivity to insulin. Metformin is generally well-tolerated and has few side effects. The recommended dosage of metformin depends on the individual’s age, weight, and other factors. It is important to discuss any potential side effects or drug interactions with a doctor before starting metformin.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Drug Class is Metformin?
Answer: Metformin is an oral antihyperglycemic drug in the biguanide drug class. It works by decreasing the amount of glucose released by the liver and decreasing the absorption of glucose from the intestines. It also increases the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which helps control blood sugar levels. Metformin is used to treat type 2 diabetes, as well as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in some cases.
How Does Metformin Work?
Answer: Metformin works by decreasing the amount of glucose released by the liver and decreasing the absorption of glucose from the intestines. It also increases the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which helps control blood sugar levels. Metformin helps to reduce the amount of glucose produced in the liver, which helps to lower blood sugar levels. It also helps to reduce the amount of glucose absorbed from food, which helps to keep blood sugar levels stable.
What Conditions is Metformin Used To Treat?
Answer: Metformin is used to treat type 2 diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in some cases. It can also be used to help manage prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as diabetes. Additionally, some research has suggested that Metformin may be useful in the treatment of certain types of cancer, including breast and ovarian cancer.
What Are the Side Effects of Metformin?
Answer: Common side effects of Metformin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bloating, and stomach upset. Other less common side effects may include headaches, dizziness, muscle pain, and changes in taste. More serious side effects can include lactic acidosis, a condition where lactic acid builds up in the blood, and kidney problems. It is important to talk to your doctor if you are experiencing any of these side effects.
What Is the Recommended Dosage of Metformin?
Answer: The recommended dose of Metformin will depend on the individual, their age, weight, and other factors. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions when taking Metformin. Generally, the starting dose is 500 mg daily, taken with meals. The dose can be increased gradually if needed, up to a maximum of 2,000 mg per day.
What Should I Do if I Miss a Dose of Metformin?
Answer: If you miss a dose of Metformin, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose. If you have any questions or concerns, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Metformin: Uses, Mechanism of action, Side effects, Contraindications
In conclusion, Metformin belongs to the drug class known as biguanides, which are medications used to treat type 2 diabetes. Metformin works by reducing glucose production in the liver, decreasing glucose absorption in the intestines, and increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin. Metformin is an effective treatment for type 2 diabetes and can help reduce the risk of complications caused by the disease.
