Drugs can have a major impact on the human body and mind, and the effects of drugs can last long after the drug has left the bloodstream. How long drugs stay in the blood is an important question for those who use drugs and for medical professionals. Knowing how long a drug stays in the blood can help determine the best treatment for a person who has taken a drug, as well as help to identify any potential risks associated with taking a drug. In this article, we’ll explore how long drugs stay in the blood, the factors that influence drug clearance from the blood, and how this can impact drug testing. We’ll also look at how drug metabolism affects the duration of drug presence in the blood. By exploring these topics, we can gain a better understanding of how long drugs stay in the blood, and how drug testing can be used to detect drugs in the body.
The length of time a drug stays in your system may depend on its half-life. Most drugs have a half-life between a few minutes and a few hours, meaning they are metabolized and/or excreted from the body relatively quickly. Some drugs, however, have a much longer half-life. For example, marijuana may stay in the system for several days or even weeks. In addition, some drugs may be detectable in the blood for only a short period of time, while other drugs may remain in the blood for longer periods of time. Therefore, the amount of time a drug stays in your system may vary depending on the drug and other individual factors.
How Long Do Drugs Stay in Blood?
Drugs can stay in the blood for a period of time ranging from a few minutes to several days, depending on a person’s metabolism, the drug’s chemical makeup and its half-life. Drugs are eliminated from the body either through excretion in the urine and feces or through metabolism, which involves breaking down the drug into smaller components.
Factors That Affect How Long Drugs Stay in the Blood
The amount of time a drug remains in the blood depends on several factors, such as the type of drug, the dose taken, the way it is taken, a person’s age, weight, and metabolism, and any underlying medical conditions. Short-acting drugs usually stay in the blood for a shorter amount of time than long-acting drugs, while drugs that are injected tend to stay in the body for a longer time than drugs taken orally.
Age and weight can also play a role in how long a drug stays in the blood. Generally, drugs remain in the body for a shorter period of time in older people and those who are overweight, as well as those with poor liver or kidney function. On the other hand, drugs may stay in the blood for a longer period of time in younger people, those with high metabolisms, and those with good liver or kidney function.
Drug Half-Life
The half-life of a drug is the amount of time it takes for the drug to be eliminated from the body. Different drugs have different half-lives, but most drugs are eliminated from the body within 24 hours. For example, the half-life of morphine is two to four hours, while the half-life of cocaine is around one hour.
The half-life of a drug is important when determining how long it will stay in the blood. The longer the half-life, the longer the drug will stay in the body. For instance, drugs with a short half-life may stay in the body for only a few hours, while those with a longer half-life may stay in the body for a few days.
Drug Testing
Drug tests are typically used to determine whether or not a person has used drugs recently. Different types of drug tests detect different types of drugs and different amounts of time. For example, urine tests can detect drugs in the body for up to several days, while blood tests can detect drugs in the body for up to 24 hours.
It is important to note that drug tests can only detect the presence of drugs in the body, not the amount of drugs used or the time since the last drug use. Therefore, it is important to understand how long a particular drug will stay in the blood in order to accurately interpret the results of a drug test.
Frequently Asked Questions
The amount of time a drug can be detected in the blood varies depending on the type of drug, the dose, and individual metabolism. The amount of time a drug can be detected in the blood also varies with the type of test used.
How Long Does Alcohol Stay in the Blood?
Alcohol is typically detectable in the blood for 6-12 hours after consumption. The amount of time it can be detected in the blood depends on several factors, including the type of test used, the amount of alcohol consumed, and the individual’s metabolism.
The body begins to metabolize alcohol as soon as it is consumed, and most people reach their peak blood alcohol concentration (BAC) within 30 minutes to an hour after drinking. BAC levels decline at a rate of about 0.015 per hour, so a BAC of 0.08% typically takes about 5 hours to decline to 0.00%. It is important to note, however, that alcohol can remain in the blood for up to 12 hours after it is consumed.
How Long Does Marijuana Stay in the Blood?
Marijuana is typically detectable in the blood for 1-2 days after consumption. The amount of time it can be detected in the blood depends on several factors, including the type of test used, the amount of marijuana consumed, frequency of use, and the individual’s metabolism.
Marijuana is detectable in the blood for a shorter amount of time than other drugs, such as cocaine or heroin. This is because the active ingredients in marijuana are broken down and eliminated from the body at a faster rate than other drugs. The body begins to metabolize marijuana as soon as it is consumed, and most people reach their peak blood concentration within 30 minutes to an hour after smoking. Marijuana metabolites decline at a rate of about 0.014 per hour, so a blood concentration of 0.02% typically takes about 2 hours to decline to 0.00%.
How Long Does Cocaine Stay in the Blood?
Cocaine is typically detectable in the blood for 1-4 days after consumption. The amount of time it can be detected in the blood depends on several factors, including the type of test used, the amount of cocaine consumed, frequency of use, and the individual’s metabolism.
Cocaine is detectable in the blood for a longer amount of time than other drugs, such as marijuana or alcohol. This is because the active ingredients in cocaine are metabolized and eliminated from the body more slowly than other drugs. The body begins to metabolize cocaine as soon as it is consumed, and most people reach their peak blood concentration within 30 minutes to an hour after snorting, smoking, or injecting the drug. Cocaine metabolites decline at a rate of about 0.015 per hour, so a blood concentration of 0.05% typically takes about 3 hours to decline to 0.00%.
How Long Does Heroin Stay in the Blood?
Heroin is typically detectable in the blood for 1-3 days after consumption. The amount of time it can be detected in the blood depends on several factors, including the type of test used, the amount of heroin consumed, frequency of use, and the individual’s metabolism.
Heroin is detectable in the blood for a longer amount of time than other drugs, such as marijuana or alcohol. This is because the active ingredients in heroin are metabolized and eliminated from the body more slowly than other drugs. The body begins to metabolize heroin as soon as it is consumed, and most people reach their peak blood concentration within 30 minutes to an hour after snorting, smoking, or injecting the drug. Heroin metabolites decline at a rate of about 0.018 per hour, so a blood concentration of 0.07% typically takes about 4 hours to decline to 0.00%.
How Long Does Methamphetamine Stay in the Blood?
Methamphetamine is typically detectable in the blood for 2-4 days after consumption. The amount of time it can be detected in the blood depends on several factors, including the type of test used, the amount of methamphetamine consumed, frequency of use, and the individual’s metabolism.
Methamphetamine is detectable in the blood for a longer amount of time than other drugs, such as marijuana or alcohol. This is because the active ingredients in methamphetamine are metabolized and eliminated from the body more slowly than other drugs. The body begins to metabolize methamphetamine as soon as it is consumed, and most people reach their peak blood concentration within 30 minutes to an hour after snorting, smoking, or injecting the drug. Methamphetamine metabolites decline at a rate of about 0.015 per hour, so a blood concentration of 0.05% typically takes about 3 hours to decline to 0.00%.
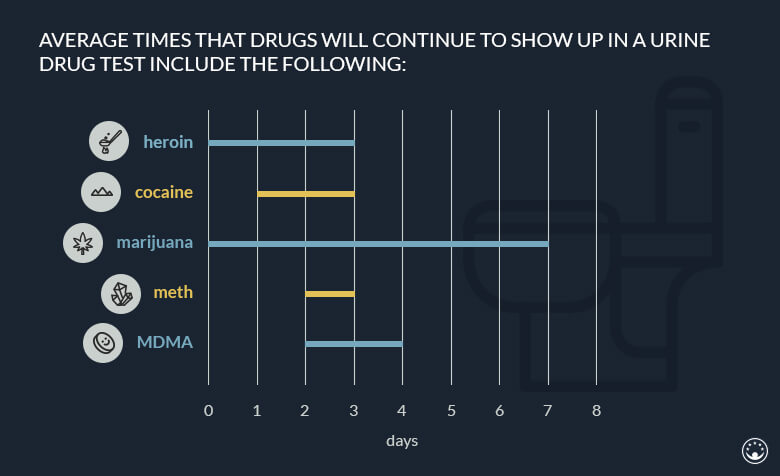
How long are different drugs detectable in your system – urine testing, hair testing, etc.
In conclusion, it is important to understand that the length of time drugs stay in the blood can vary greatly depending on the type of drug and the individual taking it. For example, drugs like amphetamines may stay in the blood for up to three days, while drugs like marijuana may stay in the system for up to 30 days. Furthermore, factors such as the user’s metabolism, age, health, and lifestyle can all have an effect on how long a drug remains in the blood. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the time frames of various drugs and be cautious about their use.
Overall, the length of time drugs stay in the blood is an important factor to consider if someone is considering using them. Knowing how long a drug remains in the system can help individuals make informed decisions about their drug use. Furthermore, it is important to be mindful of the potential consequences of using drugs and how they may affect the individual in the long run.
