Nicotine is one of the most widely used and heavily researched substances in the world. It is the primary psychoactive ingredient in tobacco products and is also used in some electronic cigarettes and other nicotine delivery systems. It is known to have both short-term and long-term effects on the brain, but how exactly does nicotine affect our most complex organ? In this article, we will explore the effects of nicotine on the brain, from its immediate effects to its long-term implications. We will discuss how nicotine affects the brain’s chemistry, its potential risks, and how to modify or reduce your nicotine intake.
Nicotine is a stimulant that affects the brain, resulting in increased alertness and increased concentration. It also increases heart rate and blood pressure, and can cause feelings of relaxation. Nicotine can also increase dopamine levels in the brain, which can lead to addiction. Long-term use of nicotine can cause physical and psychological dependence, which can have serious health consequences.
Contents
What is Nicotine and How Does it Affect Brain Functions?
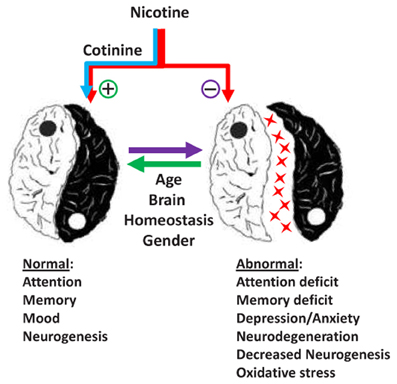
Nicotine is a stimulant found naturally in the tobacco plant. It is one of the primary ingredients in cigarettes and other tobacco products. When nicotine is inhaled or ingested, it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain, where it binds to nicotine receptors. This causes the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which leads to feelings of pleasure and relaxation. Nicotine also increases levels of the hormone adrenaline, which causes an alertness and sharpens focus.
At first, nicotine can have positive effects on mood and cognitive performance, but over time, these effects can become harmful. Nicotine can increase anxiety and cause a person to become dependent on it. Long-term nicotine use has been associated with an increased risk of developing certain neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Effects of Nicotine on the Brain
Nicotine affects the brain in several ways. It can increase alertness and concentration, as well as improve reaction time. It can also reduce pain and reduce stress. In addition, nicotine can cause relaxation and induce feelings of pleasure.
However, nicotine can also have negative effects on the brain. It can increase anxiety and irritability. It can also cause cognitive impairment, including slowed reaction time and impaired decision-making. Long-term nicotine use has been linked to an increased risk of developing neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Addiction to Nicotine
Nicotine is highly addictive. When nicotine is ingested, it quickly binds to nicotine receptors in the brain, causing a release of dopamine. This leads to feelings of pleasure and relaxation, which can create a cycle of addiction. Over time, the brain becomes dependent on nicotine and craves more of it in order to feel normal.
In addition, nicotine can cause physical withdrawal symptoms when a person stops using it. These can include headaches, irritability, sleep disturbances, and cravings for nicotine. This can make it difficult for a person to quit using nicotine and can lead to relapse.
Short- and Long-Term Health Effects of Nicotine
Short-term health effects of nicotine can include increased blood pressure and heart rate, dizziness, and nausea. It can also impair cognitive functions, such as reaction time and decision-making. Long-term nicotine use has been linked to an increased risk of developing neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Effects of Nicotine on the Heart
Nicotine can have a variety of effects on the heart. It can increase blood pressure and heart rate, which can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. In addition, nicotine can constrict blood vessels, which can make it more difficult for the heart to pump blood. Long-term nicotine use has been linked to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease and stroke.
Effects of Nicotine on the Lungs
Nicotine can cause a variety of effects on the lungs. It can increase mucus production and cause inflammation, which can make it difficult to breathe. In addition, nicotine can decrease lung function and increase the risk of developing respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Conclusion
Nicotine is a stimulant found naturally in the tobacco plant. It is the primary ingredient in cigarettes and other tobacco products. Nicotine affects the brain in several ways, including increasing alertness and concentration, as well as reducing pain and stress. However, nicotine can also have negative effects on the brain, including increased anxiety and impaired cognitive functioning. In addition, nicotine can have a variety of effects on the heart and lungs, such as increasing blood pressure and constricting blood vessels. Long-term nicotine use has been linked to an increased risk of developing neurological and cardiovascular diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine is an addictive chemical found in tobacco products that is used to increase alertness and focus. It is a stimulant that can be found in cigarettes, cigars, chewing tobacco, and other tobacco products. Nicotine acts on the nervous system by stimulating the release of adrenaline and increasing the levels of dopamine in the brain, resulting in a feeling of pleasure and relaxation.
How Does Nicotine Affect Your Brain?
Answer: Nicotine affects the brain in several different ways. It increases the levels of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, which can lead to an increased desire for nicotine. It also increases the release of adrenaline, which can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, nicotine can interfere with the normal functioning of the brain’s reward and pleasure pathways, making it harder to quit using tobacco products.
What are the Short-term Effects of Nicotine?
Answer: The short-term effects of nicotine can include increased alertness, improved concentration, and a sense of relaxation. Additionally, nicotine can cause nausea, headache, and dizziness. It can also raise heart rate and blood pressure, and can cause constriction of the blood vessels.
What are the Long-term Effects of Nicotine?
Answer: The long-term effects of nicotine can include an increased risk of several diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and various types of cancer. Additionally, nicotine can cause a decrease in cognitive function, as well as an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Nicotine can also increase the risk of addiction to other substances, such as alcohol and drugs.
Are There Any Benefits of Nicotine?
Answer: Despite the risks associated with nicotine, there are some potential benefits. Nicotine has been shown to increase alertness, improve concentration, and alleviate some symptoms of depression and anxiety. Additionally, nicotine has been suggested to have some potential benefits for patients with Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
Can You Overdose on Nicotine?
Answer: Yes, it is possible to overdose on nicotine. Nicotine overdose can cause serious health complications, such as seizures, irregular heart rhythm, and even death. Symptoms of nicotine overdose may include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, confusion, difficulty breathing, and loss of consciousness. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms.
Vaping: The Hit Your Brain Takes
In conclusion, Nicotine can be incredibly addictive and dangerous to your health. It can cause a variety of brain-related changes, from increased alertness and focus to impaired decision-making and learning. While it may be tempting to try nicotine in any form, it is important to understand the risks and potential consequences to your health and well being. Ultimately, the best advice is to choose to live a nicotine-free life.
