Drugs have long been a problem in society, and their effects on individuals and the public can be devastating. But just how many people die from drugs each year? This article will explore the current statistics on drug-related deaths, as well as the factors that contribute to the high mortality rates associated with drug use. We will also look at what measures are being taken to address the issue of drug-related deaths and how we can work to reduce the number of lives lost to drugs.
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, an estimated 70,237 people died from drug overdoses in 2019, an increase of 4.6% from 2018. This number includes deaths from both illicit drugs and prescription opioids. The majority of drug overdose deaths were caused by opioids, including prescription opioids, heroin, and fentanyl.
Contents
- Drug-Related Deaths in the United States
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: How many people die from drugs annually?
- Q2: What type of drugs are most often associated with overdose deaths?
- Q3: What age group is most affected by drug overdose deaths?
- Q4: What states have the highest rate of drug overdose deaths?
- Q5: Are drug overdose deaths increasing or decreasing?
- Q6: What is being done to reduce drug overdose deaths?
- Overdose deaths in the U.S. reached record levels in 2021
Drug-Related Deaths in the United States
Drug-related deaths in the United States are an ongoing problem, with almost 70,000 people dying in 2018 alone. This number has continued to increase over the years, with no sign of slowing down. While many of these deaths are due to illicit drug use, prescription drugs can be just as deadly. Understanding the causes and contributing factors of drug-related deaths can help us find ways to reduce the number of lives lost each year.
Drug-related fatalities can be broken down into two main categories: overdose deaths and deaths due to drug-related complications. Overdose deaths are the most common type of drug-related death, accounting for more than 66,000 deaths in 2018. These fatalities are the result of a person taking too much of a drug, often with deadly results. Drug-related complications, on the other hand, can include infections or other health issues caused by long-term drug use. These types of deaths are often preventable with proper medical care and treatment.
The types of drugs responsible for drug-related deaths can vary from year to year. In recent years, opioids have been responsible for the largest number of overdose deaths, with more than 47,000 people dying from opioid overdoses in 2018 alone. Other drugs, such as cocaine, alcohol, and benzodiazepines, are also responsible for a significant number of deaths each year.
Risk Factors for Drug-Related Death
Many factors can increase a person’s risk of dying from a drug-related death. Drug use can be particularly dangerous for those who suffer from mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety. People who use drugs in combination with alcohol or other drugs also face a higher risk of death. Additionally, certain drugs, such as opioids, are more dangerous than others and can be deadly even when taken in small amounts.
Another major risk factor for drug-related death is a lack of access to treatment and recovery services. Many people who struggle with drug addiction do not seek help due to the stigma associated with drug use and the lack of affordable treatment options. Without access to the right services, people who struggle with drug abuse are at a greater risk of overdose and other drug-related complications.
Preventing Drug-Related Deaths
The best way to prevent drug-related deaths is to reduce the number of people who use drugs in the first place. This can be done through education and awareness campaigns that focus on the risks associated with drug use. Additionally, making sure people have access to affordable treatment and recovery services is key to reducing drug-related deaths.
It is also important to reduce the stigma associated with drug use and addiction. This can help people feel more comfortable seeking help for their addiction and can reduce the risk of overdose and other drug-related complications. Finally, increasing access to naloxone, a drug that can reverse opioid overdoses, can help save lives.
Impact of Drug-Related Deaths
Drug-related deaths can have a devastating impact on individuals, families, and communities. For families, the death of a loved one due to a drug-related cause can be overwhelming and heartbreaking. Communities also suffer when drug-related deaths occur, as they must grapple with the loss of life and the associated costs.
In addition to the emotional and social impacts of drug-related deaths, there are also financial costs associated with these deaths. These costs include medical expenses, funeral costs, and other costs associated with the death. In the United States, the total cost of drug-related deaths was estimated to be $817 billion in 2018.
Conclusion
Drug-related deaths are an ongoing problem in the United States, with almost 70,000 people dying from drug-related causes in 2018. These deaths can be divided into two main categories: overdose deaths and deaths due to drug-related complications. Risk factors for drug-related death include mental health issues, drug and alcohol use in combination, and a lack of access to treatment and recovery services. Preventing drug-related deaths requires reducing the number of people who use drugs in the first place, reducing the stigma associated with drug use, and increasing access to naloxone. The emotional and social impacts of drug-related deaths can be devastating, and the financial costs are also significant.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How many people die from drugs annually?
A1: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 70,000 people died in the U.S. from drug overdoses in 2019. This is a record-high number and a 10.5% increase from 2018. The majority of these deaths were attributed to opioids, including prescription opioids, heroin, and synthetic opioids such as fentanyl. In addition to the 70,000 deaths, an estimated 2.7 million Americans are currently suffering from an opioid use disorder.
Q2: What type of drugs are most often associated with overdose deaths?
A2: According to the CDC, opioids are the most common type of drug associated with overdose deaths in the United States. These include prescription opioids, heroin, and synthetic opioids such as fentanyl. In 2019, opioids were responsible for more than 68% of all drug overdose deaths. Other drugs associated with overdose deaths include cocaine, methamphetamine, benzodiazepines, and antidepressants.
Q3: What age group is most affected by drug overdose deaths?
A3: According to the CDC, adults aged 25–54 years account for the majority of drug overdose deaths in the United States. In 2019, more than 50,000 people in this age group died from a drug overdose. This includes an estimated 27,000 people aged 25–34 years and 24,000 people aged 35–54 years.
Q4: What states have the highest rate of drug overdose deaths?
A4: According to the CDC, the states with the highest rate of drug overdose deaths in 2019 were West Virginia, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Kentucky. West Virginia had the highest rate of drug overdose deaths in the country, with a rate of 58.7 drug overdose deaths per 100,000 people. Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Kentucky had rates of 44.4, 39.7, and 38.2, respectively.
Q5: Are drug overdose deaths increasing or decreasing?
A5: According to the CDC, drug overdose deaths in the United States have been increasing since the late 1990s. In 2019, there were more than 70,000 drug overdose deaths in the United States, which is a 10.5% increase from 2018.
Q6: What is being done to reduce drug overdose deaths?
A6: There are a number of initiatives in place to reduce drug overdose deaths in the United States. The CDC is working with public health officials, healthcare providers, and other organizations to increase access to evidence-based treatment for opioid use disorder, as well as to raise awareness of the dangers of opioids and other drugs. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has also launched the Opioid Initiative, which focuses on reducing the number of opioid overdoses and deaths, as well as improving access to treatment for those with substance use disorder.
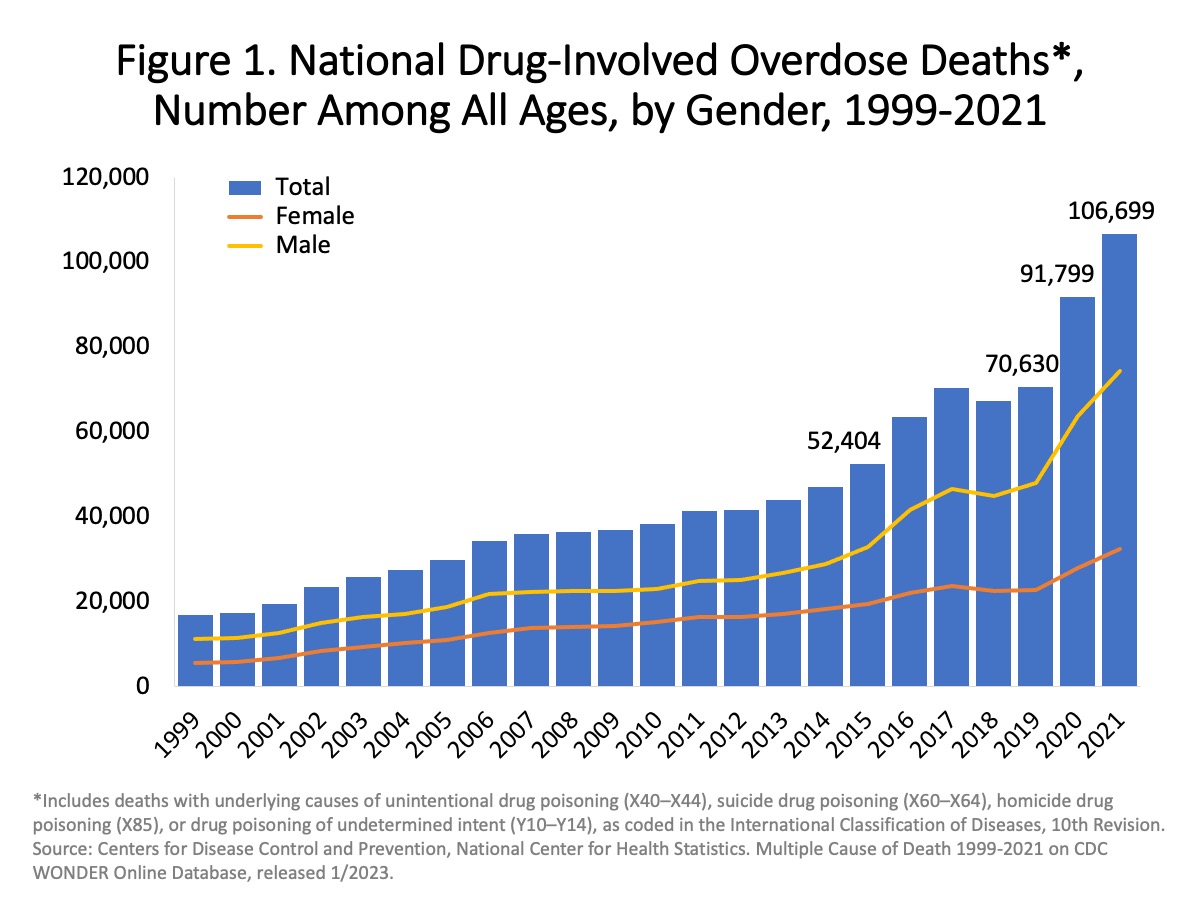
Overdose deaths in the U.S. reached record levels in 2021
The truth is, drugs have become a global menace that continues to affect people in many countries around the world. Every day, thousands of people die from the effects of drugs. While drug addiction and overdose remain a major problem, there is still hope that with the right education, support, and access to treatment, we can reduce the number of people who suffer from the devastating effects of drugs.
