Ativan, also known as lorazepam, is a benzodiazepine medication used to treat anxiety and insomnia. But is it an opiate? In this article, we will explore the pharmacological properties of Ativan, and examine whether this drug is an opiate or not. We will also discuss the potential risks and side effects associated with the use of Ativan. So, let’s dive into the world of Ativan and opiates!
No, Ativan (lorazepam) is not an opiate. It is a benzodiazepine, which is a class of drugs used to treat anxiety, insomnia, seizures and other conditions. While Ativan is not an opiate, it can be used to help manage symptoms of opiate withdrawal. It can also be used in conjunction with opiate-based pain medications.
What is Ativan?
Ativan (lorazepam) is a benzodiazepine medication commonly used to treat anxiety disorders. It is also used to treat insomnia, seizures, alcohol withdrawal, and irritable bowel syndrome. Ativan works by calming the brain and nerves and is often used in combination with other medications to treat anxiety and other related conditions.
What Are Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that act on the central nervous system to produce a calming or sedative effect. They are commonly used to treat anxiety, insomnia, seizures, muscle spasms, and alcohol withdrawal. Benzodiazepines work by binding to the GABA receptors in the brain, increasing the amount of GABA, which is a calming neurotransmitter.
Is Ativan an Opiate?
No, Ativan (lorazepam) is not an opiate. It is a benzodiazepine medication and does not contain any opiate or opiate-like compounds. Opiates are drugs that are derived from the opium poppy plant and are used to treat pain. They are also highly addictive and can lead to dependence and abuse.
What Are the Side Effects of Ativan?
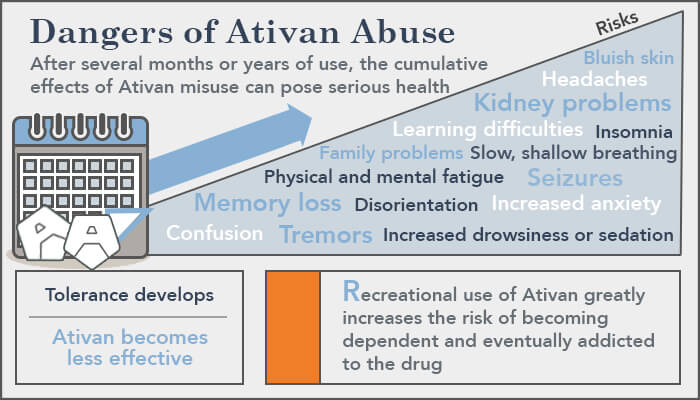
Ativan is generally a safe medication when taken as prescribed by a doctor. However, it can cause side effects, such as: drowsiness, dizziness, headache, weakness, blurred vision, difficulty concentrating, dry mouth, nausea, and vomiting. In rare cases, it can also cause more serious side effects, such as confusion, memory problems, hallucinations, agitation, aggression, and depression. It can also be habit-forming when taken for an extended period of time.
Is Ativan Addictive?
Ativan can be addictive when taken for an extended period of time. It can cause physical and psychological dependence and can lead to withdrawal symptoms when stopped suddenly. Therefore, it is important to take the medication as prescribed by a doctor and to not exceed the recommended dosage.
What Are the Risks of Taking Ativan?
Ativan can cause serious side effects, including confusion, memory problems, hallucinations, agitation, aggression, and depression. It can also cause physical and psychological dependence and can lead to withdrawal symptoms when stopped suddenly. It is important to talk to a doctor about the risks and benefits of taking Ativan before starting the medication.
Related Faq
What is Ativan?
Ativan is a brand-name prescription medication used to treat anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and other conditions. It is a benzodiazepine, which is a type of tranquilizer that works by slowing down the central nervous system. Ativan is available in tablet, liquid, and injectable forms.
Is Ativan an Opiate?
No, Ativan is not an opiate. Opiates are drugs derived from opium, a substance found in the poppy plant. Ativan is a benzodiazepine, and benzodiazepines are not opiates.
What is the difference between Ativan and Opiates?
Ativan and opiates are two different types of drugs. Ativan is a type of benzodiazepine, which are tranquilizers that work by slowing down the central nervous system. Opiates are drugs derived from opium, a substance found in the poppy plant. Opiates work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking the pain signals.
What are the side effects of Ativan?
Common side effects of Ativan include drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, depression, headache, blurred vision, and trouble concentrating. Other serious side effects include difficulty breathing, increased heart rate, and seizures.
Is Ativan habit-forming?
Yes, Ativan is habit-forming. It should be used only as directed by your doctor and should not be used for longer than prescribed. If you develop a physical or psychological dependence on Ativan, you should talk to your doctor about tapering off the medication.
Can Ativan be used to treat opioid withdrawal?
Ativan is sometimes used to treat the symptoms of opioid withdrawal, such as anxiety, insomnia, and muscle aches. However, Ativan should not be used to treat opioid addiction, as it can also be addictive. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment option for you.
The Effects of Mixing Benzos and Opiates
Ativan is a widely used drug for anxiety, panic attacks, and seizures. While it is not classified as an opiate, it does have similar effects to some opioids. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with taking Ativan and to talk to a doctor before starting any medication. Ultimately, Ativan is an effective medication for treating anxiety and other conditions, but it is important to use it responsibly and be aware of the potential side effects.
