Opiates have long been known to alter the way our brains function and produce feel-good hormones, such as dopamine. But do opiates directly affect the release of dopamine in the brain? In this article, we will explore the effects of opiates on dopamine release and how it influences our behavior and emotions. We will delve into the science behind this complex relationship and discuss the potential implications of this connection. So, if you are curious to learn more about how opiates may be affecting dopamine levels in your brain, read on!
Do Opiates Produce Dopamine?
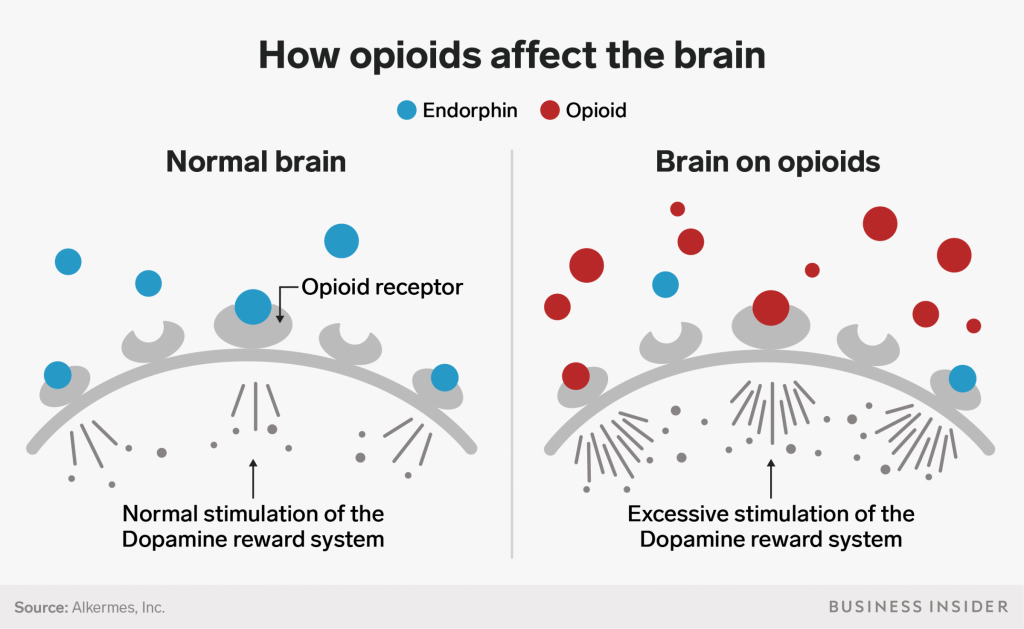
Opiate drugs, such as heroin and morphine, have long been known to influence the reward system in the brain and increase the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. This neurotransmitter is responsible for feelings of pleasure and reward, and its release is associated with addictive behaviors. While the relationship between opiates and dopamine is well-established, the exact mechanism by which opiates increase dopamine levels is still not fully understood. In this article, we will explore what is known about the relationship between opiates and dopamine and the implications for addiction treatment.
How do Opiates Increase Dopamine Levels?
The exact mechanism by which opiates increase dopamine levels is not fully understood, but there are several theories. One theory suggests that opiates act directly on dopamine receptors in the brain, increasing the availability of dopamine and resulting in a feeling of pleasure. Another theory proposes that opiates act indirectly, increasing the release of other neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, that then act on the dopamine receptors and increase dopamine levels.
What are the Implications of Opiate-Induced Dopamine Release?
The release of dopamine in response to opiate use has important implications for addiction treatment. Research suggests that dopamine plays a role in the development of drug addiction, as people who are addicted to drugs have higher levels of dopamine in the brain than those who do not use drugs. This indicates that dopamine may be a key factor in the development and maintenance of addiction. Therefore, it is important for those seeking treatment for addiction to address the dopamine levels in the brain that have been increased by opiate use.
How is Dopamine Related to Withdrawal?
The relationship between opiates and dopamine may also have implications for withdrawal symptoms. When opiate use is stopped, dopamine levels in the brain drop, resulting in withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and cravings. Therefore, it is important for those seeking treatment for addiction to address the dopamine levels in the brain that have been increased by opiate use in order to reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
What Treatments Address Opiate-Induced Dopamine Release?
There are a variety of treatments available to address the dopamine levels in the brain that have been increased by opiate use. Medication-assisted therapies, such as buprenorphine and methadone, act on the dopamine receptors in the brain to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can also help to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms by teaching patients coping skills and helping them to identify and address the root causes of their addiction.
Can Dopamine Levels be Lowered After Opiate Use?
It is possible to lower dopamine levels in the brain after opiate use, though this process may take time. Treatment with medication-assisted therapies can help to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, while psychotherapy can help to address the underlying issues that may have contributed to the addiction. In addition, lifestyle changes such as exercise, healthy eating, and adequate rest can also help to reduce dopamine levels over time.
Related Faq
What are Opiates?
Opiates are a type of drug derived from the opium poppy plant. They include drugs like morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and heroin. They are used to treat pain, but can also be abused and lead to addiction.
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a type of neurotransmitter found in the brain. It plays an important role in the reward system, helping to regulate pleasure, motivation, and learning. It is released in response to pleasurable experiences, such as eating good food, playing video games, or taking drugs.
Do Opiates Release Dopamine?
Yes, opiates can release dopamine in the brain. When taken, opiates bind to opioid receptors in the brain, activating the reward system. This causes dopamine to be released, which can lead to a feeling of euphoria and pleasure.
What are the Effects of Dopamine Release?
The release of dopamine due to opiate use can lead to feelings of pleasure, reward, and motivation. This can make opiates highly addictive, as users become dependent on the drug to experience these feelings. Over time, the brain can become desensitized to dopamine, leading to an increased tolerance and need for more of the drug.
Are There Risks Associated with Opiate Use?
Yes, there are several potential risks associated with opiate use. These include the risk of overdose, physical dependence, and addiction. Long-term use of opiates can also lead to organ damage and other health problems.
How Can Dopamine Release be Avoided?
The best way to avoid the release of dopamine due to opiate use is to avoid taking opiates altogether. If opiates are used as part of a medical treatment, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and take the drug as prescribed. It is also important to be aware of the signs of addiction and seek help if needed.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates do release dopamine in the brain, and this can be a dangerous cycle. When taken in large amounts, dopamine can cause serious issues to a person’s mental and physical health, and can even be deadly. For this reason, medical advice should always be sought before taking any opiates. Taking opiates responsibly and only when prescribed by a medical professional can help to avoid serious health problems.
